©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2026; 32(8): 115675
Published online Feb 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i8.115675
Published online Feb 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i8.115675
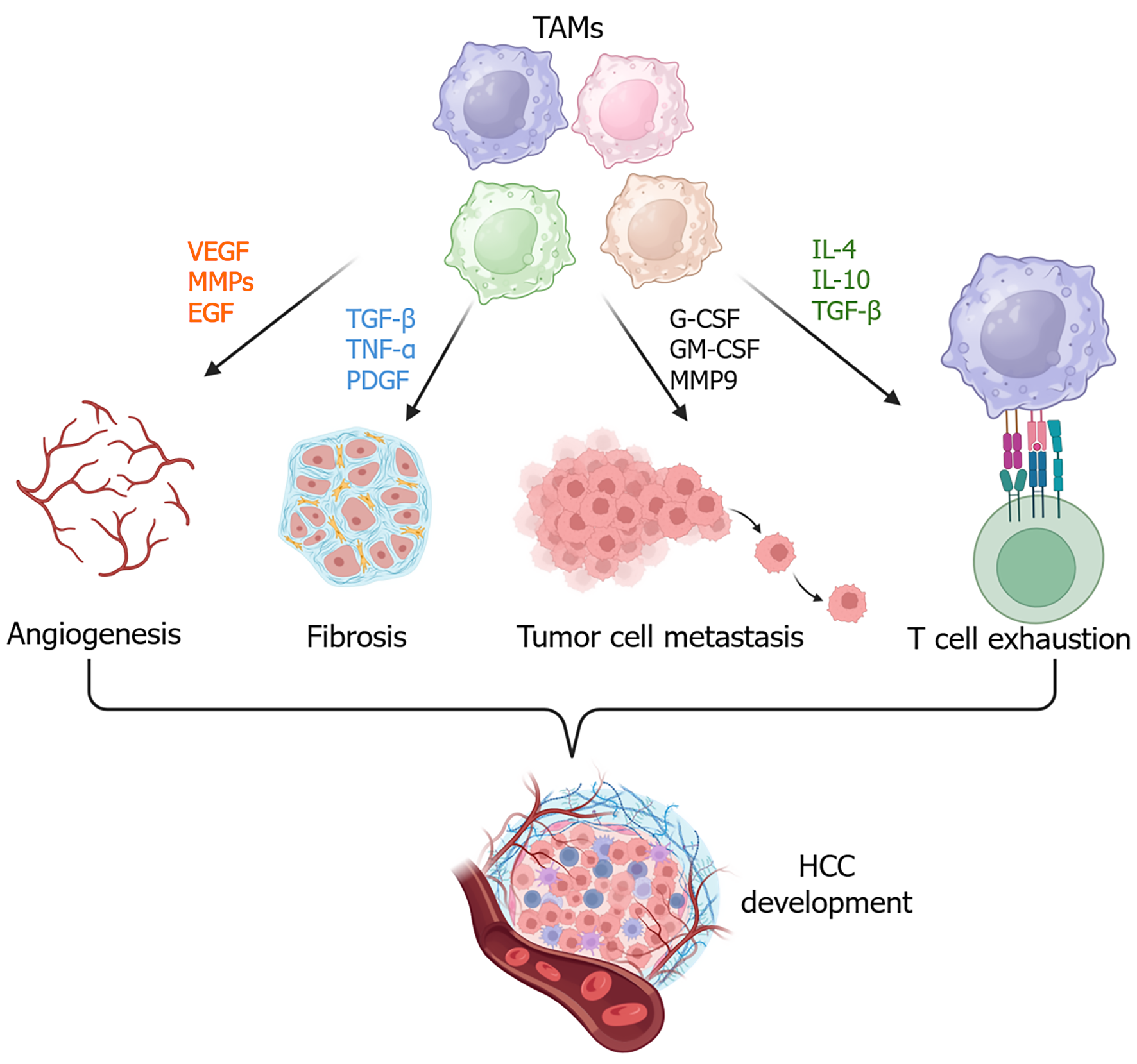
Figure 1 Tumor-associated macrophages contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma development.
Tumor-associated macrophages contribute to an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment by activating or inducing angiogenesis, fibrosis, tumor cell metastasis, and T cell exhaustion. TAMs: Tumor-associated macrophages; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; EGF: Endothelial growth factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; G-CSF: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL: Interleukin; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
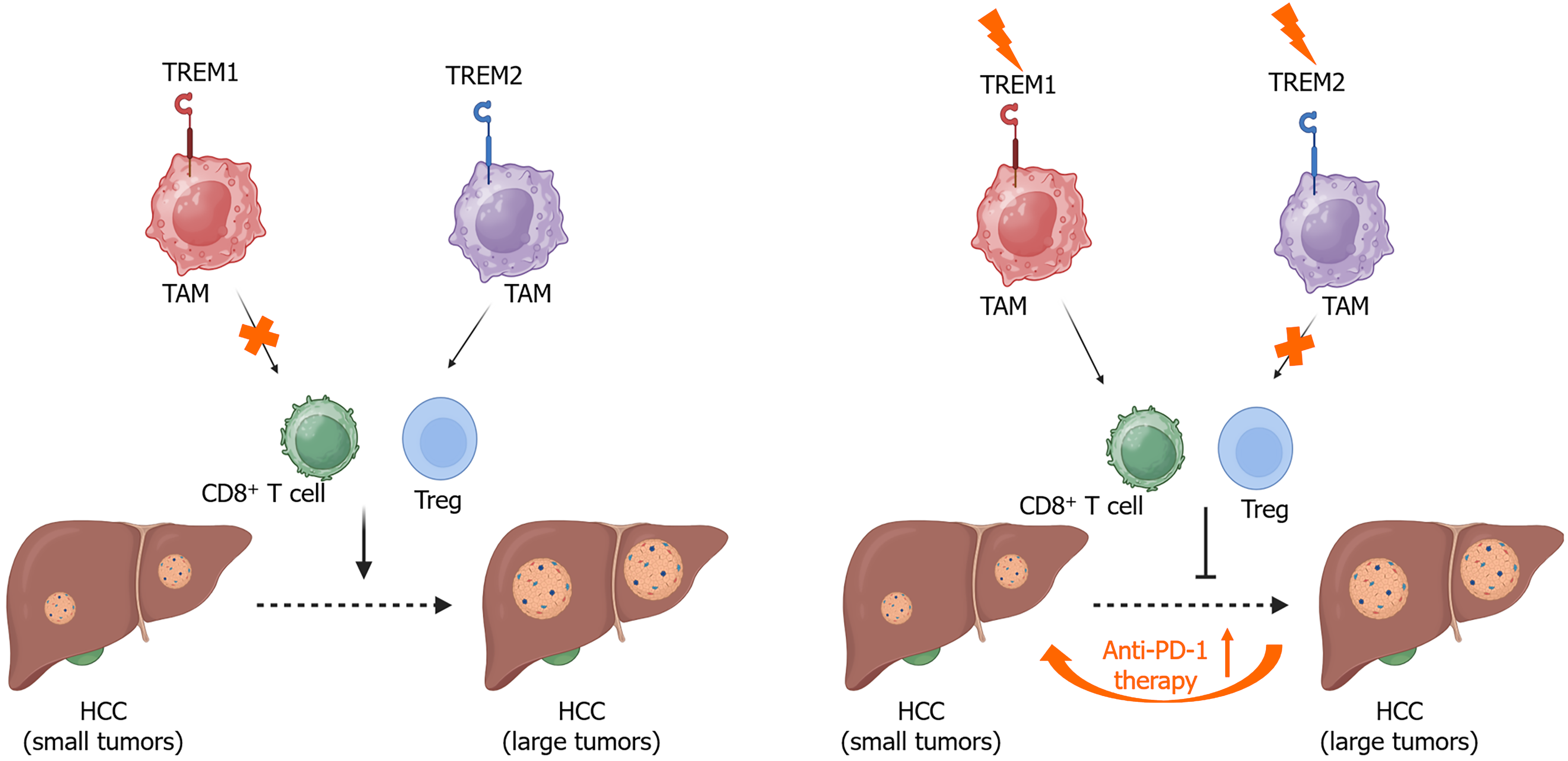
Figure 2 Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 and triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2 in tumor-associated macrophages modulate the infiltration and function of cluster of differentiation 8+ T cells and regulatory T cells, thereby impacting hepatocellular carcinoma progression.
TAMs: Tumor-associated macrophages; TREM: Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells; CD: Cluster of differentiation; Treg: Regulatory T cell; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
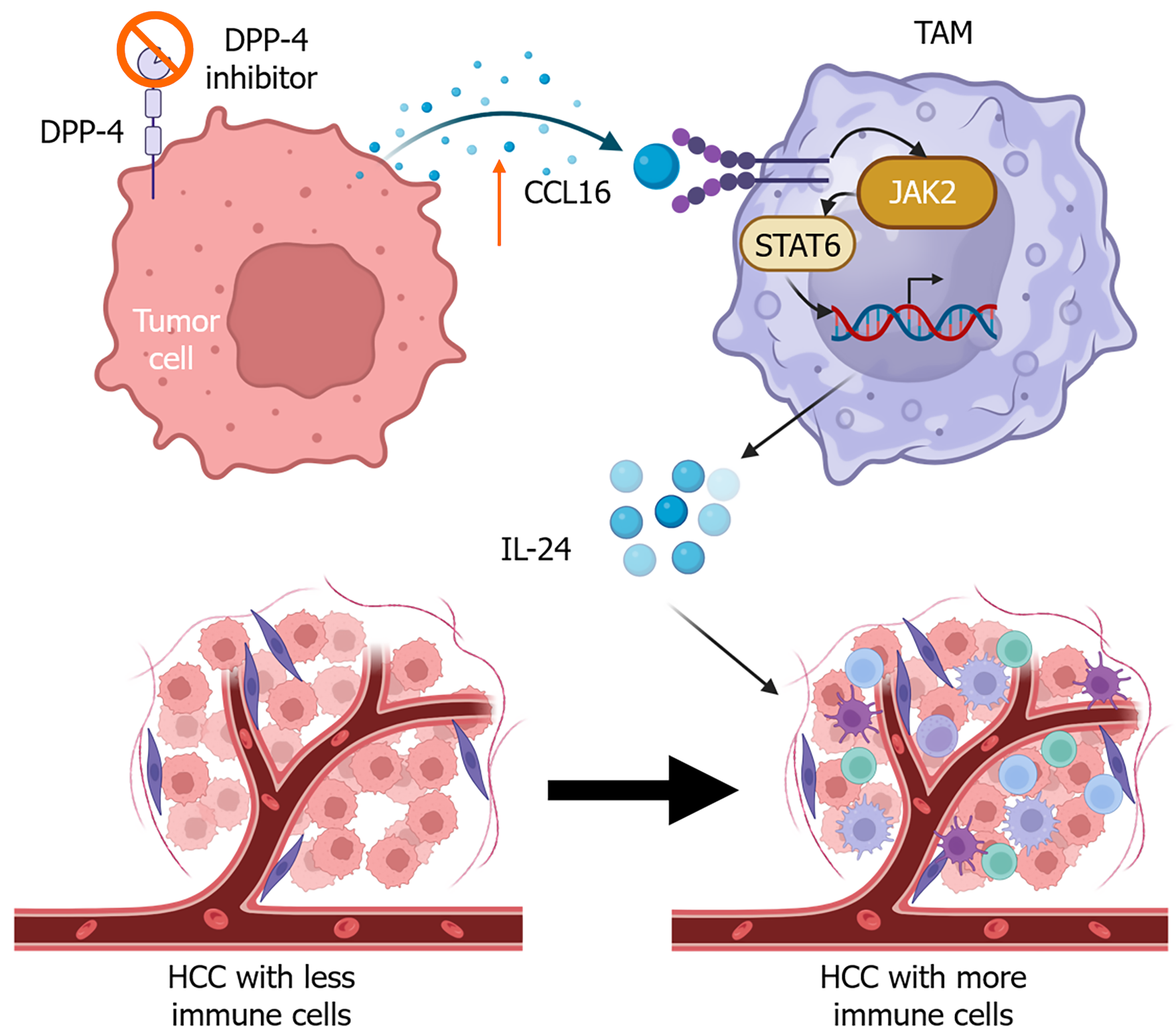
Figure 3 Treatment with a dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor increases C-C motif chemokine ligand 16 expression and immune cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment.
DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4; CCL: C-C motif chemokine ligand; STAT: Signal transduction and transcription activation; JAK: Janus kinase; IL: Interleukin; TAMs: Tumor-associated macrophages; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
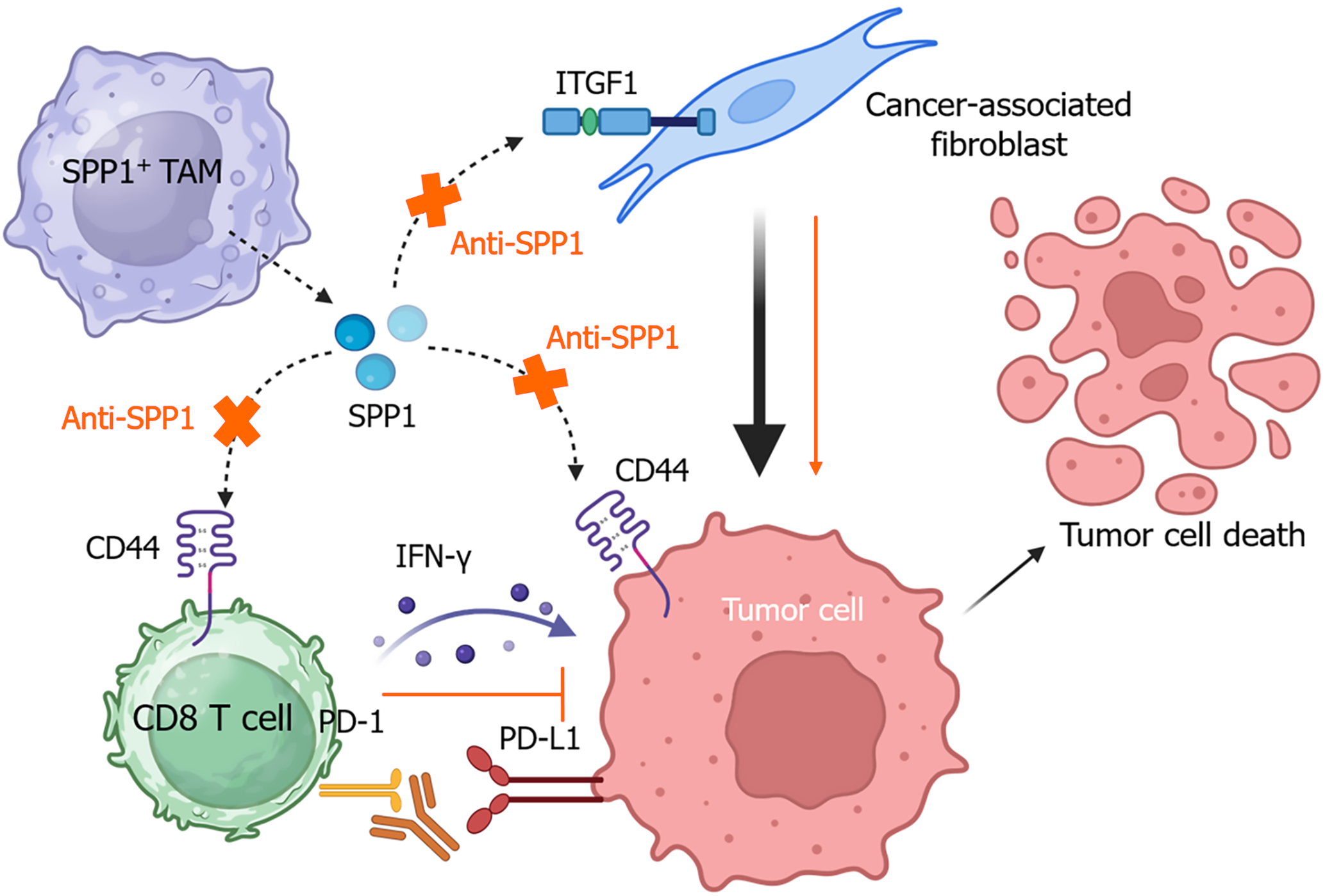
Figure 4 Blocking the secreted phosphoprotein 1 signaling pathway in tumor-associated macrophages inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth.
SPP1: Secreted phosphoprotein 1; TAMs: Tumor-associated macrophages; CD: Cluster of differentiation; IFN: Interferon; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand 1; ITGF1: Integrin subunit beta 1.
- Citation: Yang M, Zhang CY. Molecular mechanisms of tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma development and therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(8): 115675
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i8/115675.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i8.115675