©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2020; 12(10): 1184-1195
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1184
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1184
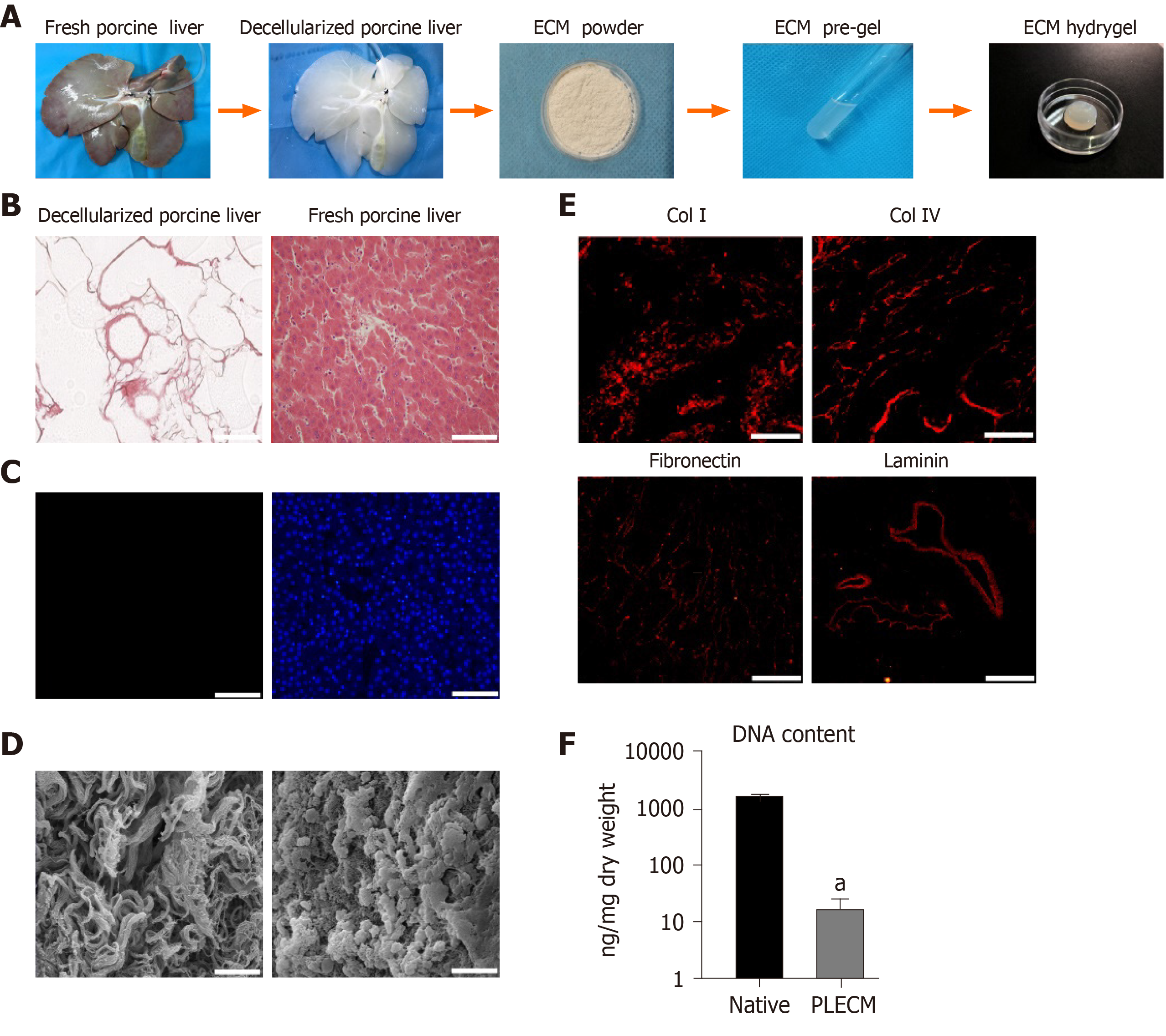
Figure 1 Formation and characterization of porcine liver extracellular matrix gel.
A: Procedure for the formation of porcine liver extracellular matrix (PLECM) gels; B: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of PLECM (left) and porcine liver (right). Scale bars = 100 μm; C: 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining of PLECM (left) and porcine liver (right). Scale bars = 100 μm; D: Scanning electron microscopy of PLECM (left) and porcine liver (right). Scale bars = 20 μm; E: Immunohistochemistry (red) for liver extracellular matrix proteins (collagen type I, collagen type IV, fibronectin, and laminin) in PLECM. Scale bars = 200 μm; F: Relative DNA content. aP < 0.05 vs PLECM. ECM: Extracellular matrix; Col I: Collagen type I; Col IV: Collagen type IV; PLECM: Porcine liver extracellular matrix.
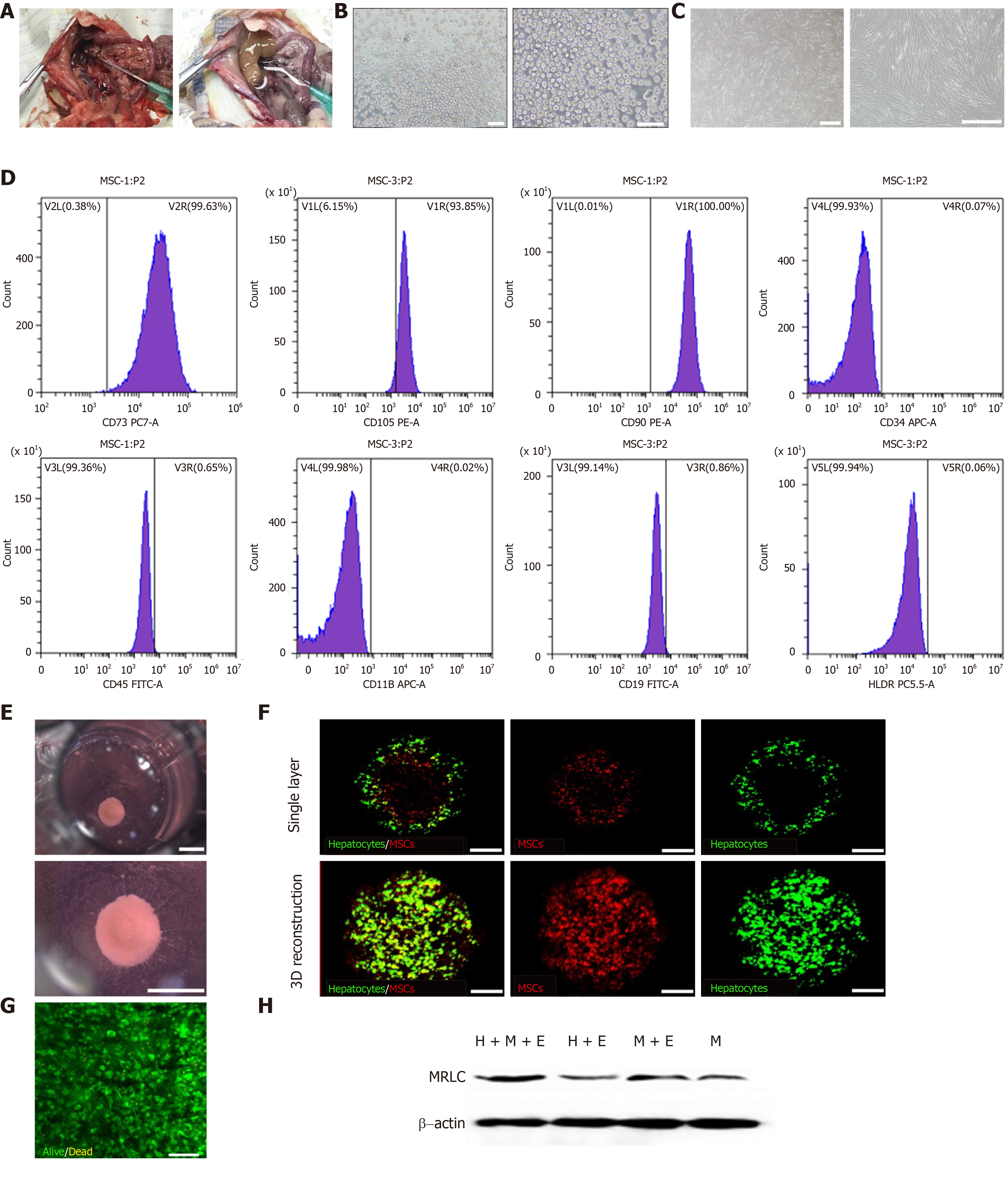
Figure 2 Self-assembly of liver organoids via mesenchymal stem cell-driven condensation.
A: Gross view of rat liver before (left) and after (right) perfusion via hepatic portal vein; B: Image of freshly isolated primary hepatocytes. Scale bars = 100 μm; C: Images of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Scale bars = 500 μm; D: Expression of cell surface markers on MSCs. MSCs were positive for the mesenchymal markers CD73, CD105, and CD90, and negative or with low expression for hematopoietic markers CD34, CD45, CD19, and CD11b, and no expression of HLA-DR; E: Gross view of organoid. Scale bars = 1000 μm; F: Confocal images of the organoids. Green: Hepatocytes; red: MSCs. Top: A single layer; bottom: 3D reconstruction. scale bars = 200 μm; G: Staining for cell viability with Fluoroquench. Scale bar = 100 μm; H: Western blot analysis of myosin-II regulatory light chain. 3D: Three dimension; MRLC: Myosin-II regulatory light chain; H+M+E group: Hepatocytes and MSCs seeded on ECM-gel pre-coated plate; H+E group: Hepatocytes seeded on ECM-gel pre-coated plate; M+E group: MSCs seeded on ECM-gel pre-coated plate; M group: MSCs seeded on ECM-gel free plate; ECM: Extracellular matrix.
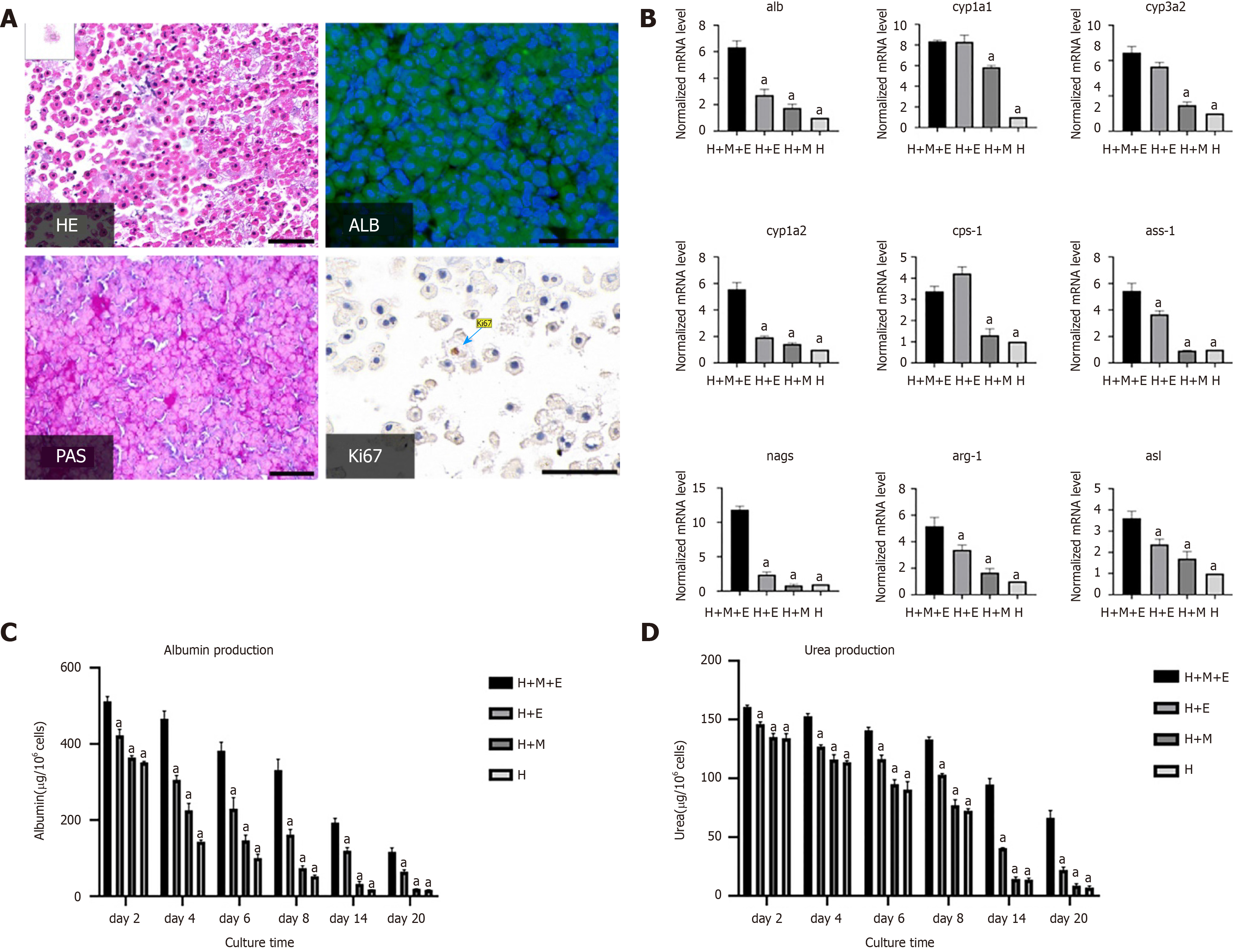
Figure 3 Liver organoids maintain the function of hepatocytes and prolong their survival time.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining, immunofluorescence staining for albumin (ALB; green), and immunohistochemical staining for Ki67. The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 100 μm; B: Gene expression analysis by q-PCR. Data were normalized to hepatocytes (H group); C: Secretion of albumin was measured by ELISA on days 2, 4, 6, 8, 14, and 20; D: Urea synthesis was measured on days 2, 4, 6, 8, 14, and 20. aP < 0.05 vs the organoid (H+M+E group). H+M+E group: Hepatocytes and MSCs seeded on ECM-gel pre-coated plate; H+E: Hepatocytes seeded on ECM-gel pre-coated plate; H+M: Hepatocytes and MSCs seeded on ECM-gel free plate; H group: Hepatocytes seeded on ECM-gel free plate; ECM: Extracellular matrix.
- Citation: He YT, Zhu XL, Li SF, Zhang BQ, Li Y, Wu Q, Zhang YL, Zhou YY, Li L, Qi YN, Bao J, Bu H. Creating rat hepatocyte organoid as an in vitro model for drug testing. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(10): 1184-1195
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i10/1184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i10.1184