©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2021; 13(12): 1919-1935
Published online Dec 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i12.1919
Published online Dec 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i12.1919
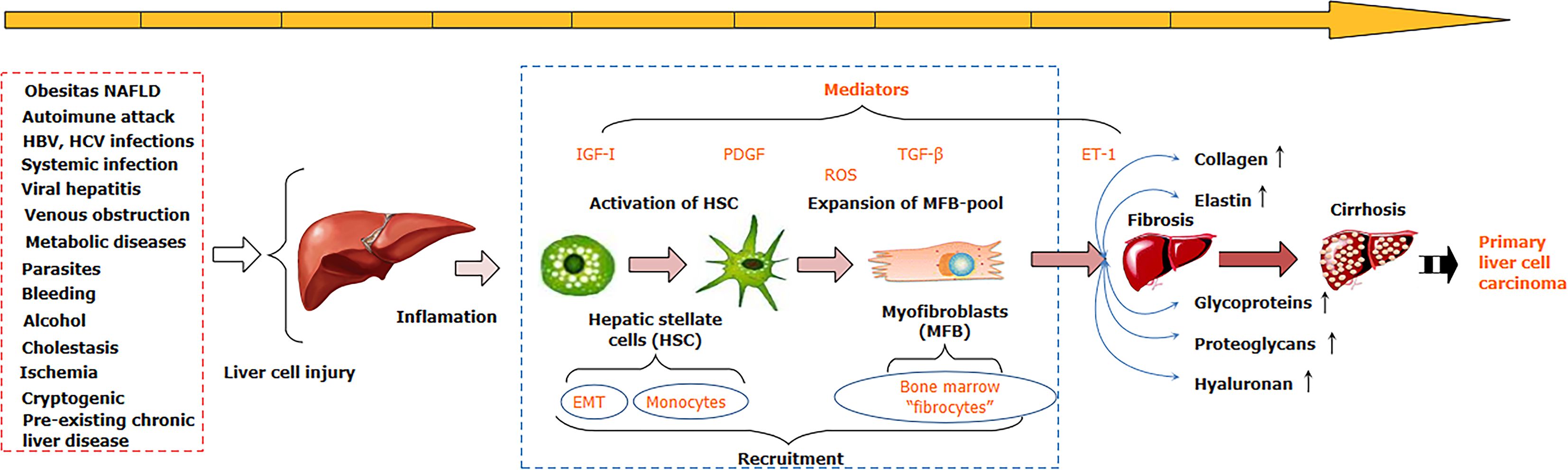
Figure 1 Factors promoting liver cell injury leading to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and carcinoma.
NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; PDGF: Platelet growth factor; IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; TGF: Tissue growth factor; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; ET-1: Endothelin-1; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
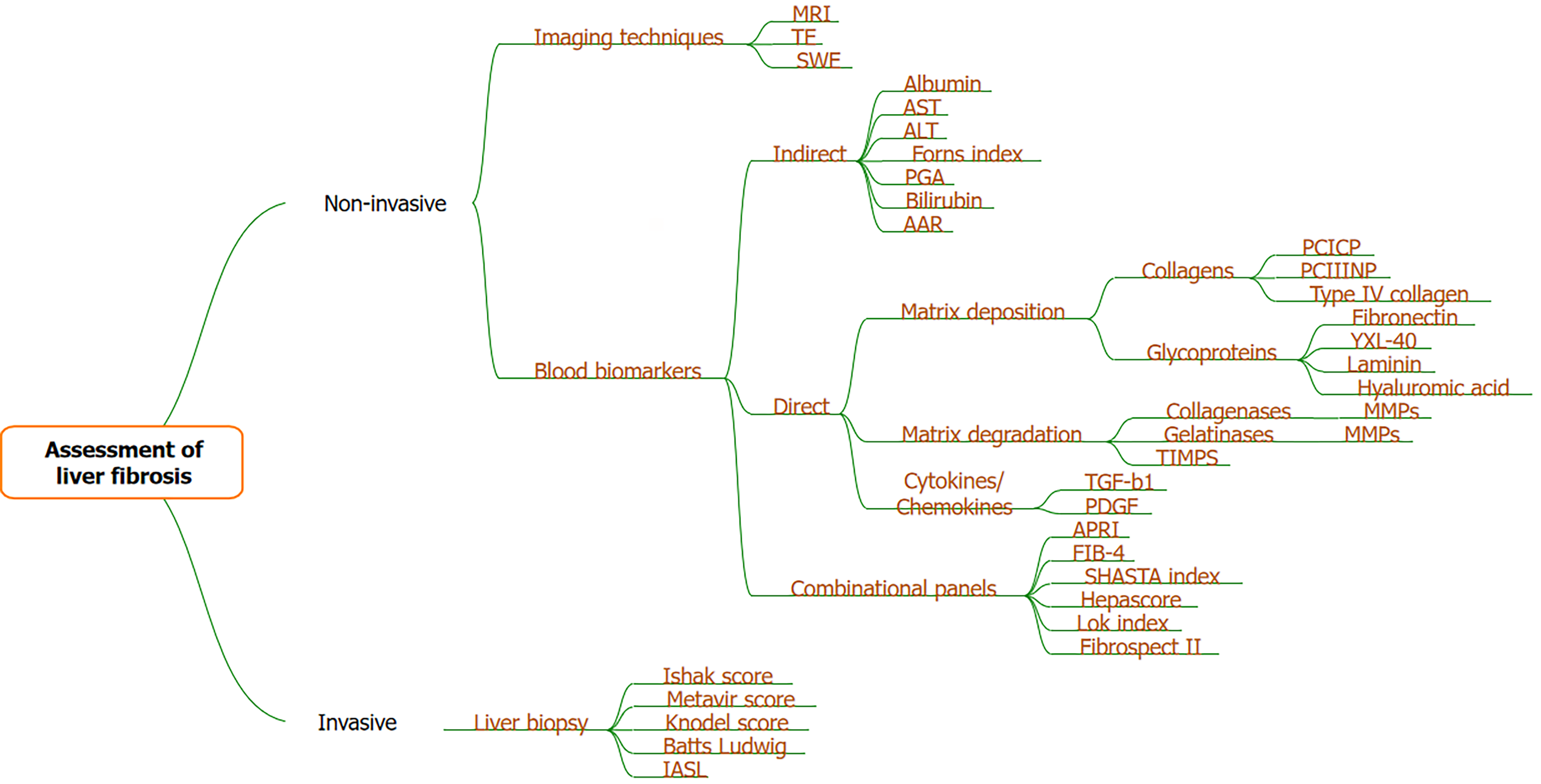
Figure 2 Various methods for assessment of liver fibrosis.
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; TE: Transient elastography; SWE: Shear wave elastography; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; AAR: Aspartate aminotransferase aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase ratio; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor β; PDGF: Platelet growth factor; APRI: Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet count ratio; FIB-4: Fibrosis-4; PCICP: Procollagen type 1; PCIIINP: Procollagen type 3; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase.
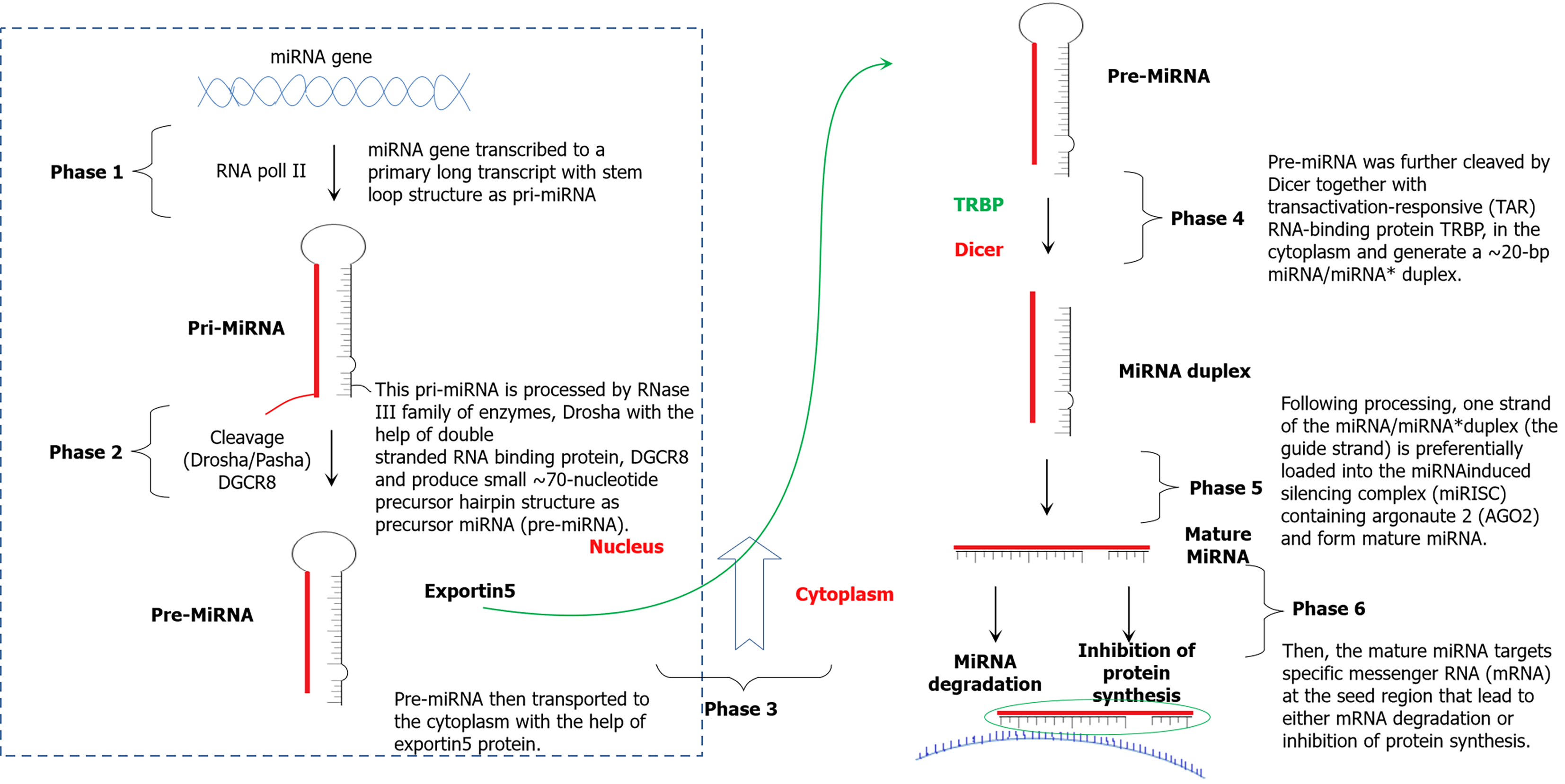
Figure 3 Process of microRNA biogenesis.
miRNA: MicroRNA.
- Citation: Kaur N, Goyal G, Garg R, Tapasvi C, Chawla S, Kaur R. Potential role of noninvasive biomarkers during liver fibrosis. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(12): 1919-1935
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i12/1919.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i12.1919