©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2026; 32(7): 114773
Published online Feb 21, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i7.114773
Published online Feb 21, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i7.114773
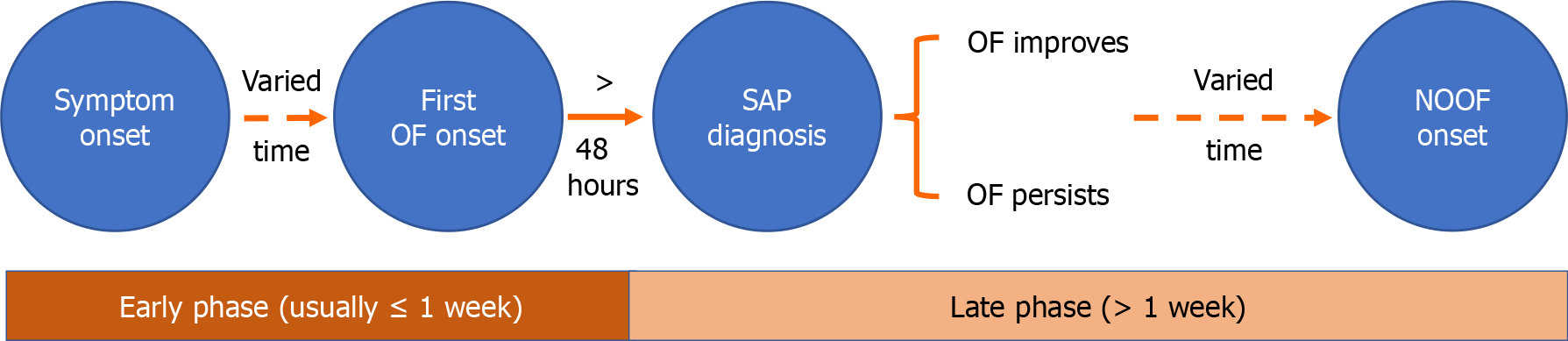
Figure 1 A schematic timeline of organ failure in acute pancreatitis.
OF: Organ failure; SAP: Severe acute pancreatitis; NOOF: New-onset organ failure.
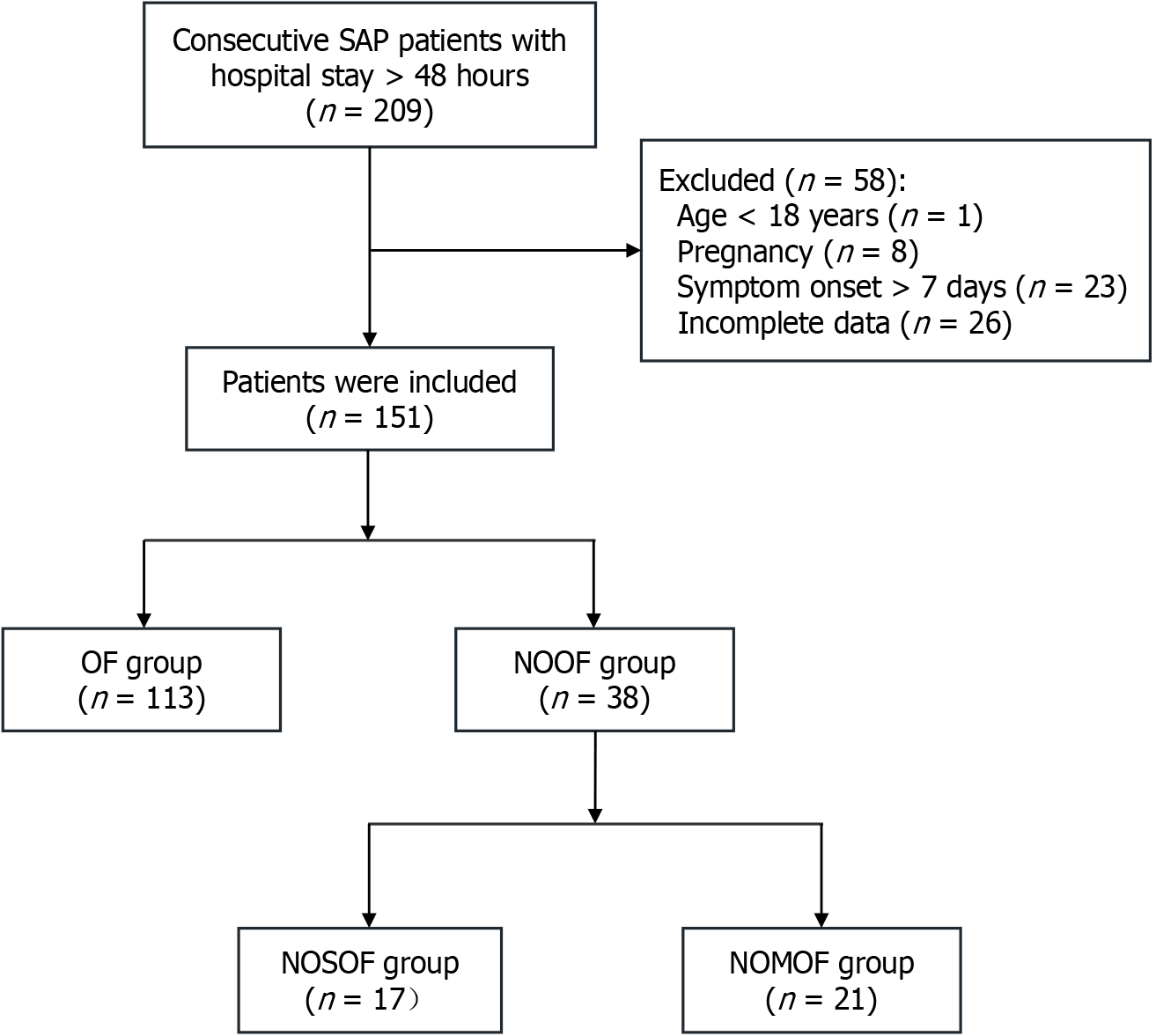
Figure 2 The flowchart of patient enrollment.
SAP: Severe acute pancreatitis; OF: Organ failure; NOOF: New-onset organ failure; NOSOF: New-onset single organ failure; NOMOF: New-onset multi-organ failure.
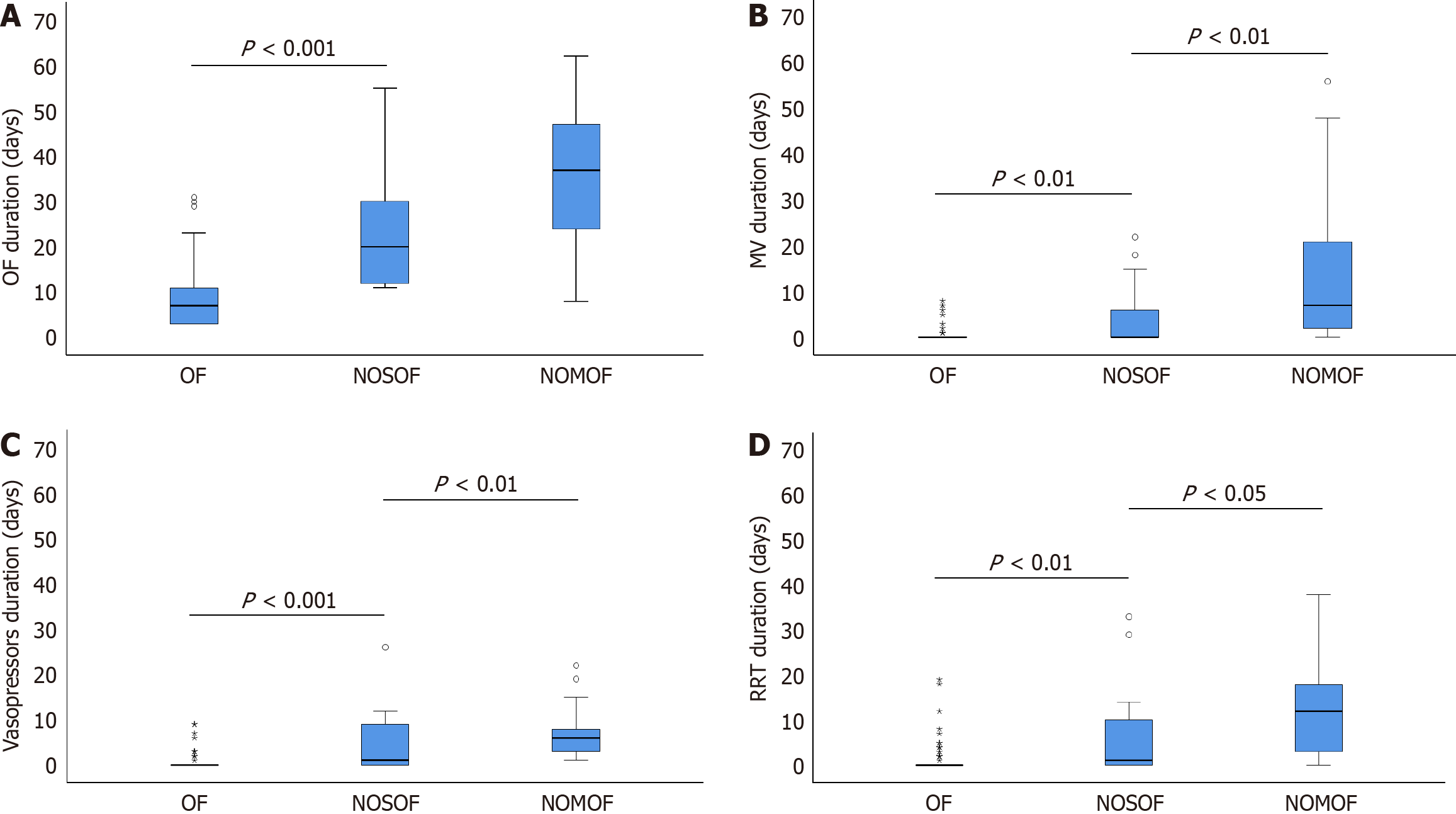
Figure 3 Comparison of organ failure, mechanical ventilation, vasopressors, and renal replacement therapy duration among organ failure, new-onset single organ failure, and new-onset multi-organ failure groups.
A: Comparison of organ failure (OF) duration among OF, new-onset single organ failure (NOSOF), and new-onset multi-organ failure (NOMOF) groups; B: Comparison of mechanical ventilation duration among OF, NOSOF, and NOMOF groups; C: Comparison of vasopressors duration among OF, NOSOF, and NOMOF groups; D: Comparison of renal replacement therapy duration among OF, NOSOF, and NOMOF groups. OF: Organ failure; NOSOF: New-onset single organ failure; NOMOF: New-onset multi-organ failure; MV: Mechanical ventilation; RRT: Renal replacement therapy.
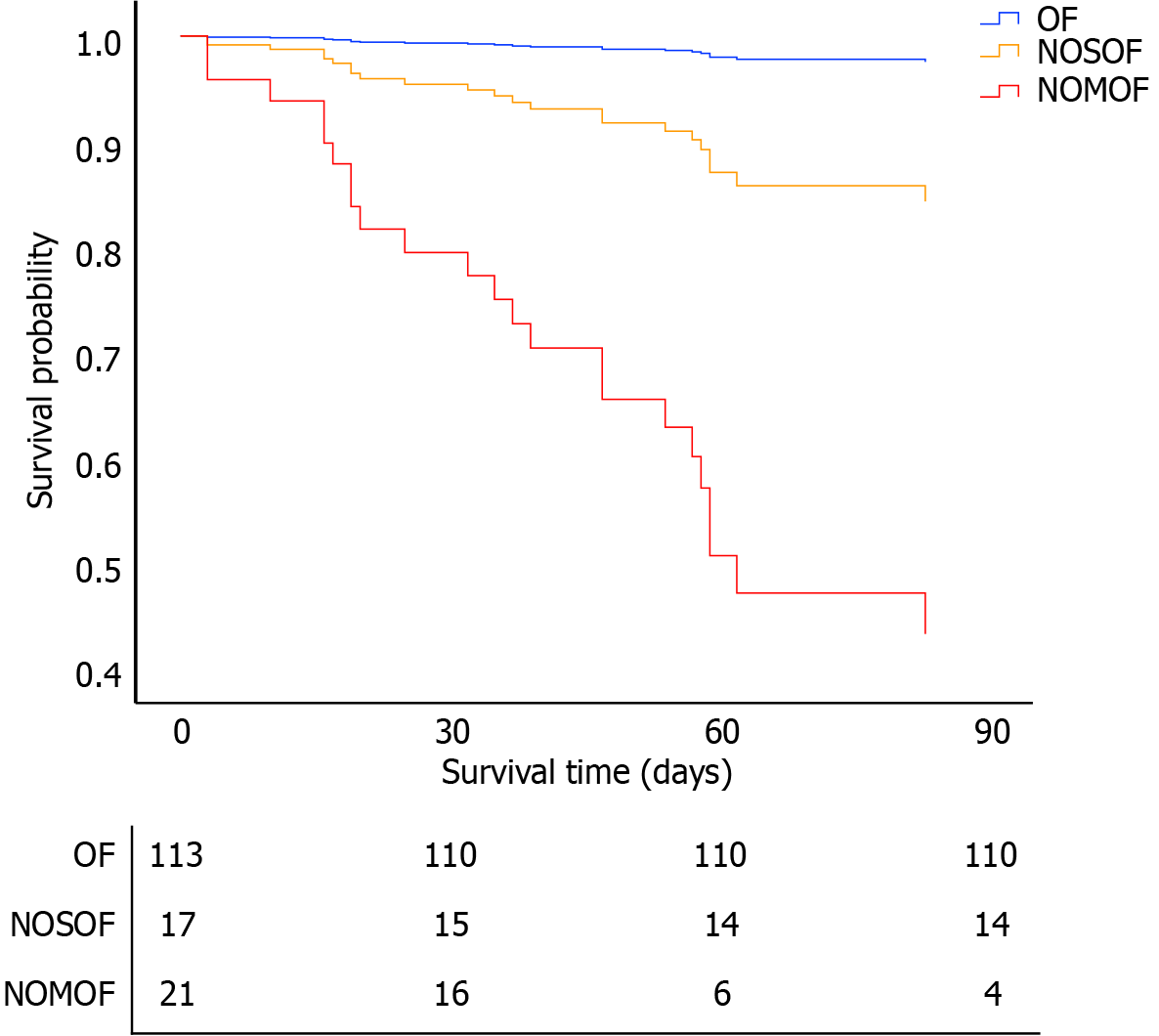
Figure 4 Cox proportional-hazards regression curves for mortality at 90 days.
After adjusting for age, sex, Bedside Index of Severity in Acute Pancreatitis score, computed tomography severity index score, infected pancreatic necrosis, open pancreatic necrosectomy, major complications, multiple organ failure on admission, organ failure duration > 2 weeks, new-onset single organ failure (hazard ratio = 6.8, 95% confidence interval: 1.4-33.5, P = 0.019), and new-onset multi-organ failure (hazard ratio = 33.2, 95% confidence interval: 9.4-117.3, P < 0.001) were significantly associated with 90-day mortality in severe acute pancreatitis patients. OF: Organ failure; NOSOF: New-onset single organ failure; NOMOF: New-onset multi-organ failure.
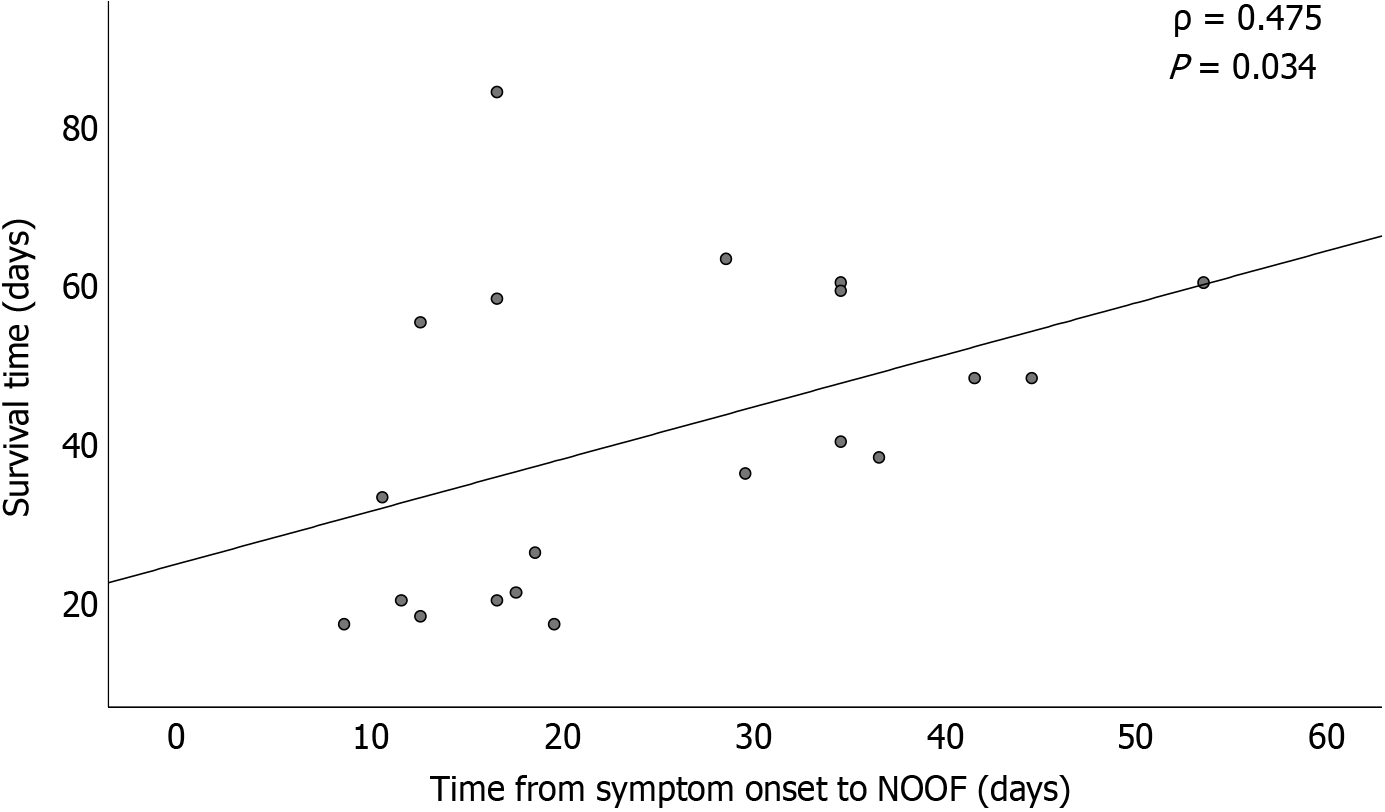
Figure 5 A positive correlation between new-onset organ failure onset time and 90-day survival by Spearman’s correlation analysis.
NOOF: New-onset organ failure.
Figure 6 A clinical management schematic for acute pancreatitis complicated by organ failure.
OF: Organ failure.
- Citation: Zhang XT, Zhu H, Chen XC, Gao T, Chen M, Zhu ZH, Zhang BY, Yu WK. New-onset persistent organ failure predicts adverse outcomes in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(7): 114773
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i7/114773.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i7.114773