©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2019; 11(3): 196-211
Published online Mar 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i3.196
Published online Mar 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i3.196
Figure 1 Characterization of isolated nucleus pulposus-derived stem cells.
A: Nucleus pulposus-derived stem cells (NPSCs) at P0 and P3 showing a homogeneous fibroblast-like morphology and vortex performance; B: NPSCs at P3 showing colony-like growth ability at a density of 1000 cells/well; C: Multilineage differentiation capacities of NPSCs in vitro. Alizarin Red staining for osteogenic differentiation, Oil Red O staining for adipogenic differentiation, and Alcian Blue staining for chondrogenic differentiation; D: Flow cytometric analysis of NPSCs surface markers revealing high expression of the mesenchymal stem cells markers CD73, CD90, and CD105, and low expression of the hematopoietic markers CD34 and CD45. FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; PE: Phycoerythrin.
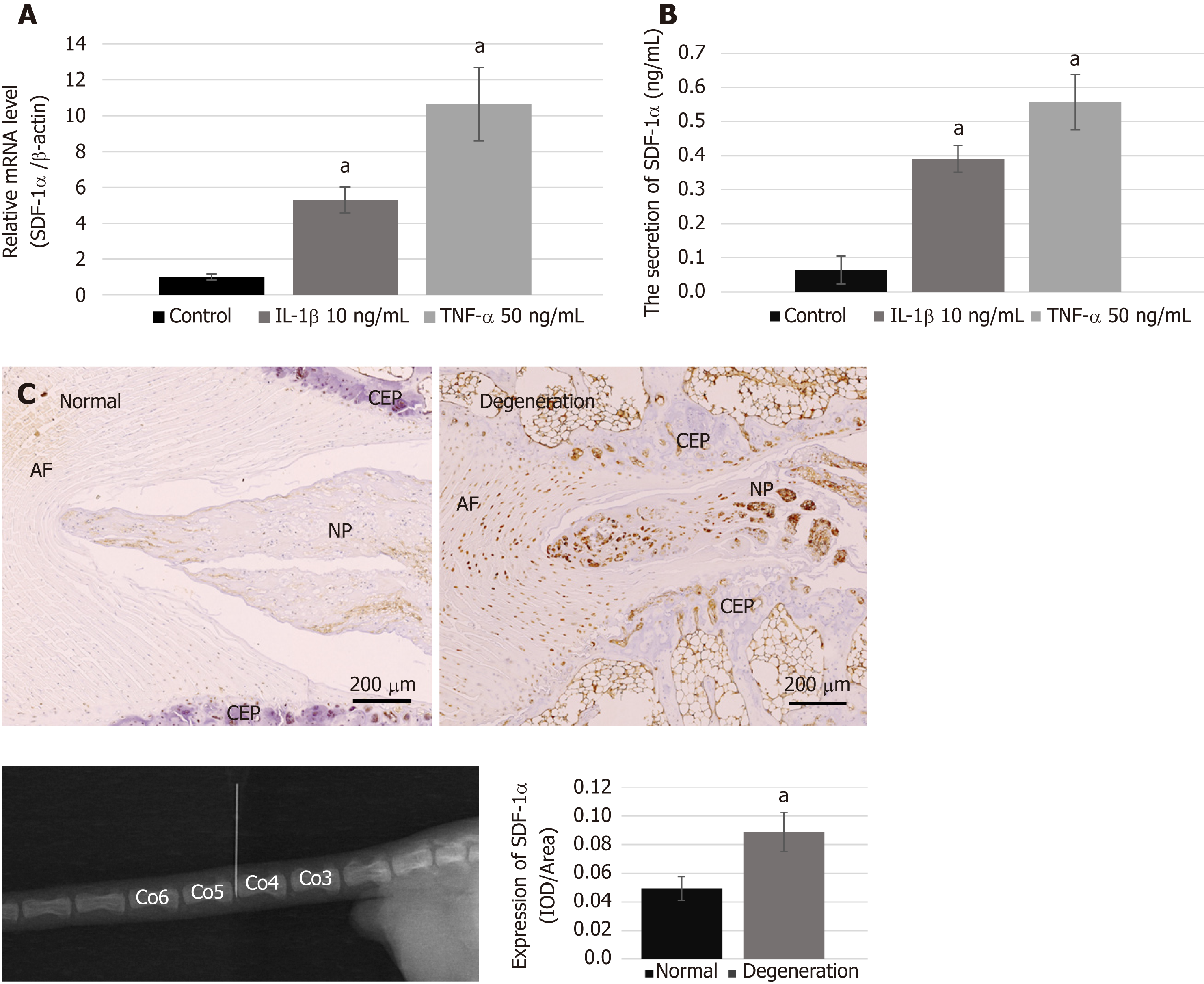
Figure 2 Expression of stromal cell-derived factor-1α and the condition of the degenerative disc.
A and B: The mRNA (A) and protein (B) levels of stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) expressed in nucleus pulposus cells with pro-inflammatory cytokines were markedly increased compared with those in normal condition, based on real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; C: Immunohistochemical analysis showing the significant upregulation of SDF-1α in the degenerative disc. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 3, aP < 0.05. SDF-1α: Stromal cell-derived factor-1α; NP: Nucleus pulposus; IOD: Integrated optical density; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL: Interleukin.
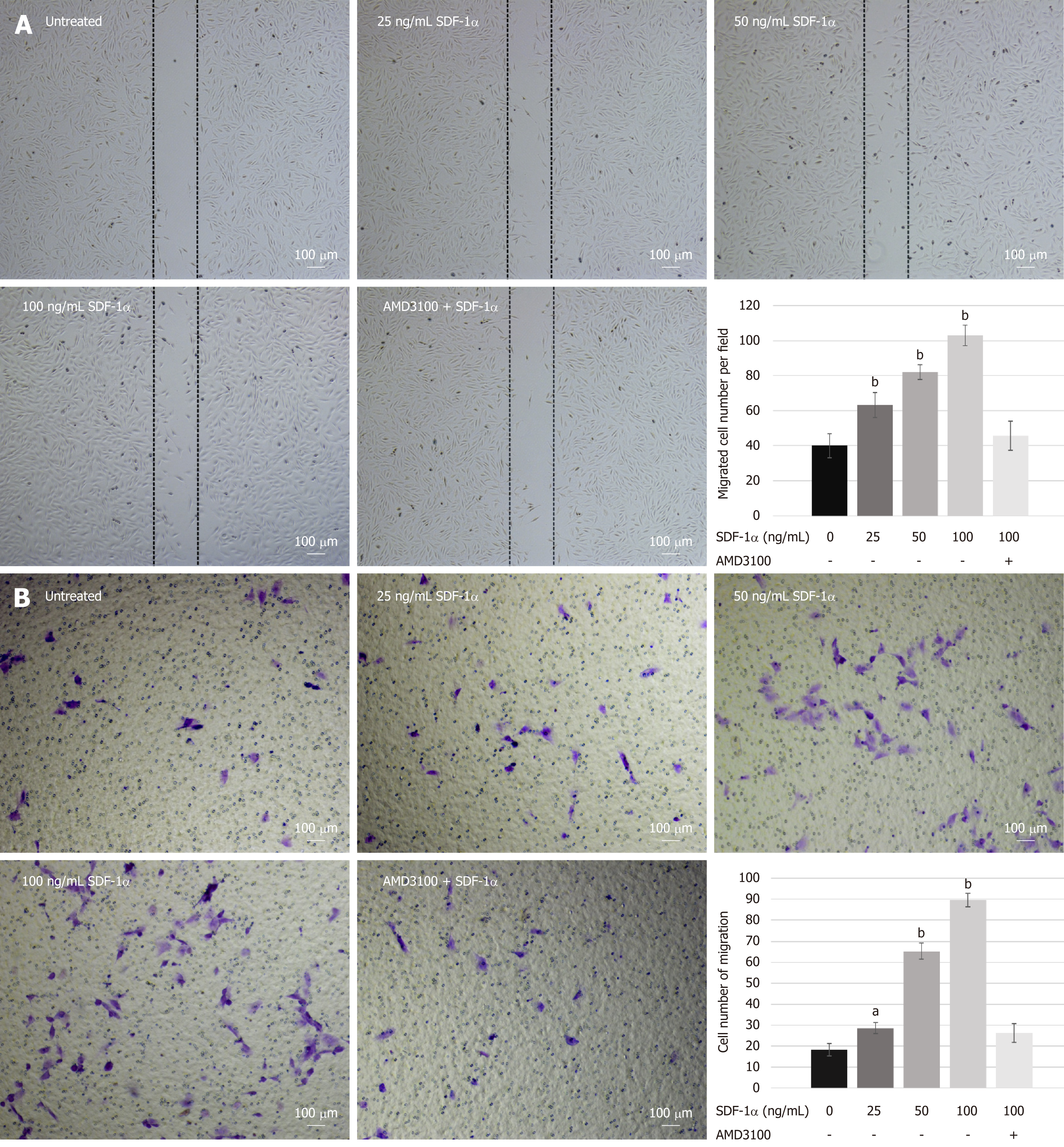
Figure 3 Migration capacity of nucleus pulposus-derived stem cells treated with stromal cell-derived factor-1α in vitro.
A and B: Wound-healing (A) and transwell migration (B) assays showed that nucleus pulposus-derived stem cells migration was enhanced by stromal cell-derived factor-1α in a dose-dependent manner but abolished by AMD3100. Data are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 3, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. SDF-1α: Stromal cell-derived factor-1α.
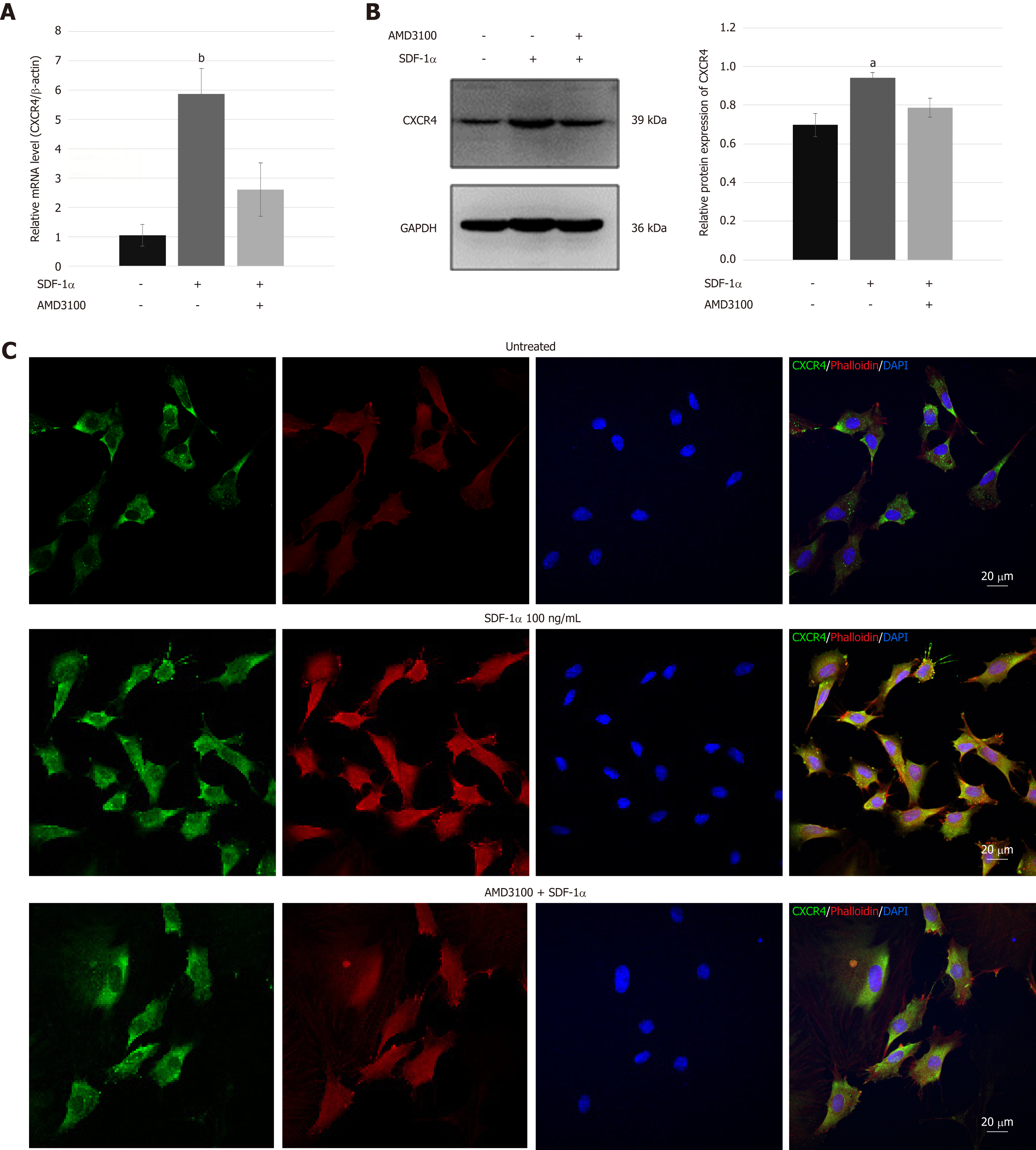
Figure 4 C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 expression in nucleus pulposus-derived stem cells.
A and B: Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (A) and immunoblotting (B) analyses of the expression of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) in nucleus pulposus-derived stem cells (NPSCs) treated with stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α); C: Immunofluorescence analysis of CXCR4 (green) and F-actin (red) in NPSCs. CXCR4 in NPSCs was not only upregulated but also transferred from the cytoplasm to membrane after treatment with SDF-1α. In addition, SDF-1α enhanced remodeling of the cytoskeleton and the formation of lamellipodia in NPSCs. These effects were inhibited by AMD3100. Data are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 3, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. CXCR4: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; SDF-1α: Stromal cell-derived factor-1α.
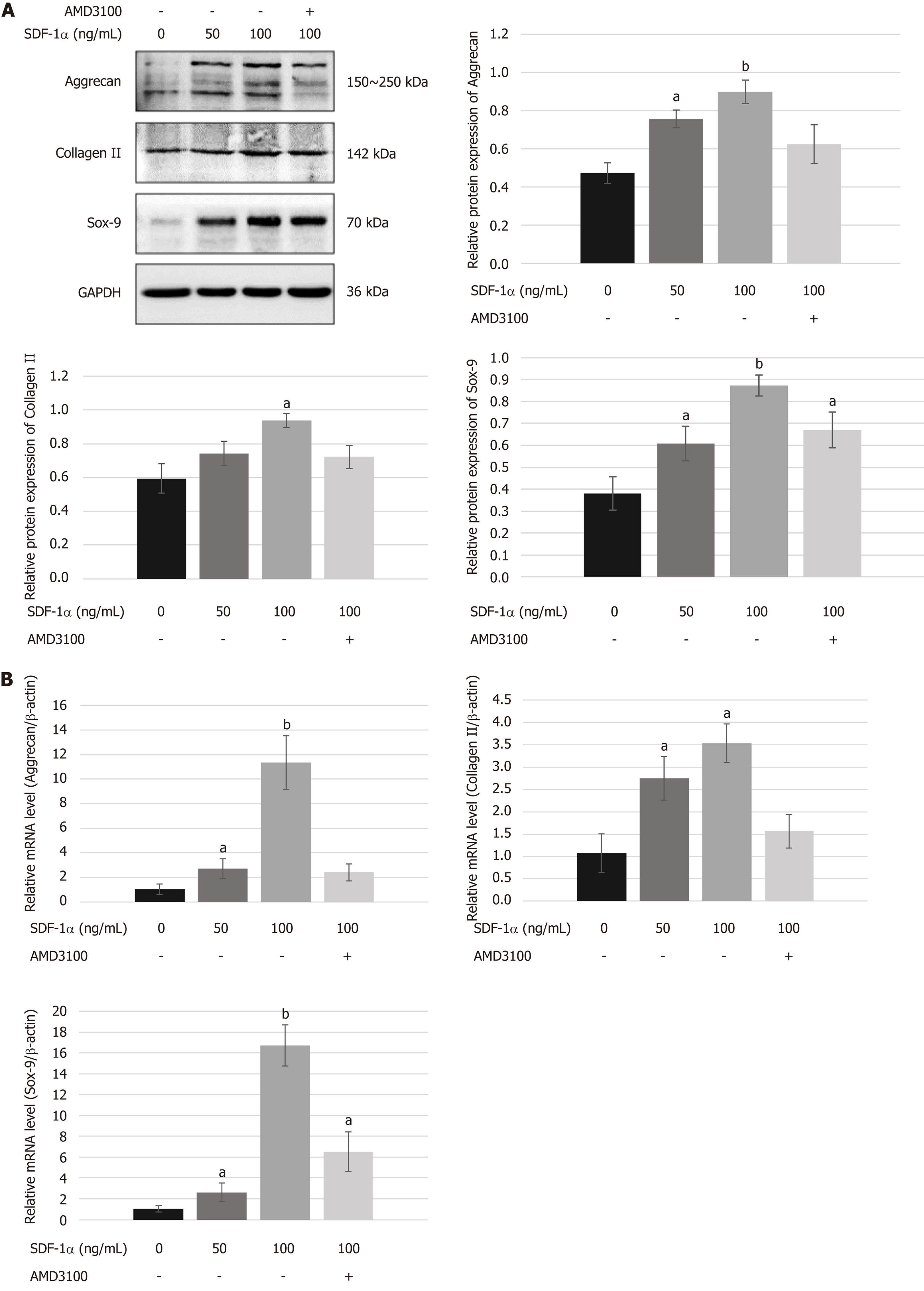
Figure 5 Effects of stromal cell-derived factor-1/C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 axis on chondrogenesis differentiation of nucleus pulposus-derived stem cells in vitro.
A and B: Western blot (A) and real-time RT-PCR (B) showed that stromal cell-derived factor-1α upregulated the expression of chondrocyte phenotypes such as aggrecan, collagen II, and Sox-9 in a dose-dependent manner. However, the upregulated expression of aggrecan and collagen II was suppressed by AMD3100. Data are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 3, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. SDF-1: Stromal cell-derived factor-1; Sox-9: SRY-related high mobility group box gene 9.
Figure 6 Effects of stromal cell-derived factor-1/C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 axis on chondrogenesis differentiation of nucleus pulposus-derived stem cells using cell micromass culture.
A: Representative images of the gross cell aggregates and comparison of the weight of the aggregates among various groups; B: Histological analysis of proteoglycan content in the aggregates using Alcian Blue staining; C: Immunohistochemical analysis of the synthesis of aggrecan and collagen II after different treatments. The results suggest that stromal cell-derived factor-1 enhanced nucleus pulposus-derived stem cells differentiation toward chondrocytes, but this effect was significantly suppressed by AMD3100. Values are the mean ± SD of three pellets per group, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. SDF-1: Stromal cell-derived factor-1; IOD: Integrated optical density.
- Citation: Ying JW, Wen TY, Pei SS, Su LH, Ruan DK. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α promotes recruitment and differentiation of nucleus pulposus-derived stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(3): 196-211
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i3/196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i3.196