©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2021; 13(12): 1813-1825
Published online Dec 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i12.1813
Published online Dec 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i12.1813
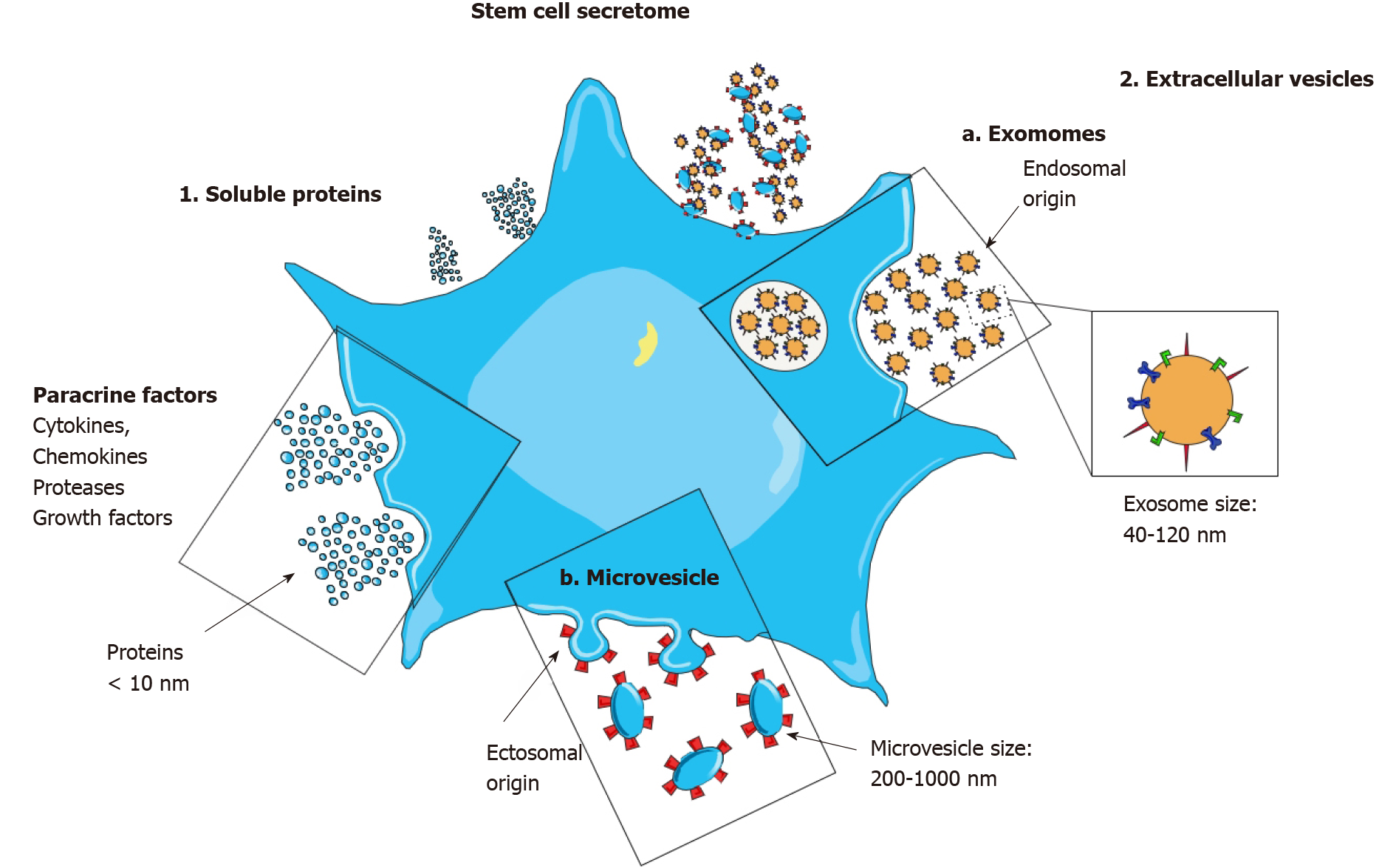
Figure 1 The stem cell secretome.
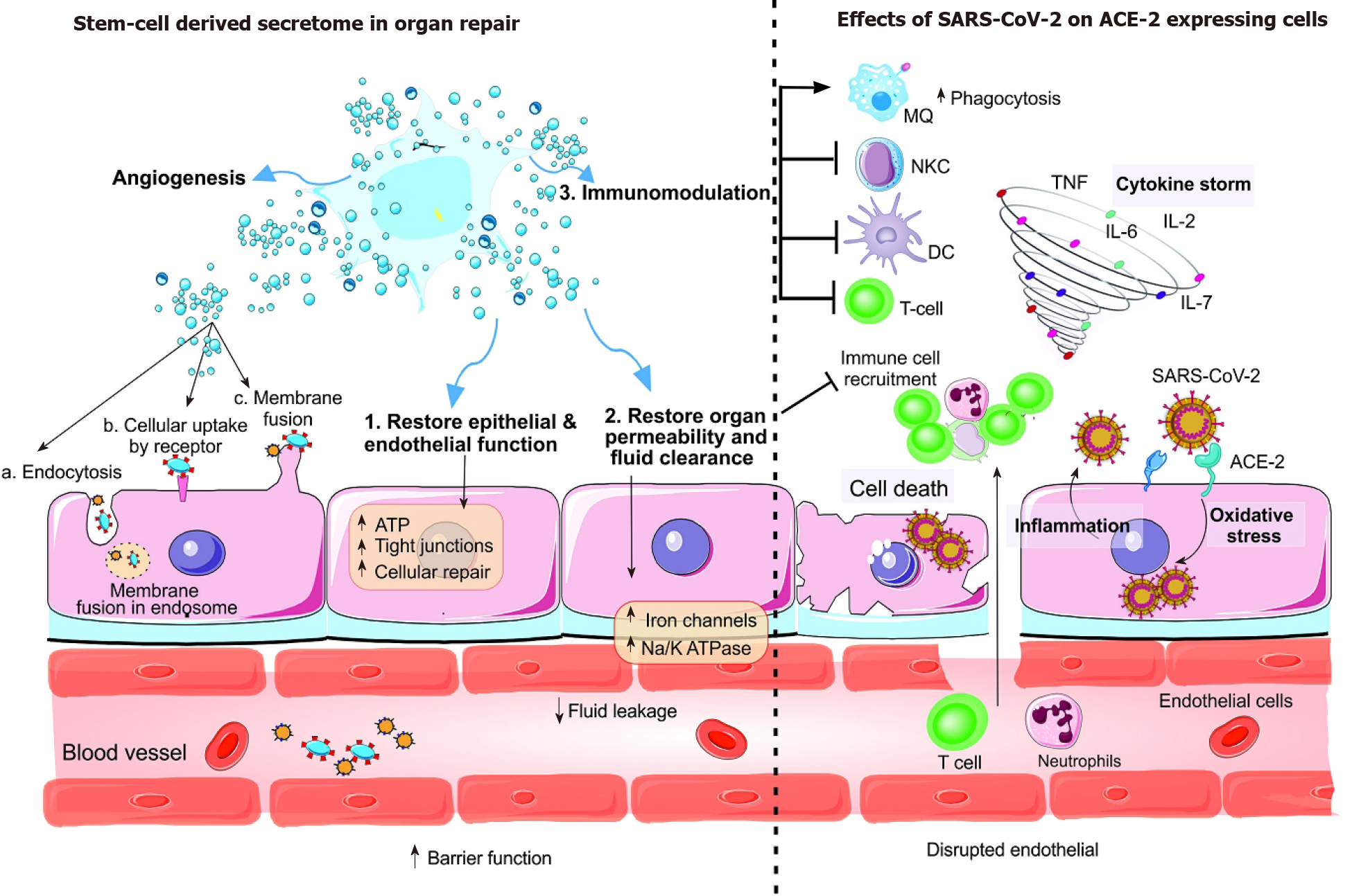
After the interaction between host angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and the spike S protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, the membrane is fused, and the viral genome is released into the cell or the virus enters the cell by clathrin-dependent/independent endocytosis. Most of the cells in human organs including the intestine, heart, kidney, and alveolar type II (AT2) cells of the lungs express ACE2 receptors. Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (EMMPRIN or CD147) and two proteases transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) are required for virus entry into the host cell. The lungs are damaged after direct destruction of capillary endothelial cells and AT2, the renin-angiotensin system is disrupted or the immune response is diminished indirectly. Following virus-induced infection, pathogen-associated molecular patterns lead to recognition of the virus by the innate immune system, activation of nuclear factor-κappa B and IRF3 pathways, type I interferon (IFN) expression and consequently activation of the JAK/STAT pathway and finally the expression of IFN-stimulated genes (ISG) which have anti-viral activity. The abovementioned effective immune response is required for successful virus clearance and clinical disappearance of the disease. Nonetheless, the IFN response may be delayed due to evasion of IFN and ISG mediated killing by the virus which in turns leads to hyper-inflammatory neutrophils and macrophage infiltration at the pulmonary site accompanied by pro-inflammatory cytokines including granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, tumor necrosis factor, MCP1, and interleukin-1b/2/6/7/8/17[3]. This hyper-activation of T lymphocytes and the innate response is called the ‘cytokine storm’ and is responsible for lung disorders including acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumonitis, viral sepsis, respiratory and organ failure. A high number of pro-inflammatory cytokines leads to hyaluronan synthase 2 induction which elevates hyaluronan production and fluid accumulation in the lungs[78]. In critical cases of coronavirus disease 2019, the virus enters the peripheral blood and translocates to various target organs including kidney, heart, and intestine and can cause multiple organ failure. ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; DC: Dendritic cell.
Figure 2 Immunomodulation by the stem cell secretome.
The behavior of immune cells is altered by the secretion of various immunomodulatory factors. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) secrete SOD3 which inhibits neutrophil activation and infiltration of leukocytes. Also, MSCs secrete PGE2, SDF-1, and interleukin (IL)-10 and lead to macrophage polarization to the M2 phenotype. Furthermore, MSCs induce HLAG5 secretion (shift to CD4β CD25β T reg population), Il-4 secretion (shift to Th2 population), constitutive expression of transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), HGF, COX2, IL-10, IDO, and PGE2 which in turn inhibit T-cell proliferation. The secretion of IL-2 prevents inactivated NK cell proliferation, and secretion of HLAG5, TGF-β1, IDO, and PGE2 prevent cytokine secretion. In addition, MSCs cause B cells arrest in the G0/G1 phase and reduce the level of circulating immunoglobulins and secretion of CXCR4, CXCR5, CXCR7 by B cells. Due to the high amount of ISG gene expression, MSCs induce an antiviral response in the lungs. After secretion of immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and microRNAs mediators and their extracellular vesicles-mediated transfer, MSCs lead to regulatory lymphocyte and M2 macrophage production. Differentiation of MSCs to various lung epithelial cells or differentiation of host tissue-resident stem cells lead to the secretion of numerous growth factors and angiogenic factors to stimulate revascularization, and consequently repair structural injury. Recovery of alveolar cell functions, their ATP stores, and metabolic capacity is feasible by direct transfer of functional mitochondria. Anti-fibrotic cytokines in high amounts reduce collagen fibers and subsequently hyper-inflammation and oxidative stress. A combination of anti-viral drugs with the immunomodulatory cargo of MSCs exosomes is a promising intervention tool in disease treatment[54]. Remdesivir is the best example of drug loading on exosomes[79]. Nevertheless, more studies are needed to clarify the exact mechanism of the specificity, targeted delivery and safety of exosomes.
- Citation: Ardalan M, Chodari L, Zununi Vahed S, Hosseiniyan Khatibi SM, Eftekhari A, Davaran S, Cucchiarini M, Roshangar L, Ahmadian E. Stem cell-derived biofactors fight against coronavirus infection. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(12): 1813-1825
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i12/1813.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i12.1813