©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Apr 26, 2022; 14(4): 287-302
Published online Apr 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i4.287
Published online Apr 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i4.287
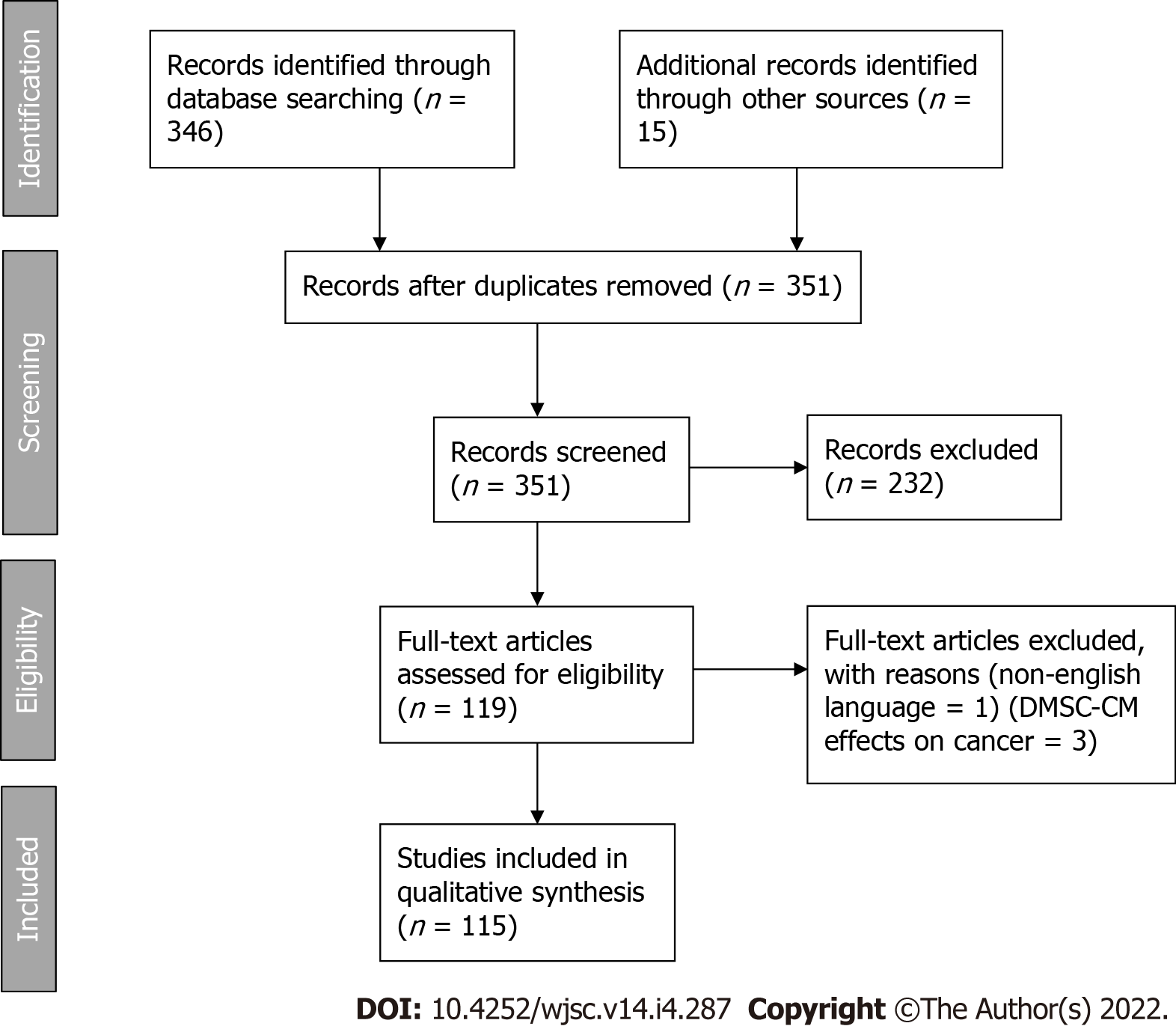
Figure 1 PRISMA 2009 flow diagram.
DMSC-CM: Dental mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium.
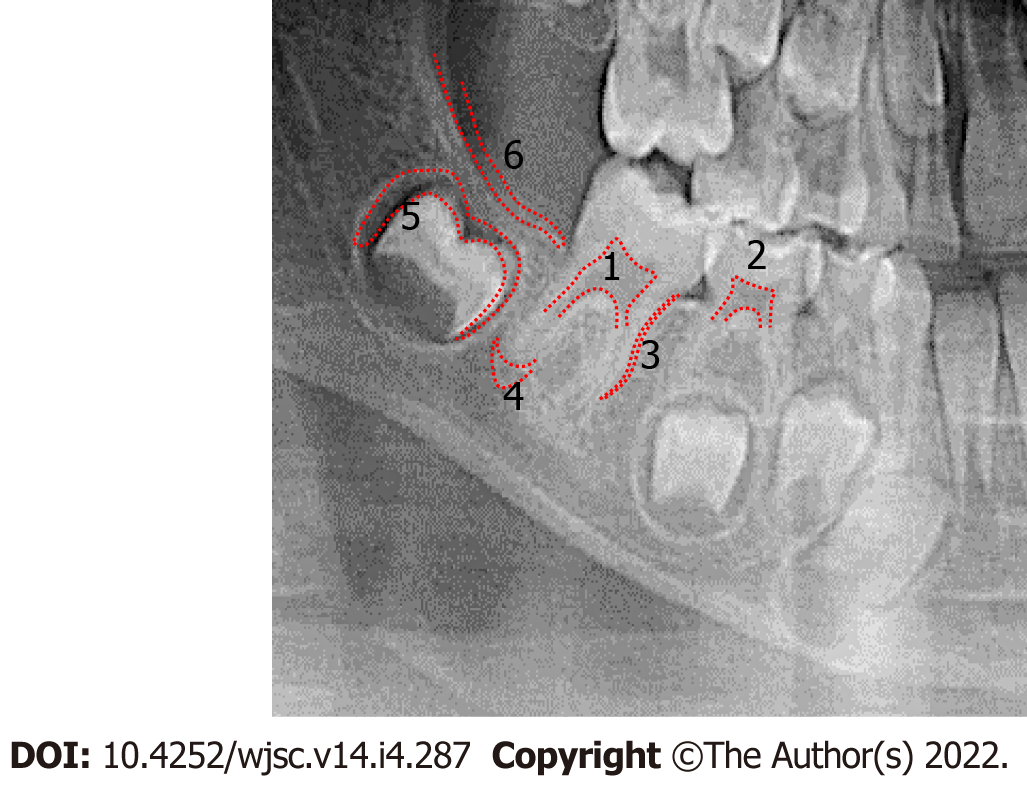
Figure 2 Orthopantomogram X-ray, with representative sources of various dental mesenchymal stem cells.
(1) Dental pulp stem cells; (2) Stem cells from human exfoliated teeth; (3) Periodontal ligament stem cells; (4) Stem cells from apical papilla; (5) Dental follicle stem cells; and (6) Gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
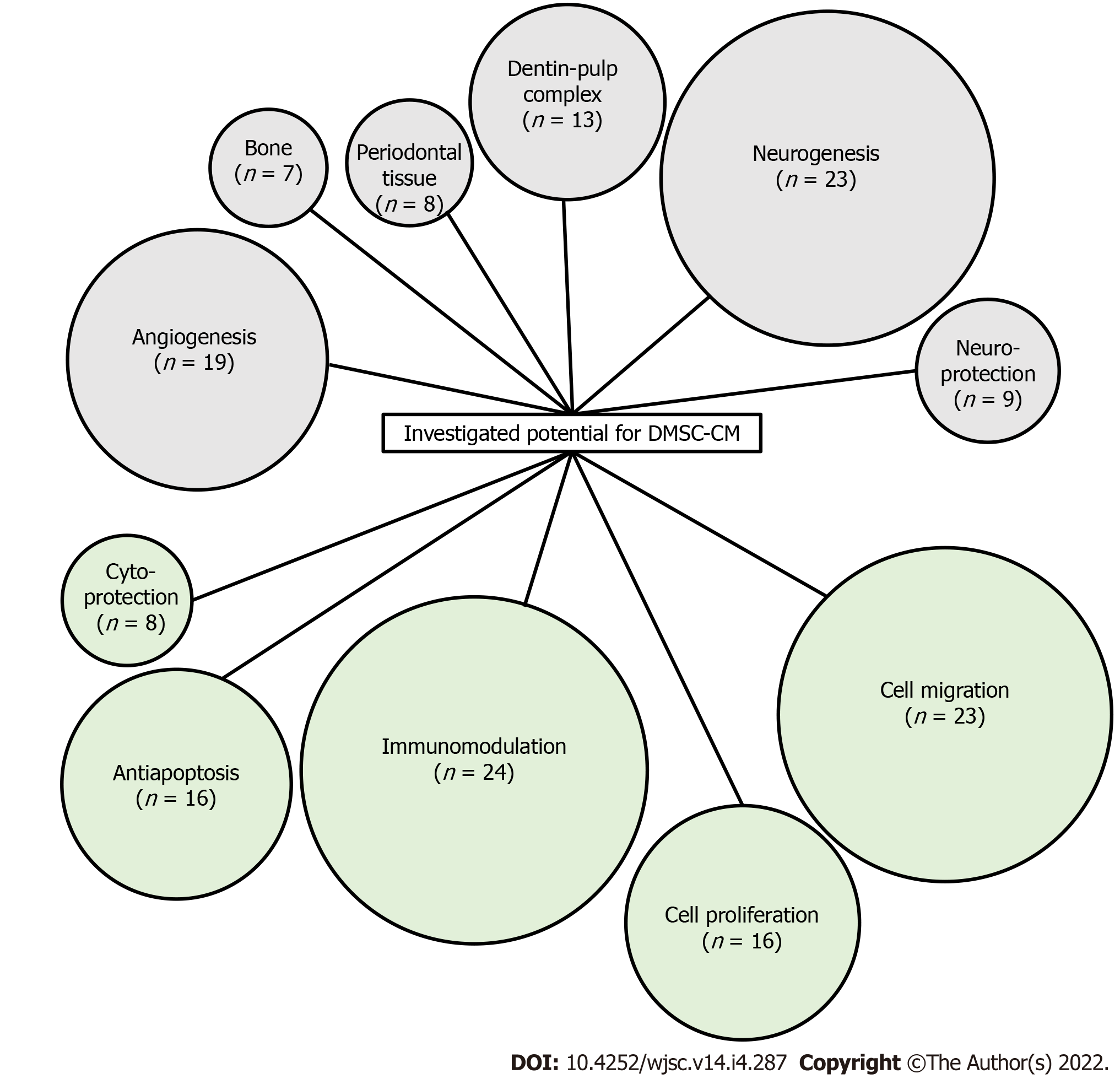
Figure 3 Schematic representation of the characteristics investigated as potential applications of dental mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium.
Number in brackets indicates the number of publications considering the activity. DMSC-CM: Dental mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium.
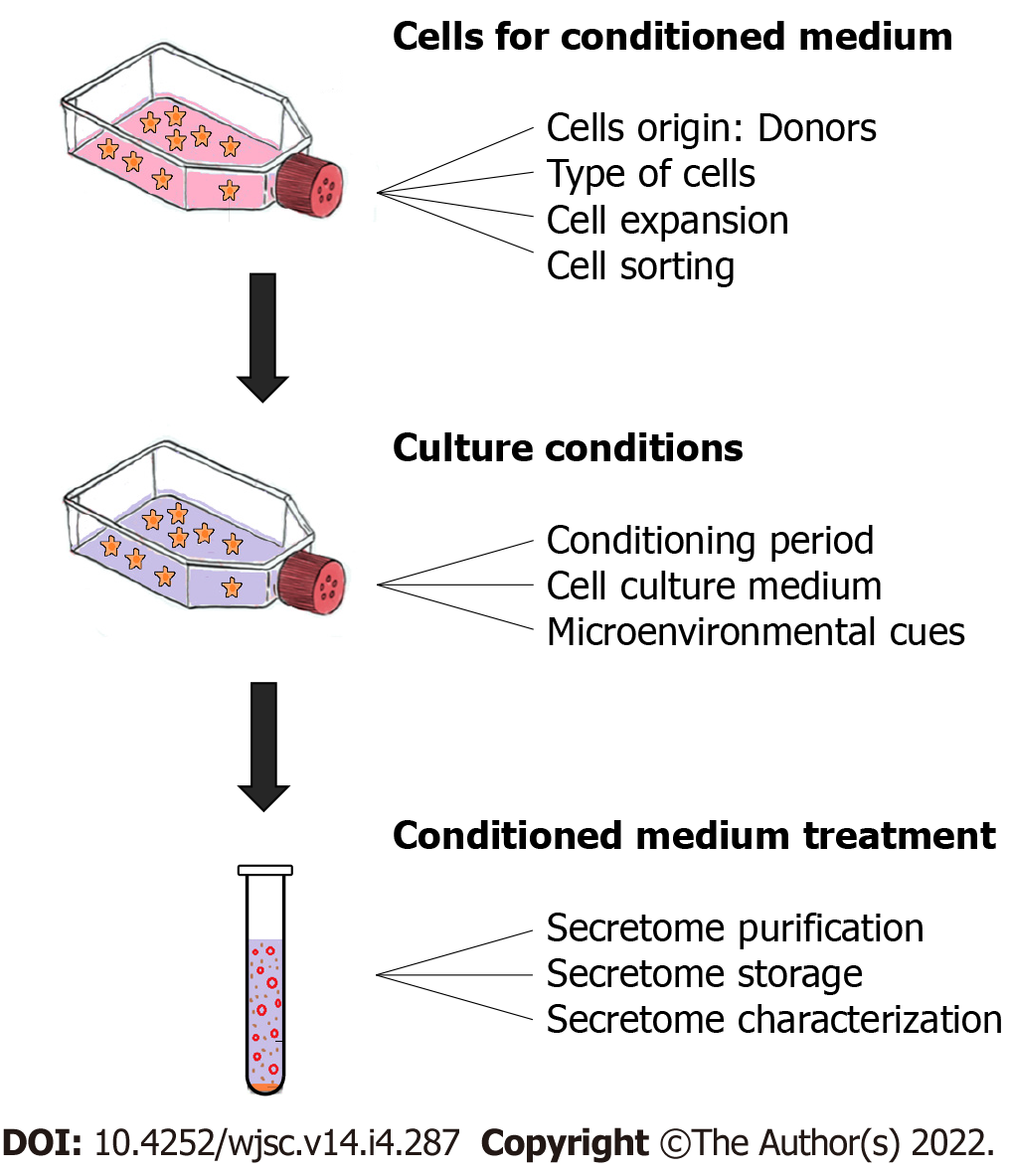
Figure 4 Schematic representation of the 3 main steps of evaluation, with corresponding key points.
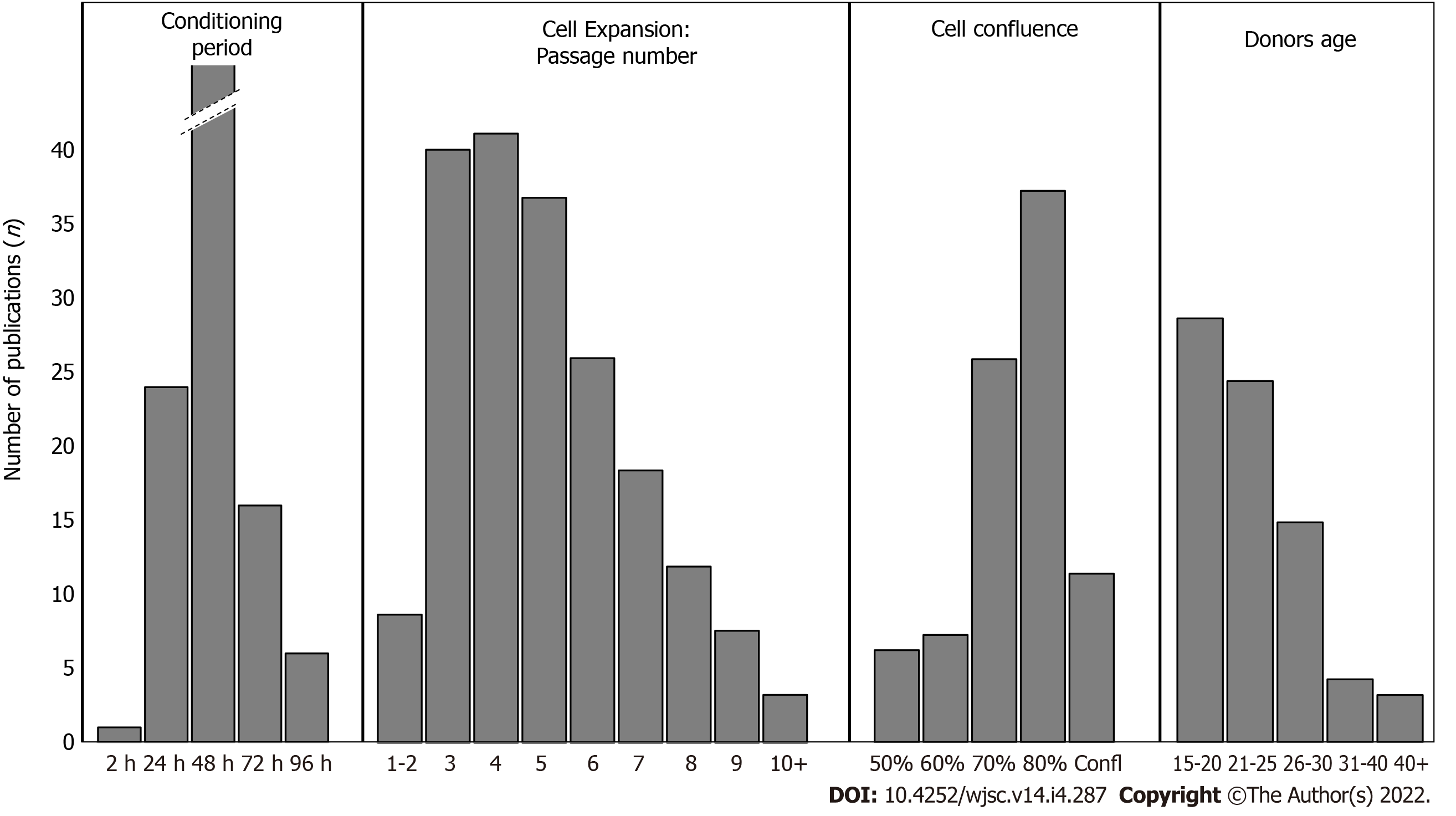
Figure 5 Histograms showing the number of publications for each parameter from the 4 specific key points: Conditioning period; Cell passage number; Cell confluence; Donor age.
- Citation: Chouaib B, Cuisinier F, Collart-Dutilleul PY. Dental stem cell-conditioned medium for tissue regeneration: Optimization of production and storage. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(4): 287-302
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i4/287.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i4.287