Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2021; 13(8): 1094-1111
Published online Aug 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1094
Published online Aug 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1094
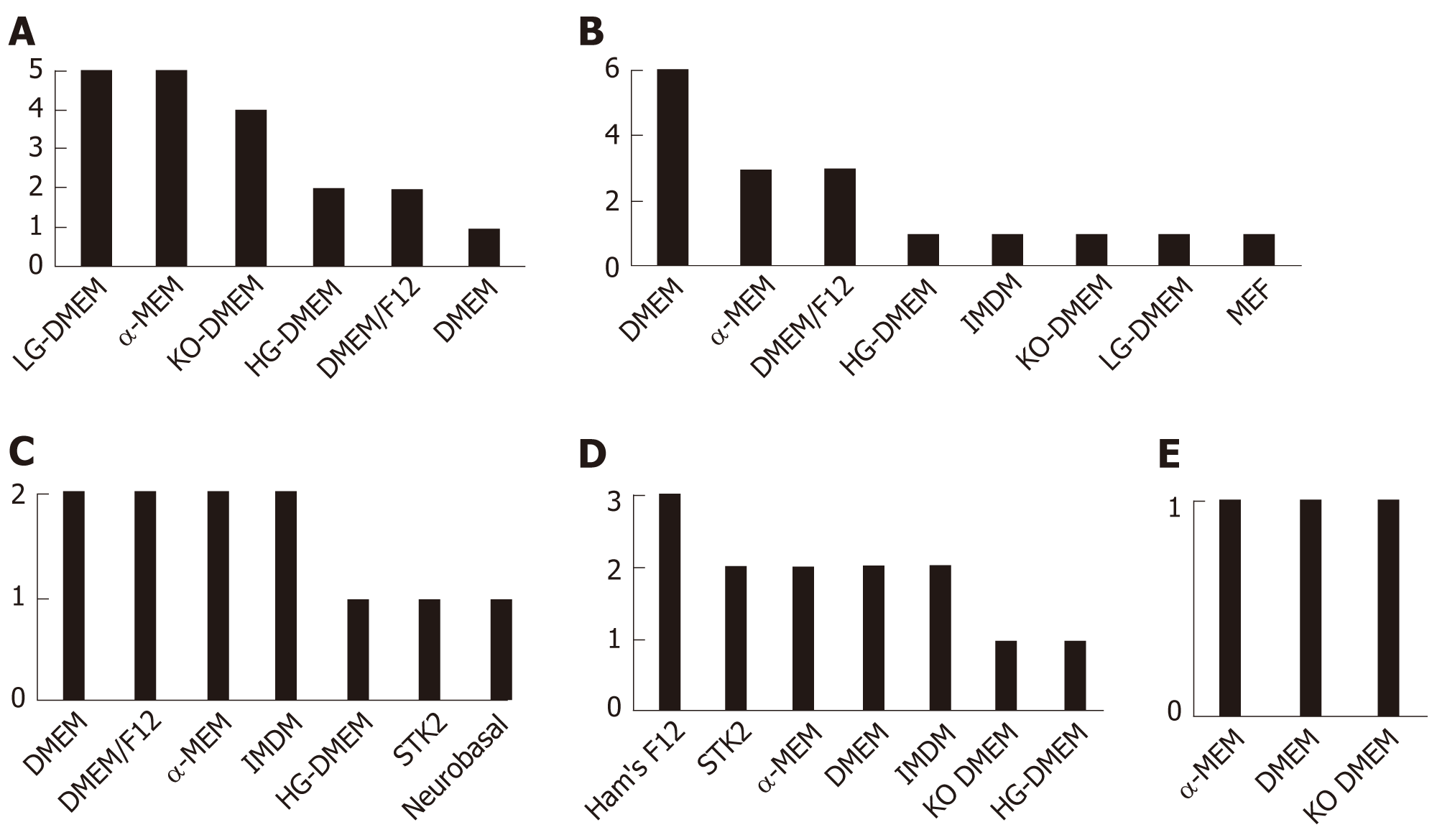
Figure 1 Basal commercial media used to produce induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
The relative frequencies of media used by the 32 studies are displayed as number of events within each of the five categories of protocols being described: Mesenchymal stem cell Switch (A), Embryoid Bodies (B), Specific Differentiation (C), Pathway Inhibitor (D), and Platelet Lysate (E). DMEM: Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; DMEM/F12: Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium F12; Ham's F12: Medium formulated for single-cell plating of near-diploid Chinese hamster ovary cells; HG-DMEM: High glucose Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; IMDM: Iscove's modified Dulbecco's media; KO-DMEM: Knockout Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; LG-DMEM: Low glucose Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; MEF: Mouse embryonic fibroblast media; αMEM/MEM: Minimum essential medium Eagle.
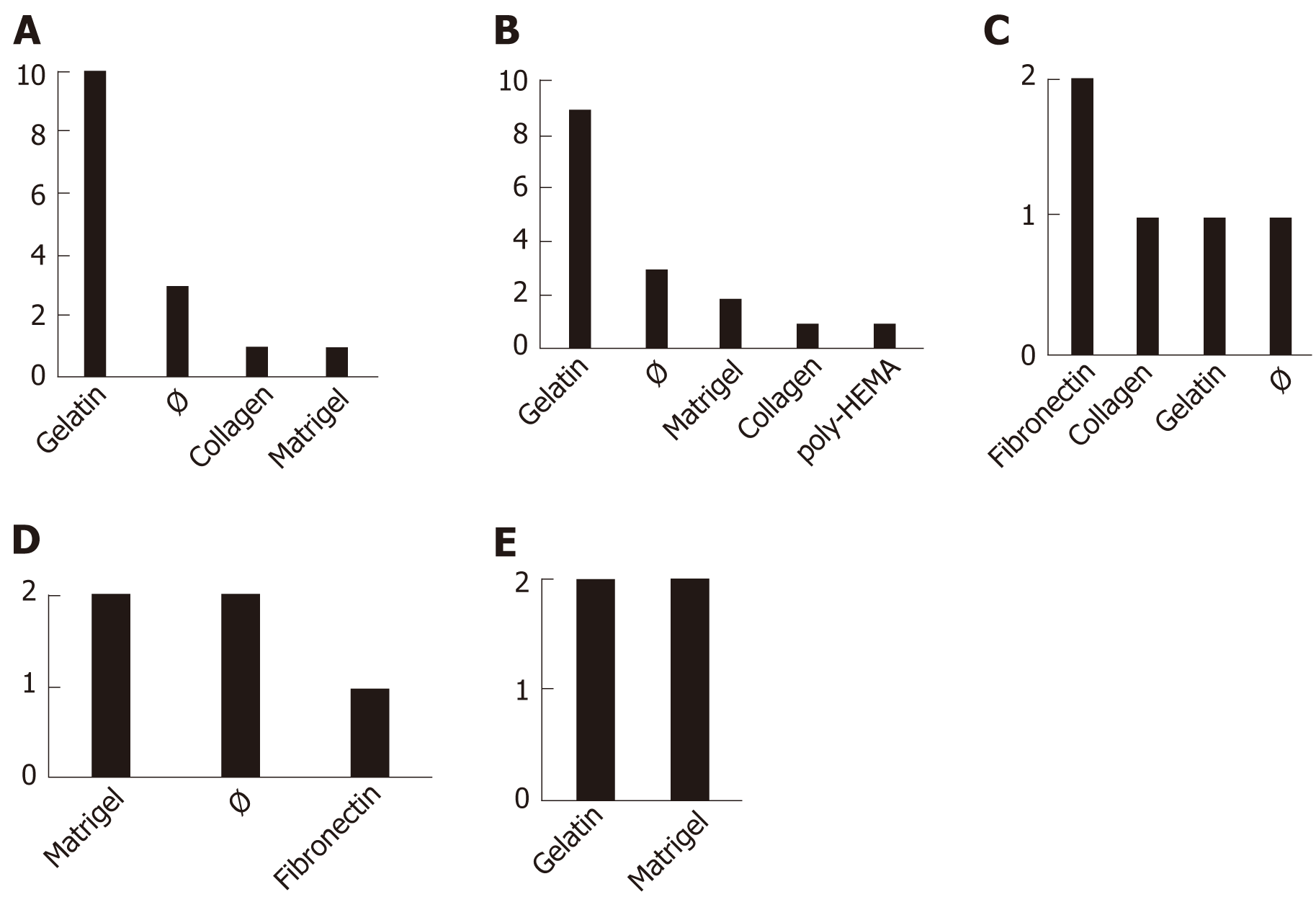
Figure 2 Coatings used to produce induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
The relative frequencies of coatings used by the 32 studies are displayed as number of events within each of the 5 categories of protocols being described: Mesenchymal stem cell Switch (A), Embryoid Bodies (B), Specific Differentiation (C), Pathway Inhibitor (D), and Platelet Lysate (E). Note that some studies use more than one type of coating. The symbol “Ø” indicates (absence of coating). poly HEMA: Polymer forming hydrogel in water.
- Citation: Dupuis V, Oltra E. Methods to produce induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Mesenchymal stem cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(8): 1094-1111
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i8/1094.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1094