©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2015; 7(6): 956-975
Published online Jul 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i6.956
Published online Jul 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i6.956
Figure 1 Synthetic biodegradable tubes of polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinyl alcohol loaded with COOH-functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes MWCNTs (polyvinyl alcohol-carbon nanotubes, polyvinyl alcohol-carbon nanotubes tube-guides), and polyvinyl alcohol loaded with polypyrrole (polyvinyl alcohol-polypyrrole, polyvinyl alcohol-polypyrrole tube-guides).
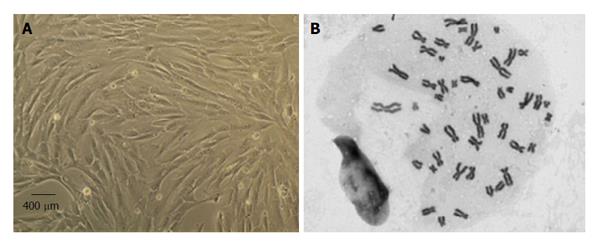
Figure 2 Mesenchymal stem cells culture and expansion.
A: Isolated mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from the Wharton’s jelly of umbilical cord presented a fusiform, fibroblast-like morphology in culture (magnification: 100 ×); B: Selected metaphases from MSCs in culture, showing normal number of chromossomes (46, XY) (magnification: 1000 ×).
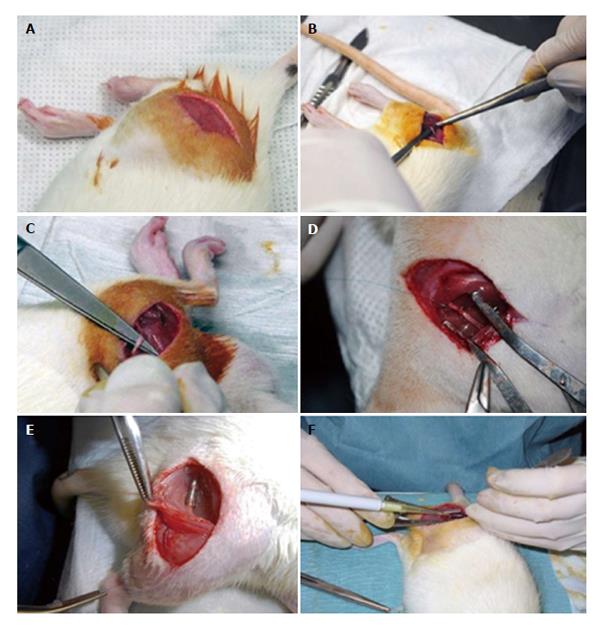
Figure 3 Surgery of the rat sciatic nerve neurotmesis injury model.
Under deep anesthesia the right sciatic nerve was exposed unilaterally through a skin incision extending from the greater trochanter to the mid-half distally followed by a muscle splitting incision (A). After nerve mobilization (B), a transection injury was performed (neurotmesis) using a straight microsurgical scissors (C). In group 5 (End-to-End) after neurotmesis, immediate cooptation with 7/0 monofilament polypropylene suture was performed (D). Implantation of the tube-guide in the 10 mm gap (E). Local application of the mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), the MSCs suspension filled the polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-carbon nanotubes (CNTs) tube-guide lumen (group 6: PVA-CNTs-MSCs) (F).
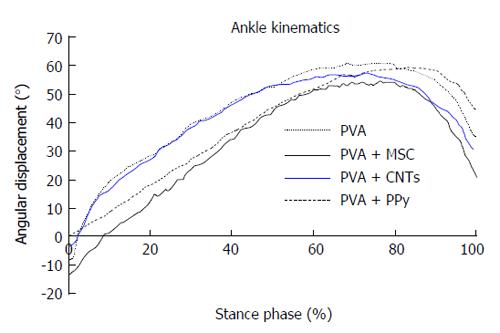
Figure 4 Kinematic plots in the sagittal plane for the ankle angle (°) as it moves through the stance phase, during the transection injury study.
The mean of each group is plotted. PVA: Polyvinyl alcohol; CNTs: Carbon nanotubes; PPy: Polypyrrole; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells.
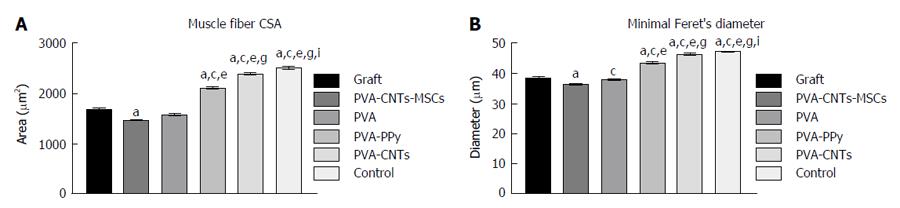
Figure 5 Graphical representation of the mean of area (A) and “minimal Feret’s diameter” (B) of control, regenerated tibialis anterior muscle fibers at week-20 after neurotmesis (Graft) and neurotmesis with the proximal and distal nerve stumps sutured to a polyvinyl alcohol (polyvinyl alcohol) tube and polyvinyl alcohol coated tubes (polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinyl alcohol polypyrrole and polyvinyl alcohol carbon nanotubes).
Values are presented as mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05 vs Graft; cP < 0.05 vs Graft PVA CNTs MSCs; eP < 0.05 vs Graft PVA; gP < 0.05 vs Graft PVA PPy; iP < 0.05 vs Graft PVA CNTs. PVA: Polyvinyl alcohol; CNTs: Carbon nanotubes; PPy: Polypyrrole; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells.
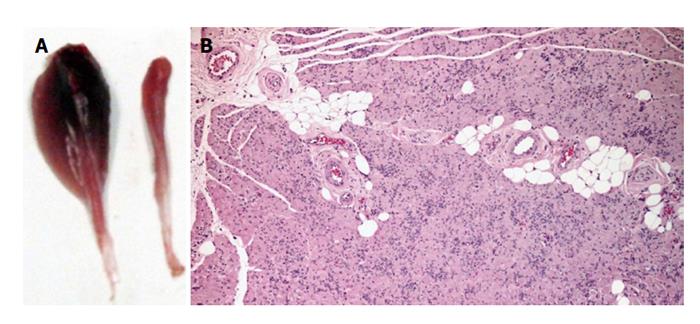
Figure 6 Macroscopic appearance of control tibialis anterior muscle and histological haematoxylin and eosin staining of a transverse section of tibialis anterior muscle.
A: Macroscopic appearance of control tibialis anterior (TA) muscle (left) and 20 wk following neurotmesis and surgical treatment with PVA CNTs MSCs (right); B: Histological haematoxylin and eosin staining of a transverse section of TA muscle from PVA CNTs MSCs group. Magnification 40 ×. PVA: Polyvinyl alcohol; CNTs: Carbon nanotubes; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells.
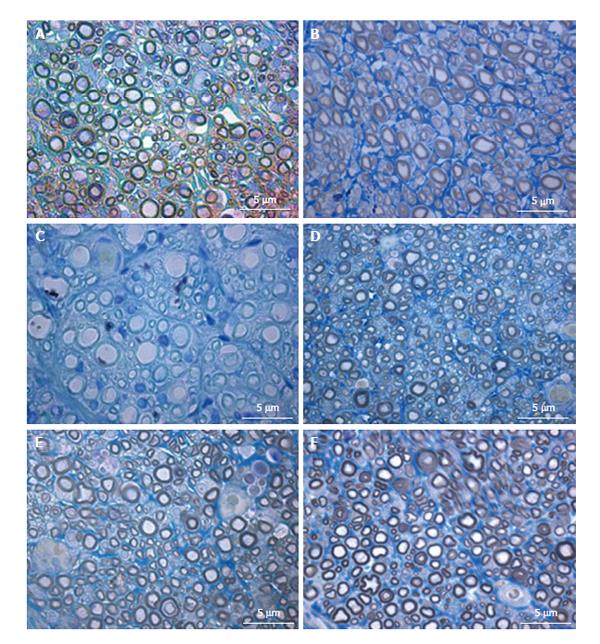
Figure 7 Histological appearance of regenerated nerve fiber in the different groups of neurotmesis.
A: PVA; B: PVA-CNTs; C: PVA-PPy; D: PVA-CNTs-MSCs; E: Graft; F: End-to-end suture (magnification: 1000 ×). PVA: Polyvinyl alcohol; CNTs: Carbon nanotubes; PPy: Polypyrrole; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Ribeiro J, Pereira T, Caseiro AR, Armada-da-Silva P, Pires I, Prada J, Amorim I, Amado S, França M, Gonçalves C, Lopes MA, Santos JD, Silva DM, Geuna S, Luís AL, Maurício AC. Evaluation of biodegradable electric conductive tube-guides and mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(6): 956-975
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i6/956.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i6.956