©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2018; 10(5): 43-56
Published online May 26, 2018. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v10.i5.43
Published online May 26, 2018. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v10.i5.43
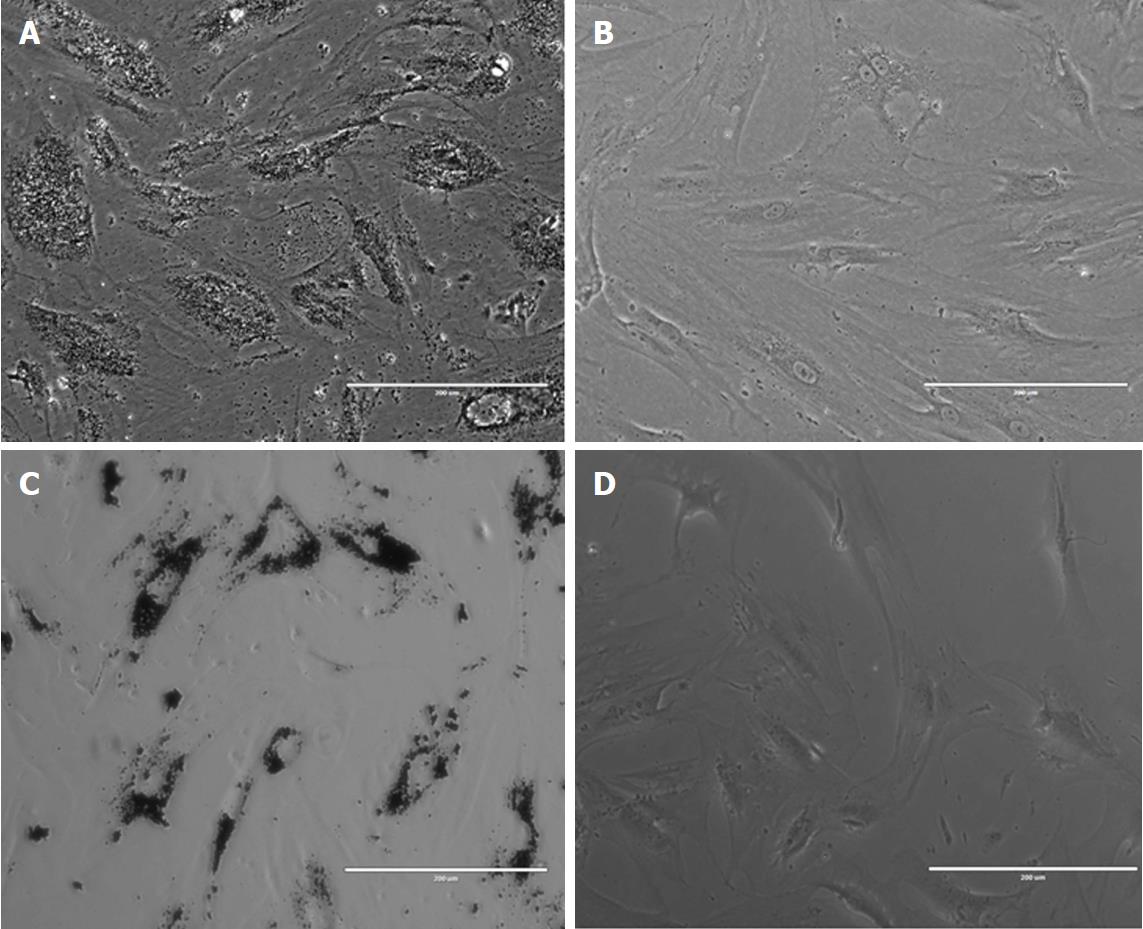
Figure 1 Stem and progenitor cells loaded with magnetic nanoparticles added to culture media.
A: human osteoblasts loaded with Fe-Cr-Nb-B magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs); B: Non-loaded human osteoblasts; C: Human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells loaded with Fe-Cr-Nb-B MNPs; D: Non-loaded human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
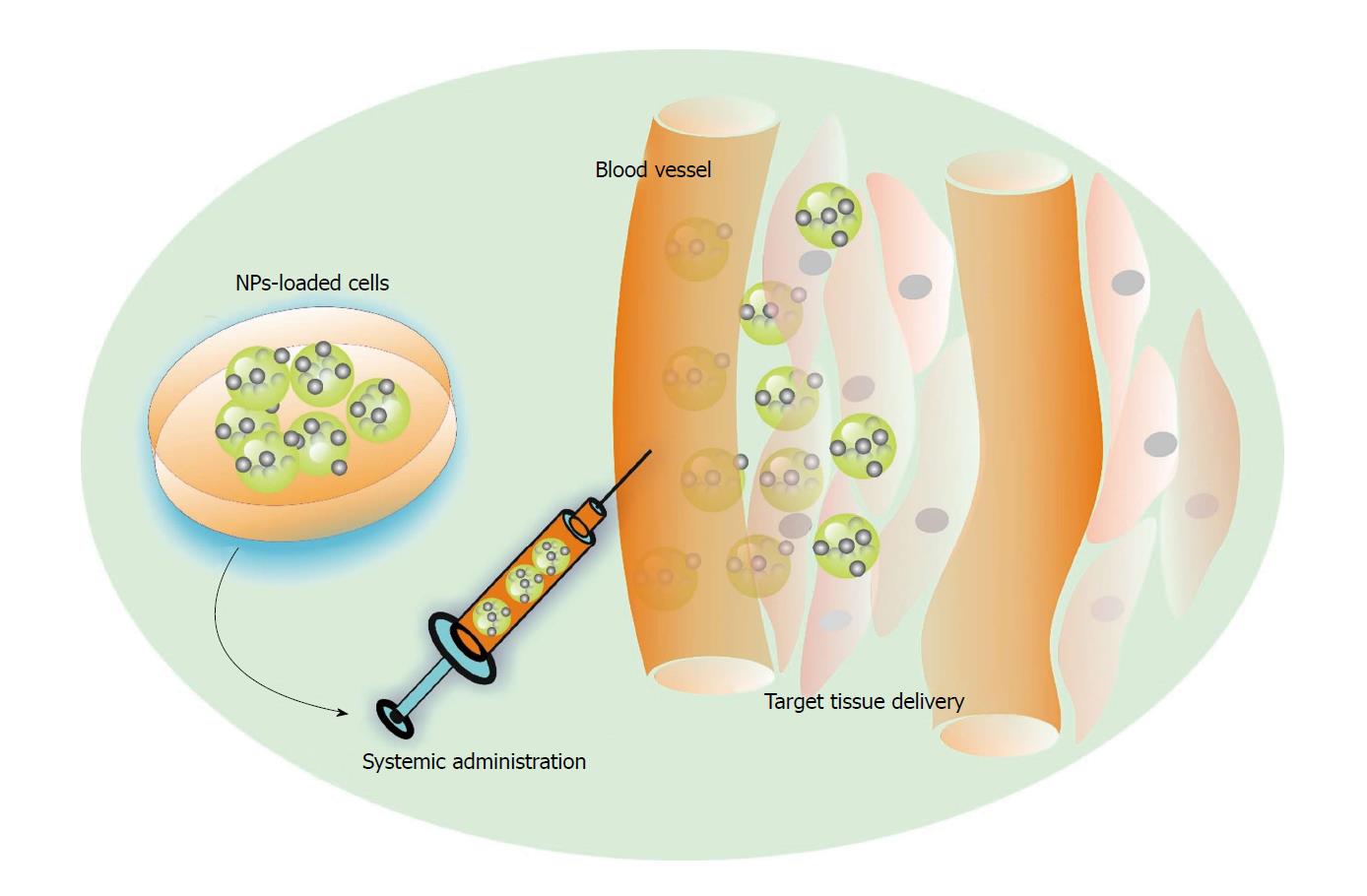
Figure 2 Possible scenario for nanoparticle-loaded stem cell delivery of bioactive molecules towards target organs.
Stem cells loaded or decorated with nanoparticle attached to their membrane can be delivered via systemic infusion (intravenous or intraarterial) to migrate by means of blood flow, homing to regenerative sites.
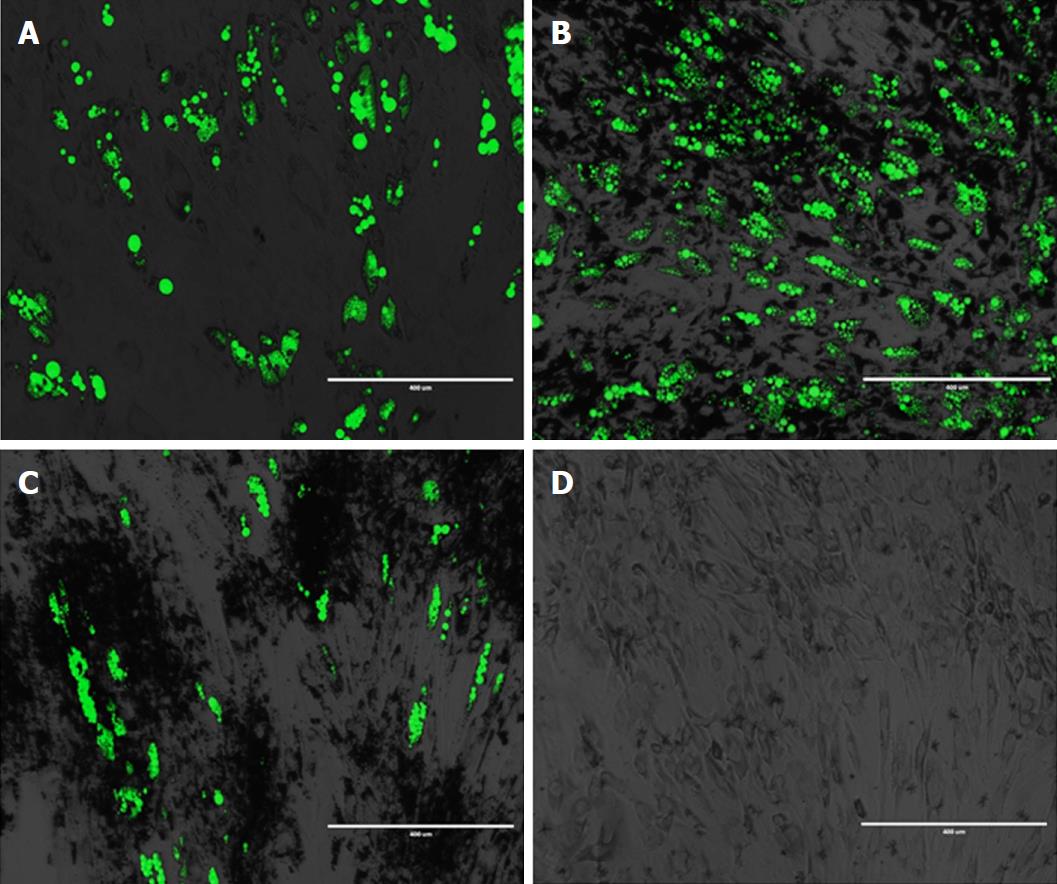
Figure 3 Adipogenic differentiation of human primary adipose-derived stem cells loaded with bare and chitosan-coated Fe-Cr-Nb-B magnetic nanoparticles.
A: Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) cells; B: ADSC-magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs); C: ADSC-C-MNPs; D: Control of differentiation (ADSCs grown in normal culture media).
- Citation: Labusca L, Herea DD, Mashayekhi K. Stem cells as delivery vehicles for regenerative medicine-challenges and perspectives. World J Stem Cells 2018; 10(5): 43-56
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v10/i5/43.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v10.i5.43