©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2022; 14(2): 319-337
Published online Feb 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i2.319
Published online Feb 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i2.319
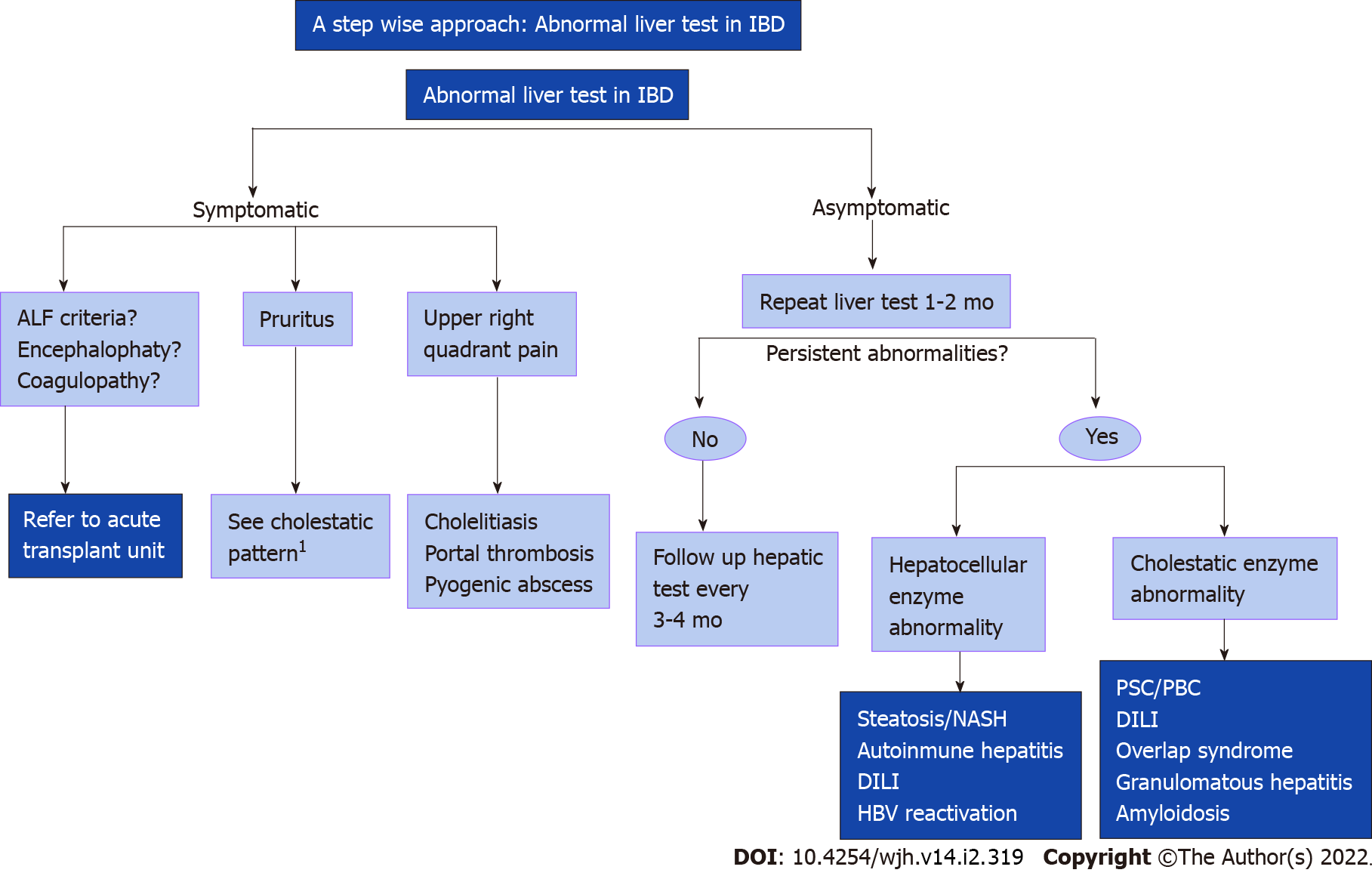
Figure 1 A stepwise approach: Abnormal liver test in inflammatory bowel disease.
1If the study is negative consider liver biopsy. Created with Biorender. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; ALF: Acute liver failure; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; PSC: Primary sclerosing cholangitis; PBC: Primary biliar cholangitis; DILI: Drug induced liver injury.
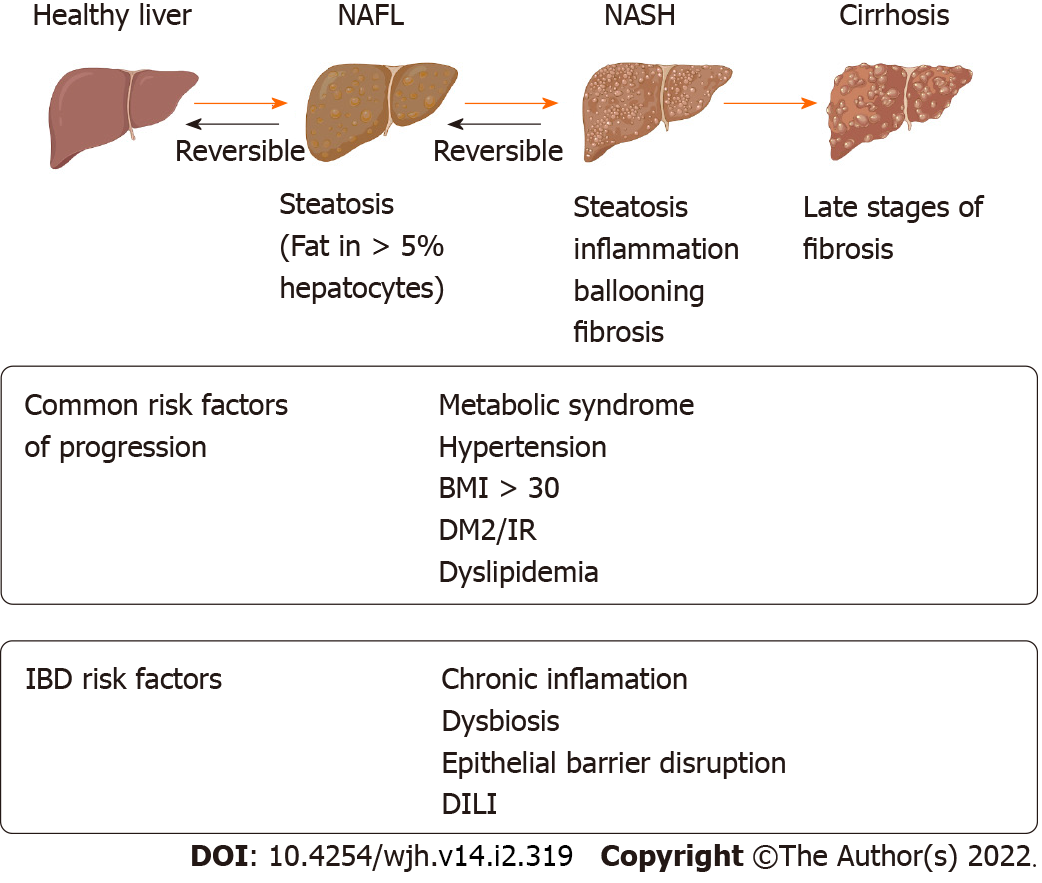
Figure 2 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease risk factor in inflammatory bowel disease.
Created with Biorender. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; NAFL: Nonalcoholic fatty liver; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; BMI: Body mass index; DM2: Diabetes mellitus 2; IR: Insulin resistance; DILI: Drug induced liver injury.
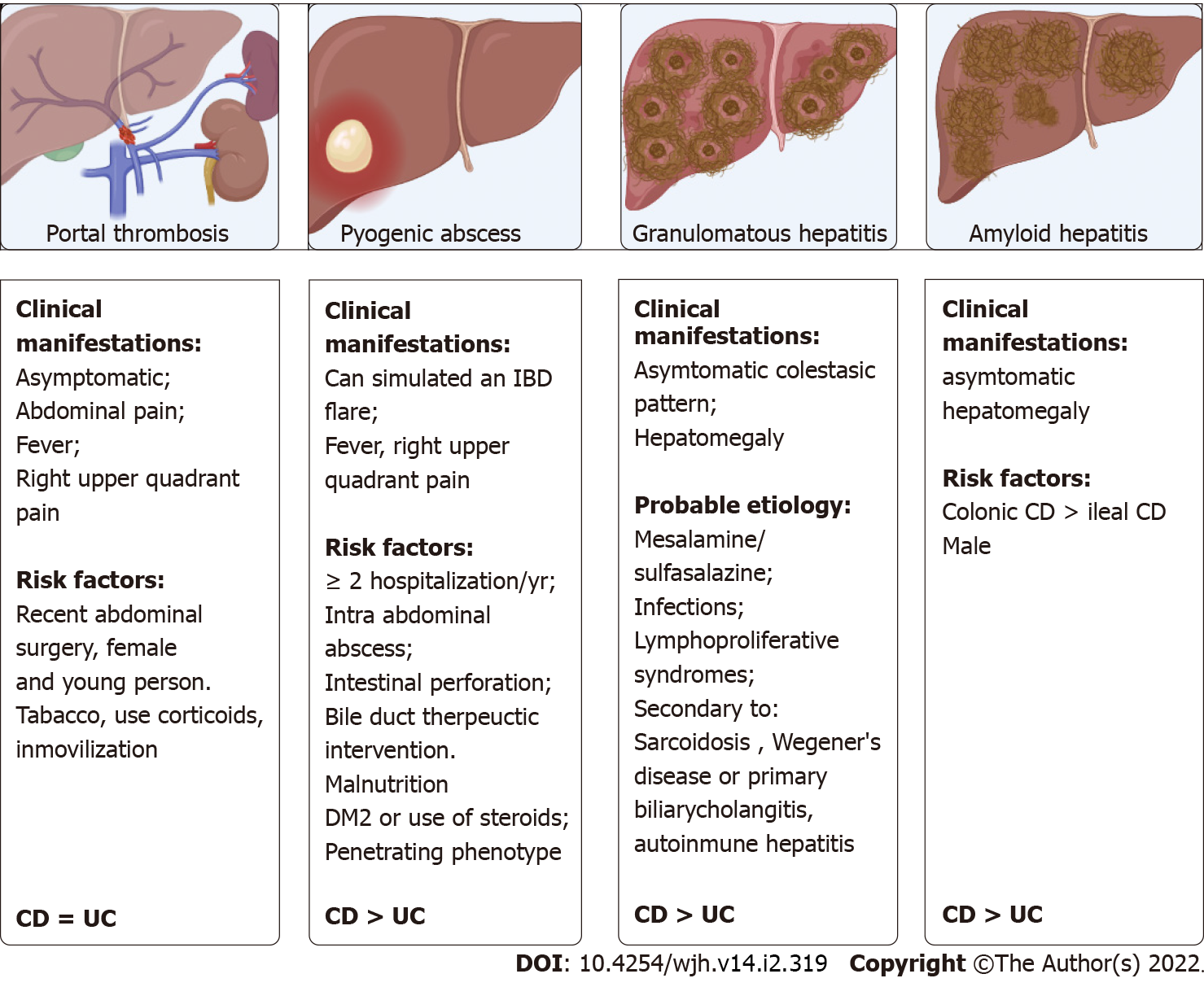
Figure 3 Others hepatic manifestations.
Created with Biorender. DM2: Diabetes mellitus 2; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; CD: Crohn’s disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
- Citation: Núñez F P, Castro F, Mezzano G, Quera R, Diaz D, Castro L. Hepatobiliary manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease: A practical approach. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(2): 319-337
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i2/319.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i2.319