©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2024; 16(11): 978-984
Published online Nov 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.978
Published online Nov 26, 2024. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.978
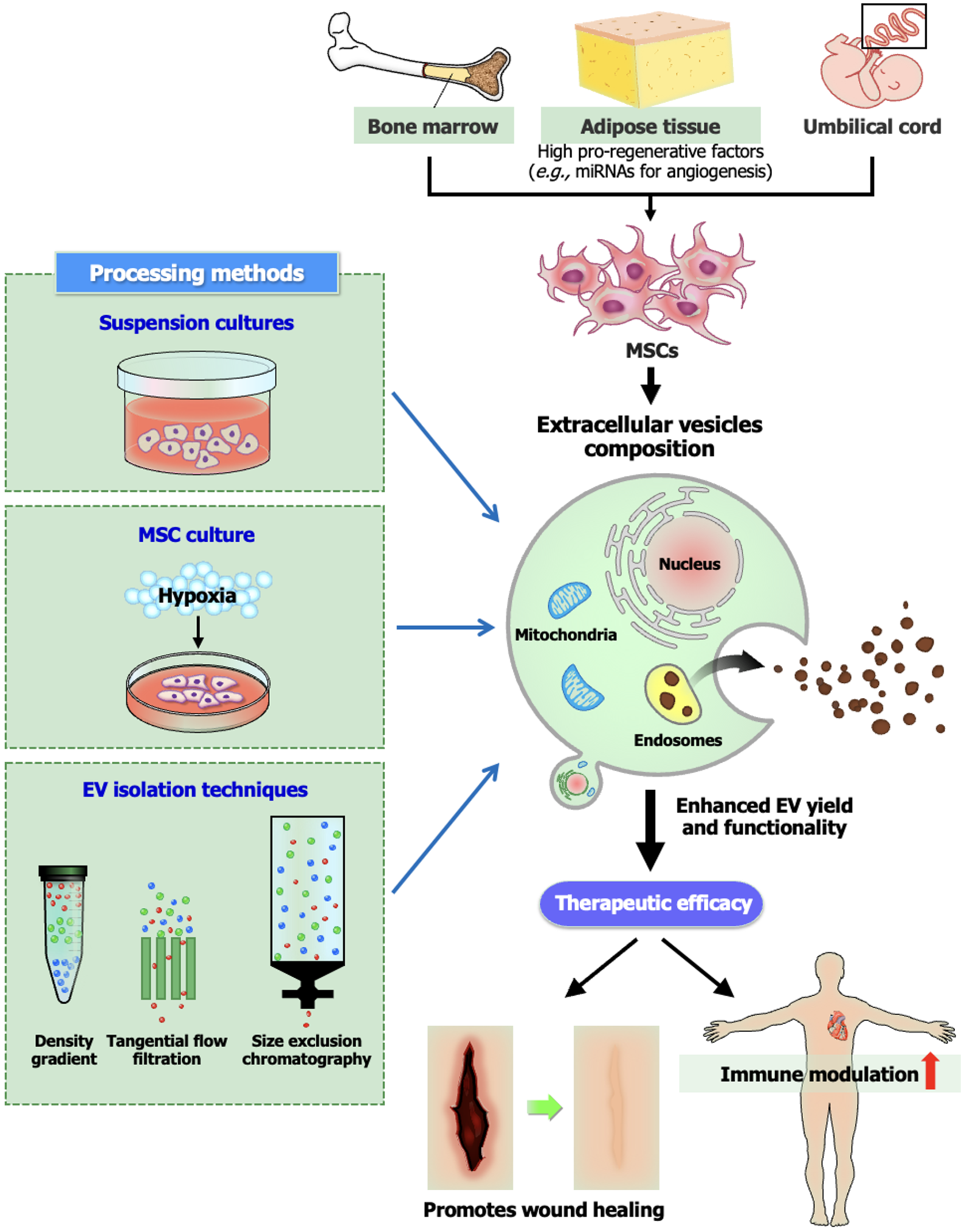
Figure 1 Effects of various mesenchymal stem cell sources and processing protocols on extracellular vesicle composition and the
- Citation: Cheng CH, Hao WR, Cheng TH. Refining adipose-derived stem cell isolation for optimal regenerative therapy. World J Stem Cells 2024; 16(11): 978-984
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v16/i11/978.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v16.i11.978