©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2015; 7(1): 137-148
Published online Jan 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.137
Published online Jan 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.137
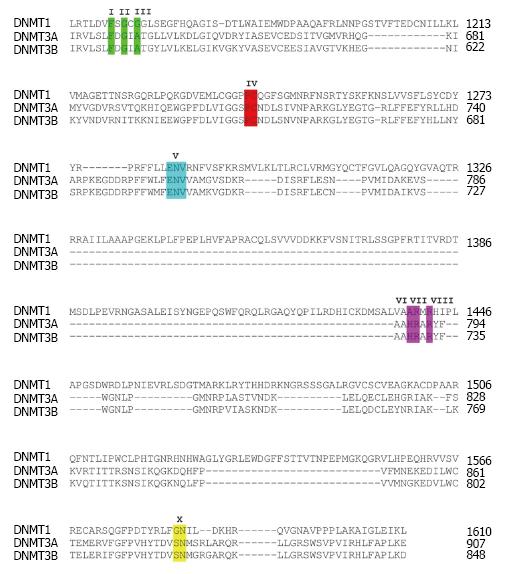
Figure 1 High similarity of critical amino acid residues at the catalytic domain of DNA methyltransferases.
Multiple alignment of amino acids within the catalytic domain of three catalytically active human DNA methyltransferases DNMT1, DNMT3A and DNMT3B is shown. Highlighted amino acids with roman letters shown above indicate critical residues of the catalytic domain. DNMT: DNA methyltransferases.
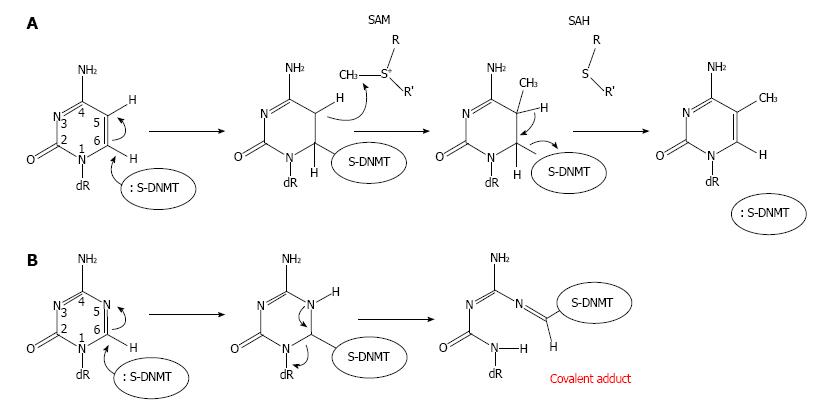
Figure 2 Mechanism of DNA methylation and its inhibition by 5-Aza-2’-deoxycytidine via covalent trapping.
A: Cytosine methylation by a DNMT is initiated by the formation of a covalent bond between the cytosine base and a cysteine residue at the active site of the methyltransferase. SAM then transfers a methyl group to the cytosine generating a methylcytosine. B: A DNMT is covalently trapped by the DNA-incorporated 5-Aza-2’-deoxycytidine (Aza-dC) adduct. The sulfhydryl group of the cysteine residue at the active site of DNMT forms a covalent bond with C6 of the Aza-dC in DNA. However, the active methyl group from SAM cannot be transferred to Aza-dC by DNMT. This covalent trapping mechanism then leads to a gradual loss of free DNMTs, because they are covalently linked with Aza-dC within DNA. Therefore, the loss of free DNMTs then precedes passive DNA demethylation. Thus cells expressing high levels of DNMTs will respond to Aza-dC at a higher extent compared with cells expressing low levels of DNMTs (see Figure 3). R: Methionine/cysteine; R’: Adenosine; Dr: Deoxyribose-5-phosphate; DNMT: DNA methyltransferases.
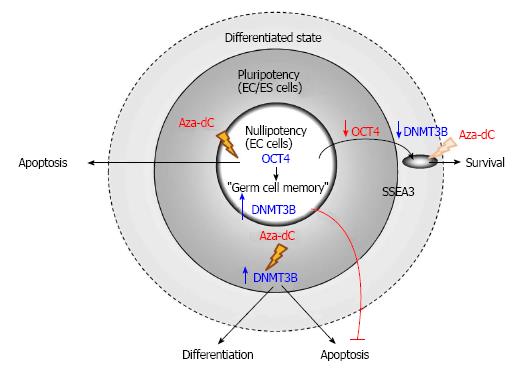
Figure 3 5-Aza-2’-deoxycytidine induces apoptosis of human teratocarcinoma stem cells but not their differentiated counterparts.
Human nullipotent embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells, the stem cells of teratocarcinoma, are highly sensitive to 5-Aza-2’-deoxycytidine (Aza-dC), which induces apoptosis of the cancer stem cells. On the other hand, OCT4-knockdown differentiated nullipotent EC cells are resistant toward Aza-dC treatment. In human pluripotent EC cells NTERA2, DNMT3B mediates apoptosis induced by Aza-dC, whereas the enzyme mediates differentiation of human ES cells induced by the inhibitor. DNMT: DNA methyltransferases; ES: Embryonicstem; OCT4: Octamer-binding transcription factor 4.
- Citation: Wongtrakoongate P. Epigenetic therapy of cancer stem and progenitor cells by targeting DNA methylation machineries. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(1): 137-148
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i1/137.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.137