©Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2026.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2026; 18(2): 114032
Published online Feb 26, 2026. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v18.i2.114032
Published online Feb 26, 2026. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v18.i2.114032
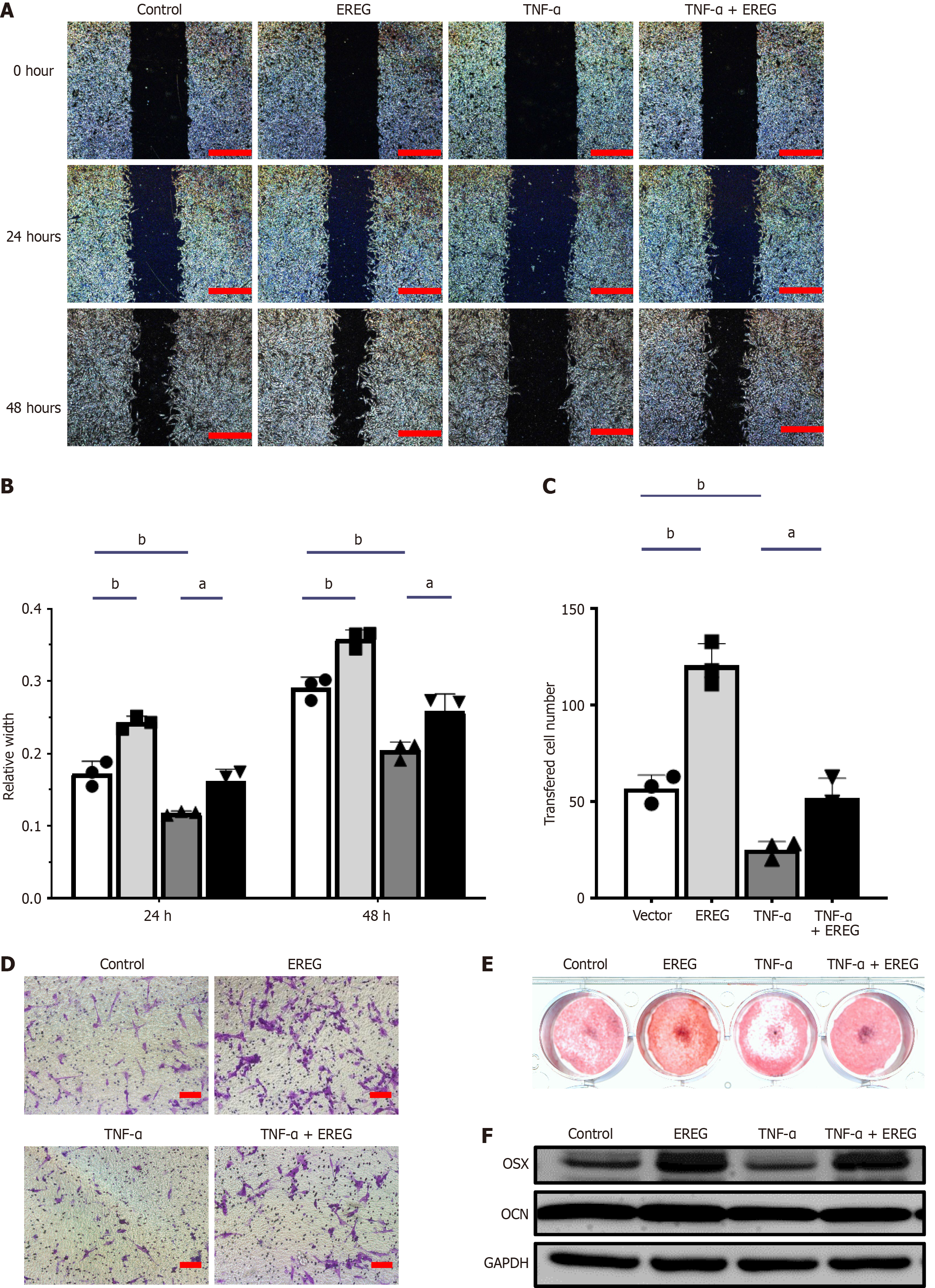
Figure 1 Supplementation with epiregulin enhanced the migration, chemotaxis, and osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow stem cells under inflammatory conditions.
A and B: Scratch-simulated wound migration assay results (n = 3, one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA]). Scale bar: 500 μm; C and D: Transwell chemotaxis assay results (n = 3, one-way ANOVA). Scale bar: 50 μm; E: Alizarin Red staining; F: Expression of osterix (OSX) and osteocalcin (OCN) was revealed in mouse bone marrow stem cells that were cultured in the inflammatory condition by western blotting. Error bars represent standard deviation. aP ≤ 0.05; bP ≤ 0.01. EREG: Epiregulin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
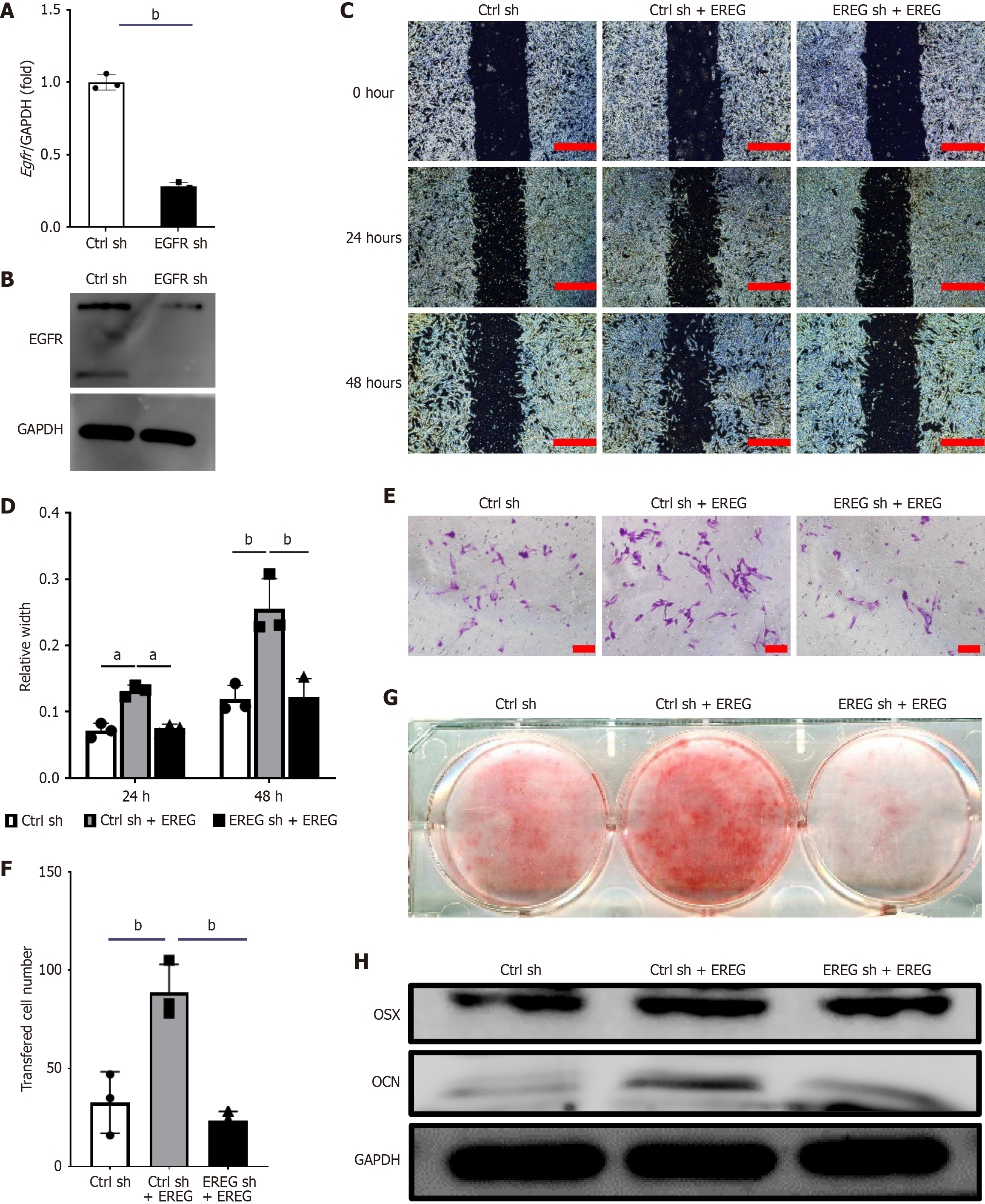
Figure 2 Knockdown of epidermal growth factor receptor blocked the positive effects of epiregulin on migration, chemotaxis, and osteo
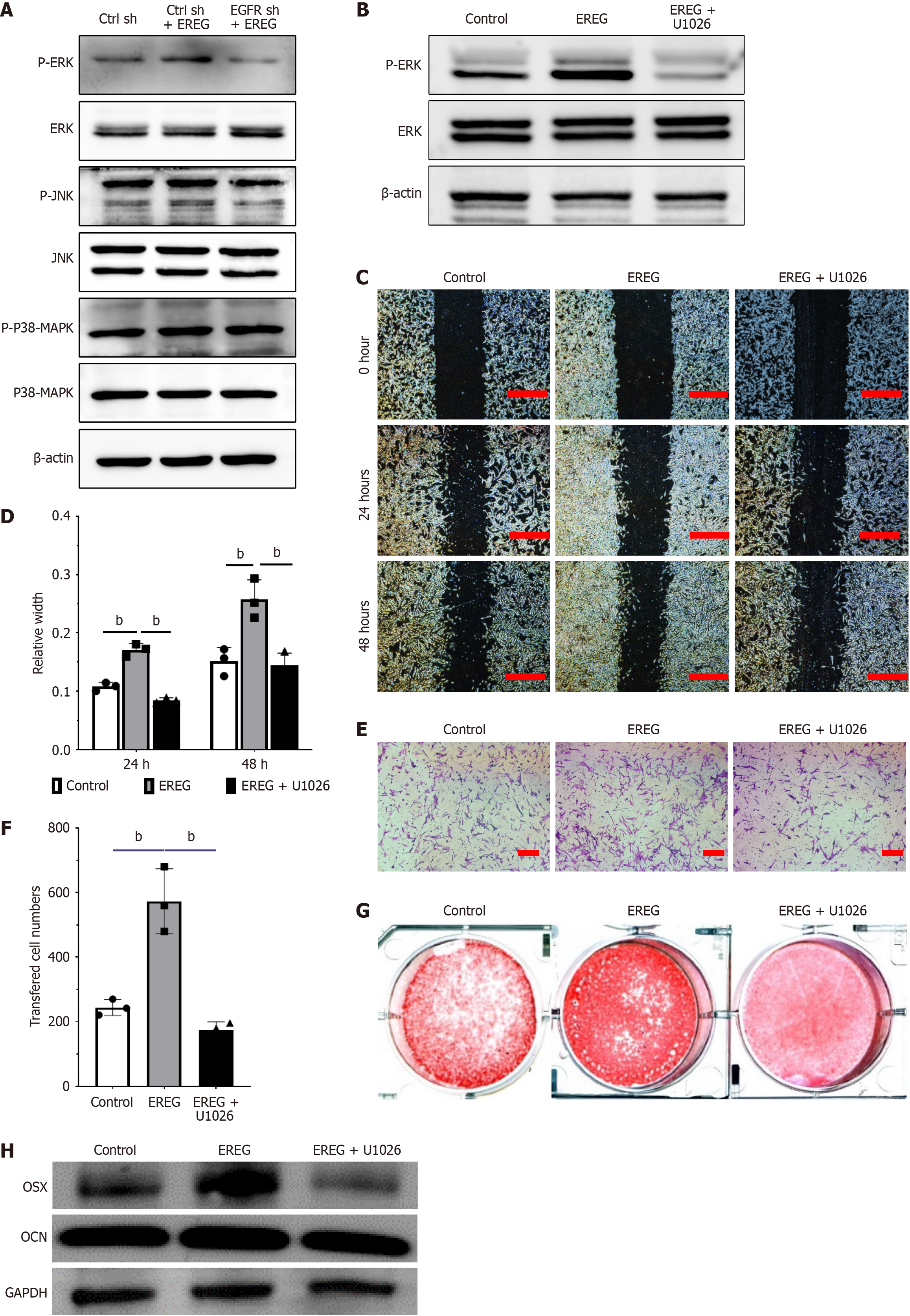
Figure 3 Epiregulin activated the epidermal growth factor receptor-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway to promote migration, chemotaxis, and osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow stem cells under inflammatory conditions.
A: Expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway were revealed in mouse bone marrow stem cells (mBMSCs) that were cultured in the inflammatory condition by western blotting. β-actin was used as the internal control; B: Expression of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK) and ERK were detected in mBMSCs that were cultured in the inflammation condition by western blotting; C and D: Scratch-simulated wound migration assay results (n = 3, one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA]). Scale bar: 500 μm; E and F: Transwell chemotaxis assay results (n = 3, one-way ANOVA). Scale bar: 100 μm; G: Alizarin red staining; H: Expression of osterix (OSX) and osteocalcin (OCN) were revealed in mBMSCs that were cultured in the inflammatory condition by western blotting. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3). aP ≤ 0.05; bP ≤ 0.01. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; EREG: Epiregulin; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
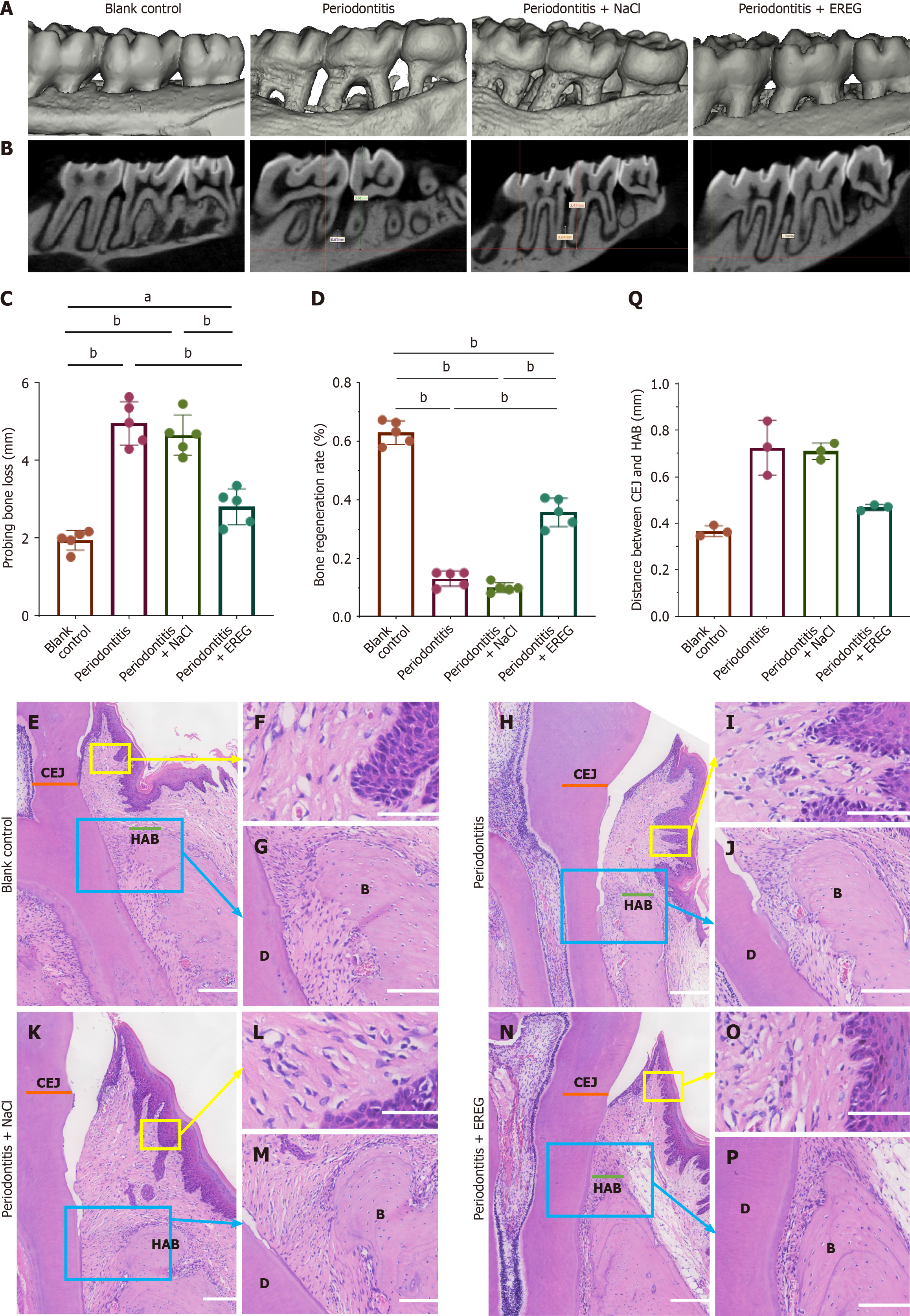
Figure 4 Local injection of epiregulin promoted the regeneration of periodontal tissue in a rat model of periodontitis.
A: Three-dimensional micro-computed tomography reconstruction of mouse maxillary from the three groups; B: Sagittal-sectional images of maxillary; C and D: Micro-computed tomography measurement of bone formation (n = 5, one-way analysis of variance); E-M: Hematoxylin and eosin staining indicated new periodontal tissue regeneration from coronal-sectional images of maxillary in the blank control group (E), periodontitis group (H), periodontitis + sodium chloride (NaCl) (K) and periodontitis + epiregulin (EREG) (N). Scale bar: 200 μm; hematoxylin and eosin staining indicated Sharpey’s fibers in the blank control group (G), periodontitis group (J), periodontitis + NaCl (M) and periodontitis + EREG (P). Scale bar: 100 μm; hematoxylin and eosin staining indicated inflammatory cells infiltration in the blank control group (F), periodontitis group (I), periodontitis + NaCl (L) and periodontitis + EREG (O). Scale bar: 50 μm; Q: Quantitative analysis of distance between cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) and height of alveolar bone (n = 3, Kruskal-Wallis test). Error bars represent the standard deviation. aP ≤ 0.05; bP ≤ 0.01. B: Bone; D: Dentin; HAB: Height of alveolar bone.
- Citation: Zhao YC, Li GY, Chen S, Wang YL, Feng JY, Cao Y. Epiregulin enhances periodontal tissue regeneration by promoting bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell functions under inflammatory niches. World J Stem Cells 2026; 18(2): 114032
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v18/i2/114032.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v18.i2.114032