©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2016; 8(3): 73-87
Published online Mar 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i3.73
Published online Mar 26, 2016. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i3.73
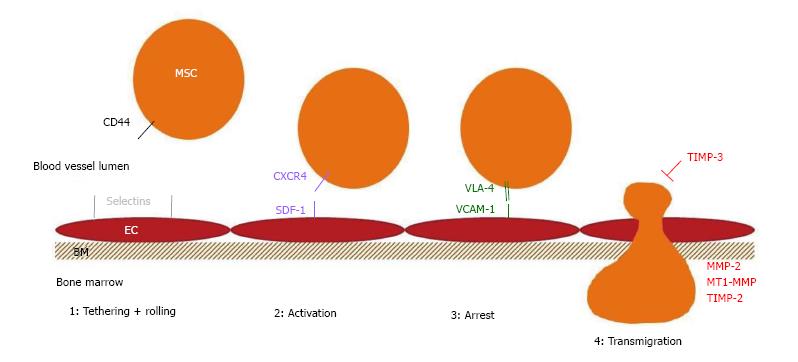
Figure 1 Overview of the homing molecules that are expressed on human mesenchymal stromal cells and known to be involved in the different steps of the bone marrow homing of mesenchymal stromal cells.
EC: Endothelial cell; BM: Basement membrane; CD: Cluster of differentiation; SDF-1: Stromal cell derived factor 1; VLA-4: Very late antigen 4; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; MT1-MMP: Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase; MSC: Mesenchymal stromal cell.
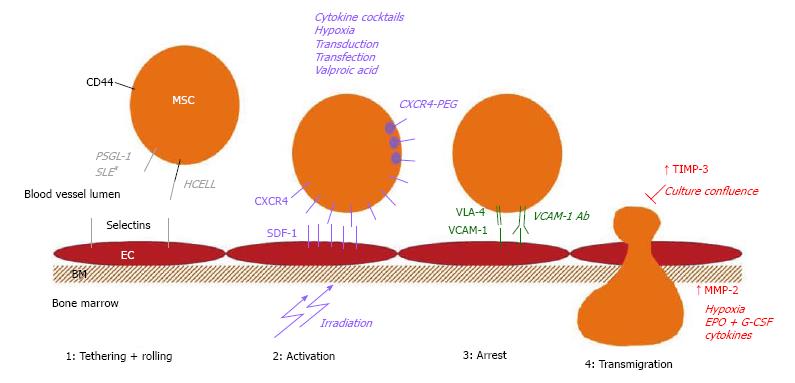
Figure 2 Schematic overview of the different strategies that can be used to improve homing in the different steps of mesenchymal stromal cell migration.
CD: Cluster of differentiation; EC: Endothelial cell; BM: Basement membrane; HCELL: Hematopoietic cell E-/L-selectin ligand; PSGL-1: P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1; SLEX: Sialyl Lewis X; SDF-1: Stromal cell derived factor 1; VLA-4: Very late antigen 4; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; Ab: Antibody; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; EPO: Erythropoietin; G-CSF: Granulocyte colony stimulating factor; MSC: Mesenchymal stromal cell.
- Citation: De Becker A, Riet IV. Homing and migration of mesenchymal stromal cells: How to improve the efficacy of cell therapy? World J Stem Cells 2016; 8(3): 73-87
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v8/i3/73.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v8.i3.73