©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2026; 32(8): 115291
Published online Feb 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i8.115291
Published online Feb 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i8.115291
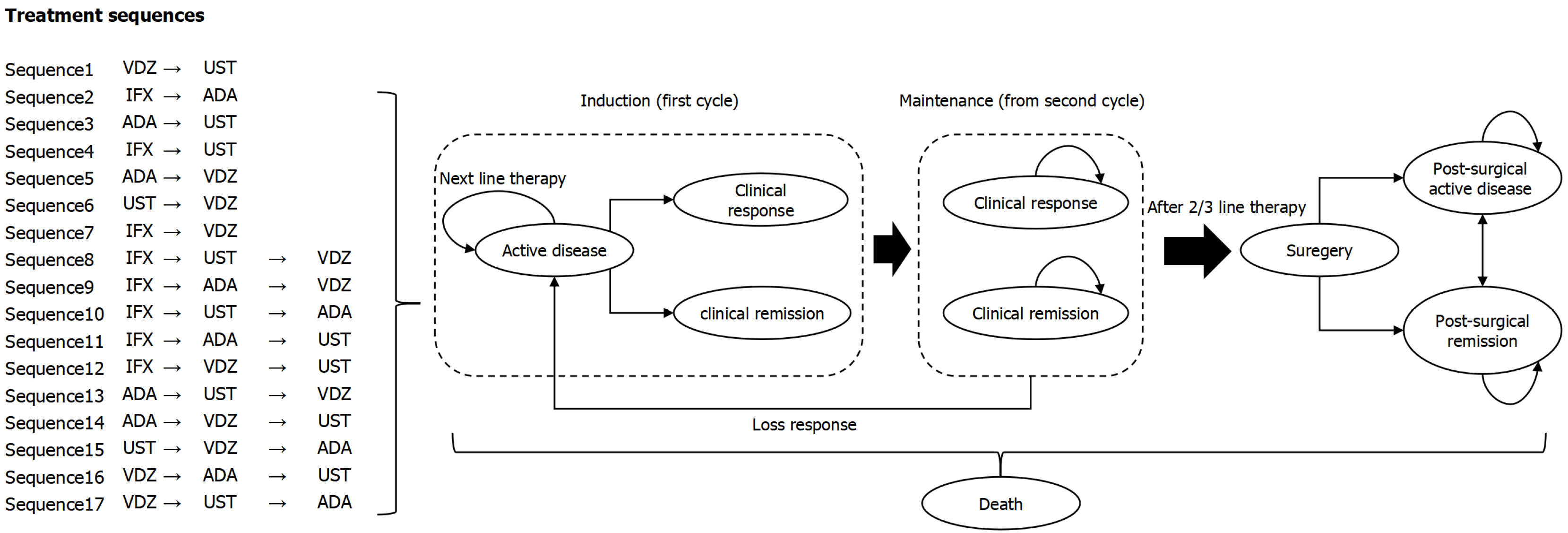
Figure 1 Treatment sequence and model structure for moderate to severe Crohn’s disease.
ADA: Adalimumab; IFX: Infliximab; UST: Ustekinumab; VDZ: Vedolizumab.
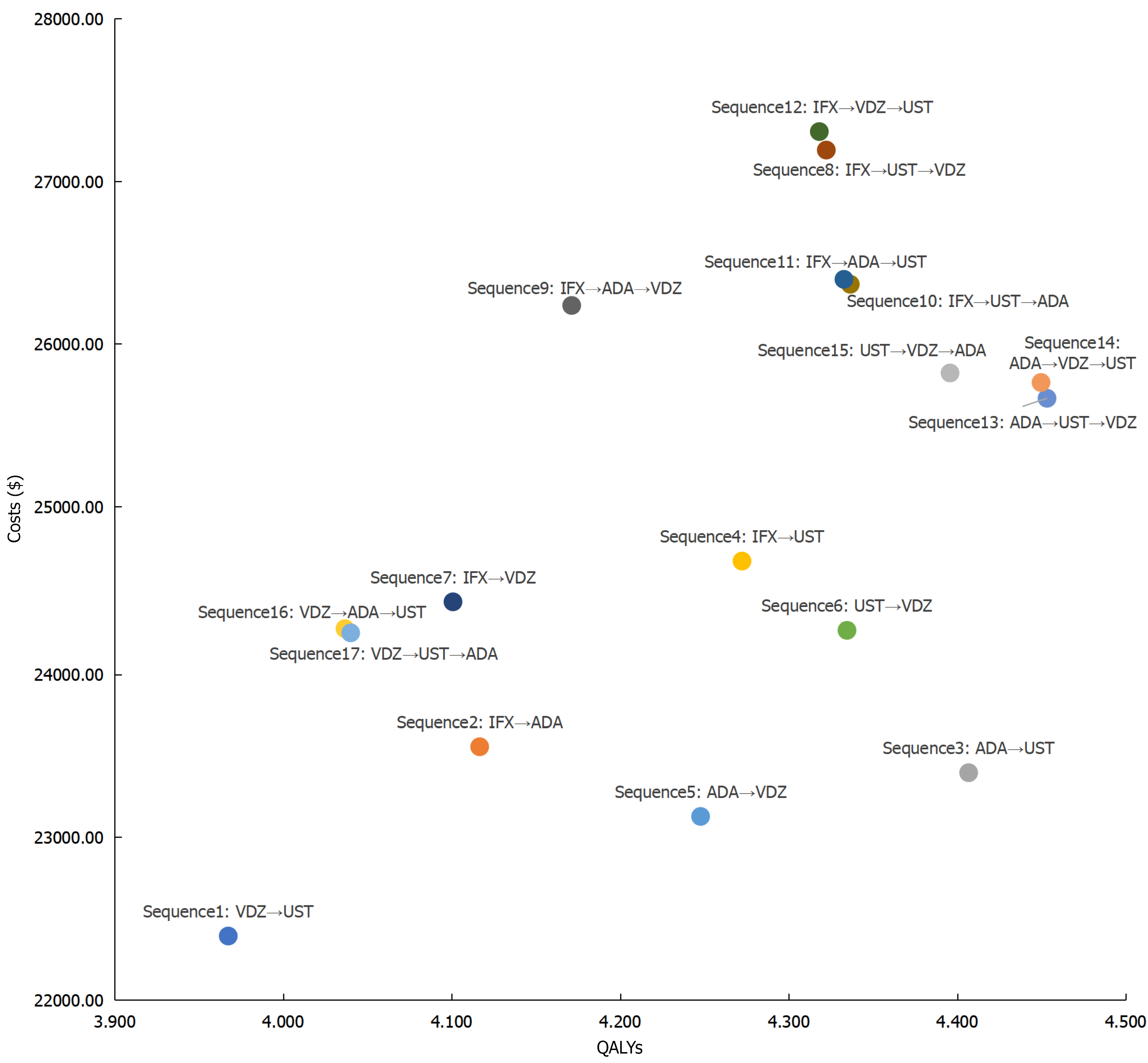
Figure 2 Cost-effectiveness scatter plot of different treatment sequences for biologic-naïve Crohn’s disease patients.
ADA: Adalimumab; IFX: Infliximab; QALYs: Quality-adjusted life years; UST: Ustekinumab; VDZ: Vedolizumab.
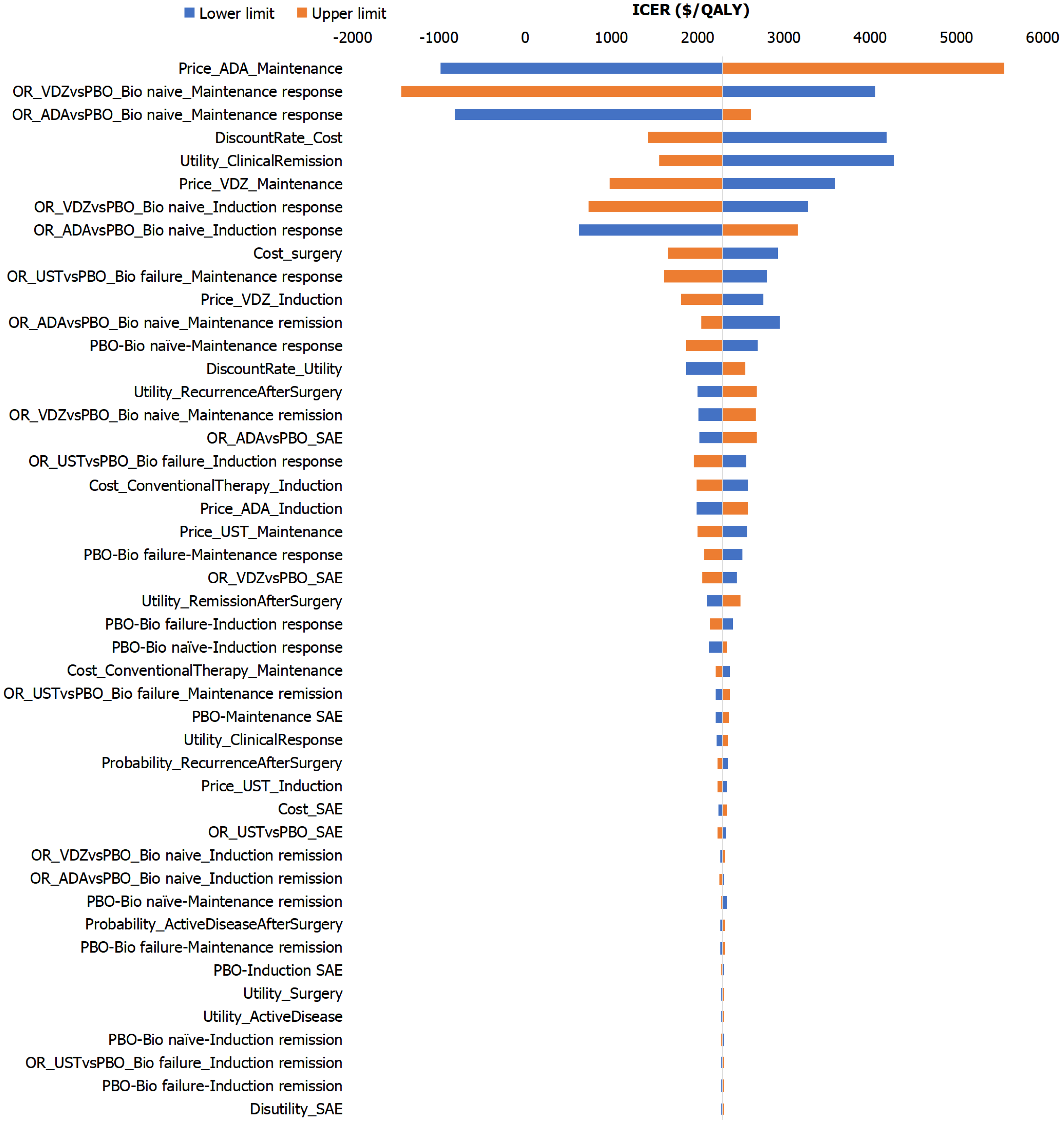
Figure 3 Tornado diagram for one-way sensitivity analysis: Sequence 1 (vedolizumab-ustekinumab) vs sequence 3 (adalimumab-ustekinumab) in biologic-naïve Crohn’s disease patients.
ADA: Adalimumab; Bio: Biologics; ICER: Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; IFX: Infliximab; OR: Odds ratio; PBO: Placebo; QALYs: Quality-adjusted life years; SAEs: Serious adverse events; UST: Ustekinumab; VDZ: Vedolizumab.
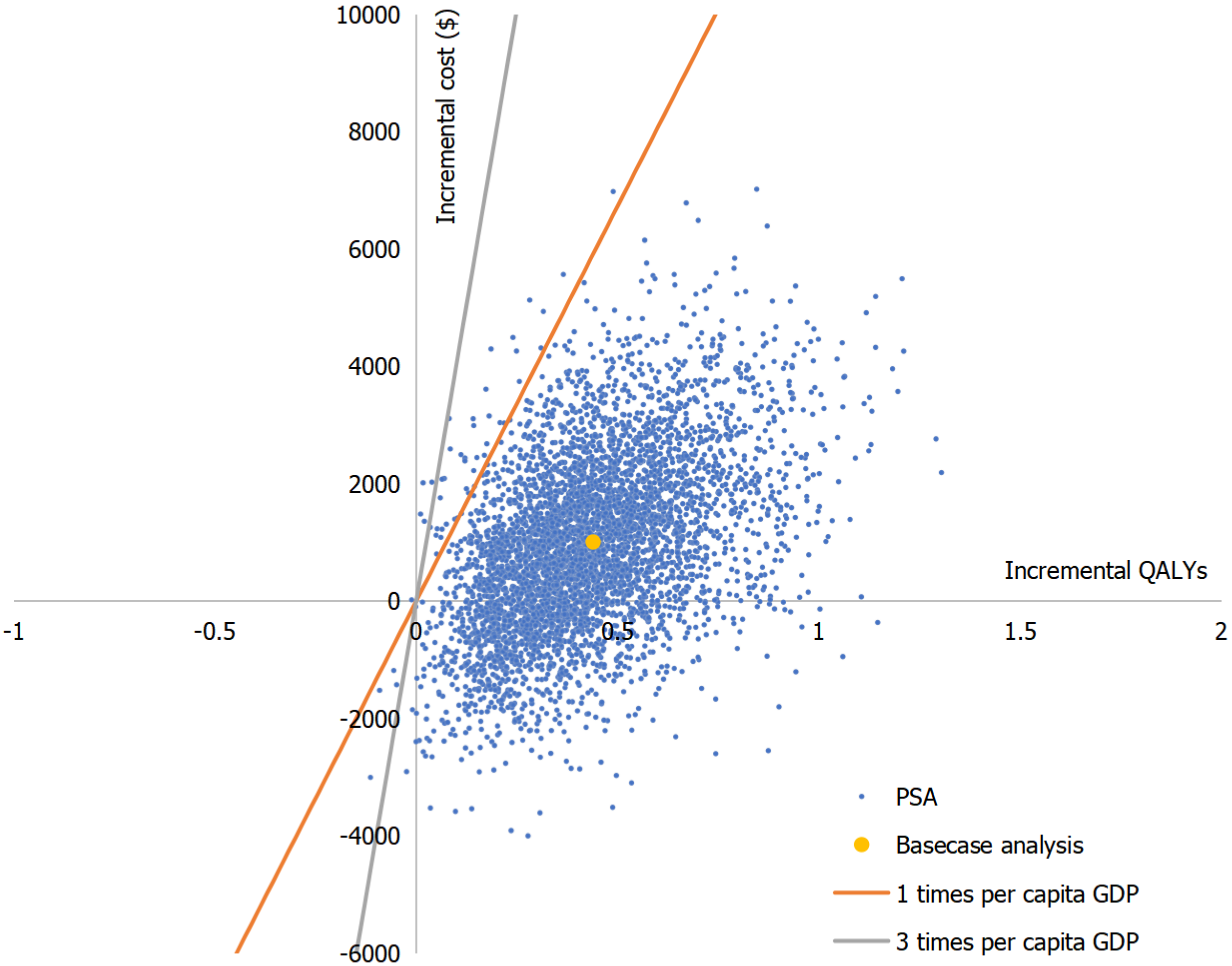
Figure 4 Cost-effectiveness scatter plot of sequence 1 (vedolizumab-ustekinumab) vs sequence 3 (adalimumab-ustekinumab) in biologic-naïve Crohn’s disease patients.
PSA: Probabilistic sensitivity analysis; QALYs: Quality-adjusted life years.
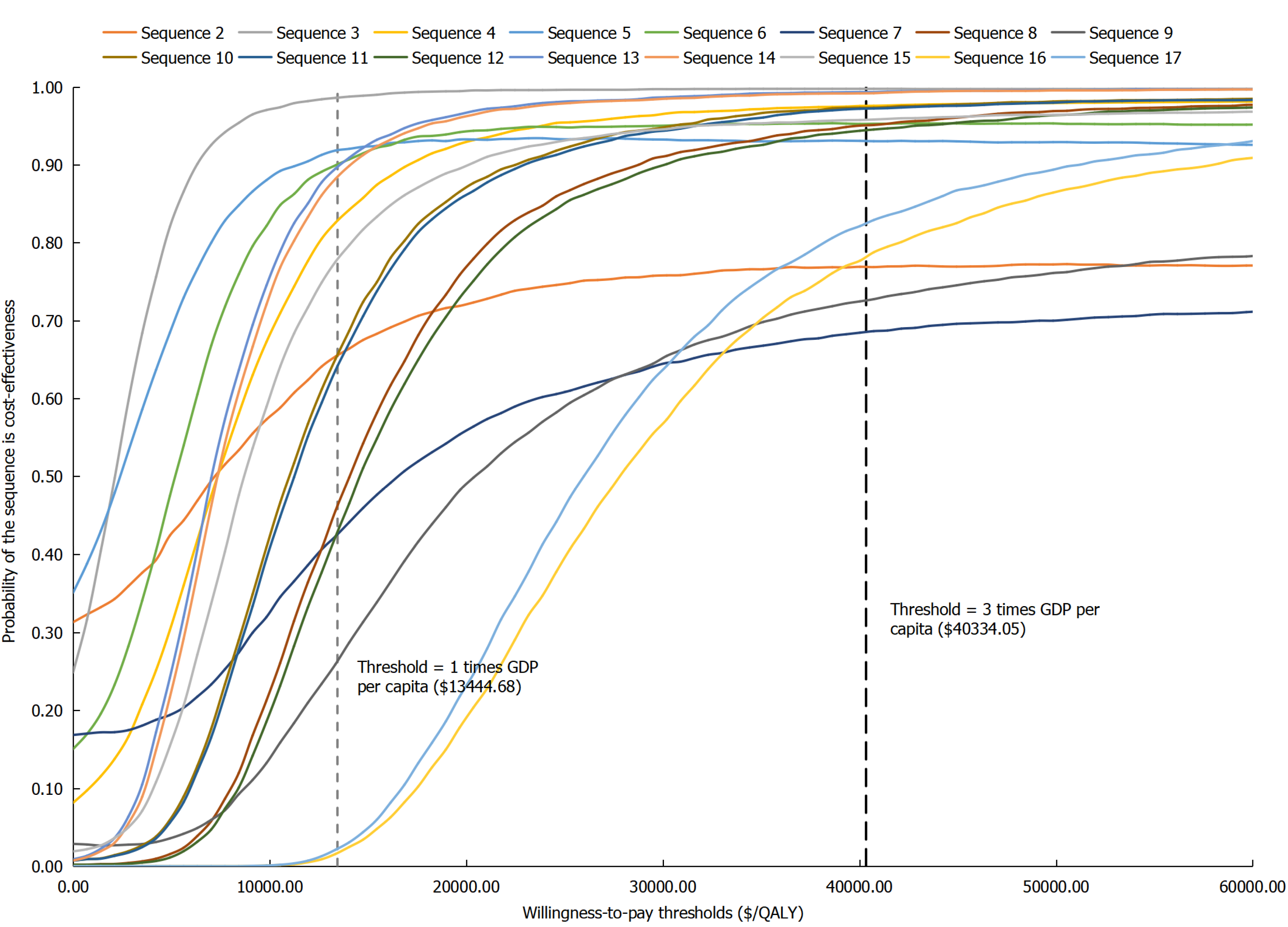
Figure 5 Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve of treatment sequences vs sequence 1 for biologic-naïve Crohn’s disease patients.
QALYs: Quality-adjusted life years.
- Citation: Wu Y, Tao LB, Liu C, Wang FX, Yan Y, Sun S. Cost-effectiveness of different strategies with biologics for the treatment of moderate to severe Crohn’s disease in China. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(8): 115291
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i8/115291.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i8.115291