©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2026; 32(5): 113024
Published online Feb 7, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i5.113024
Published online Feb 7, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i5.113024
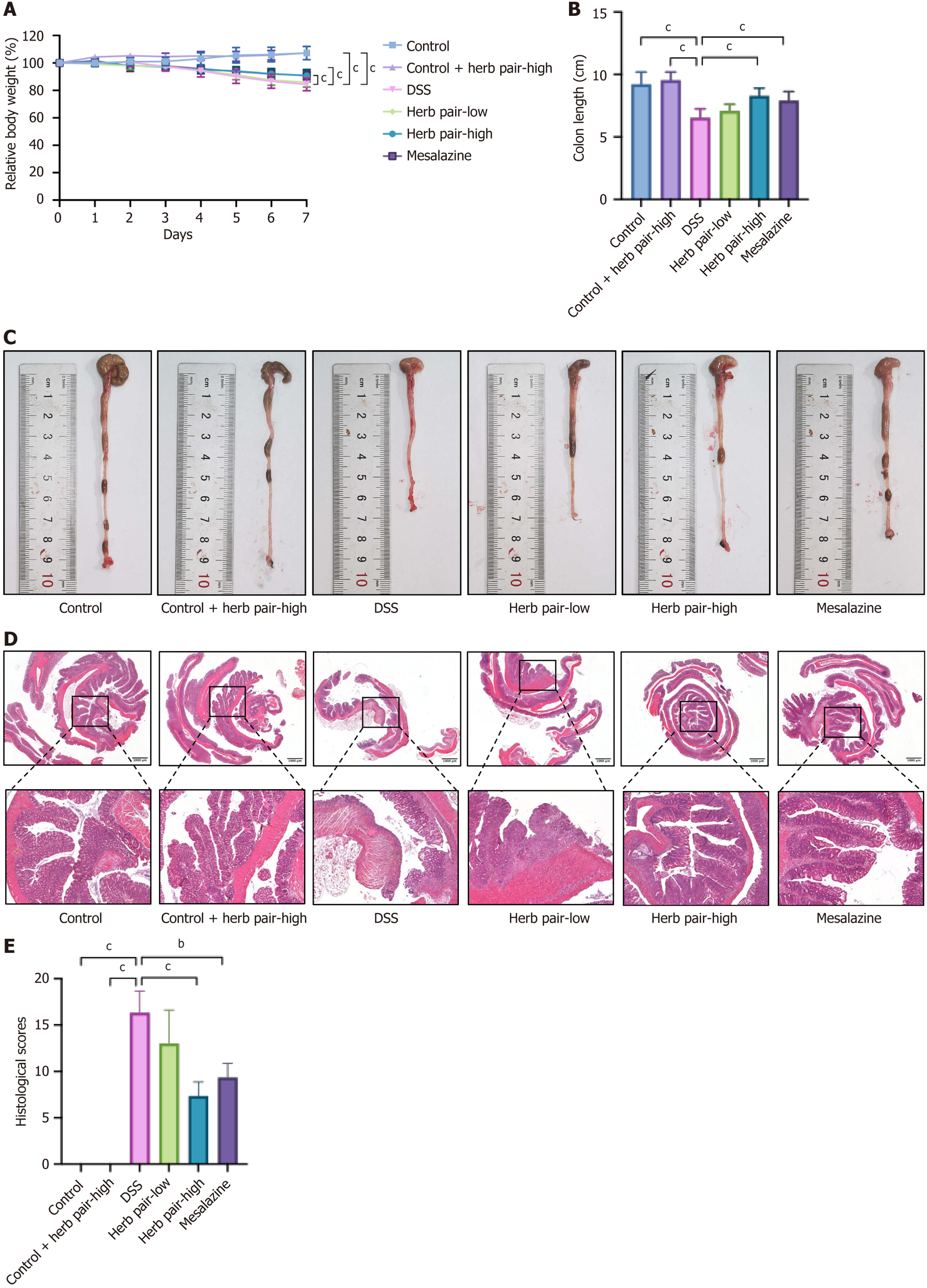
Figure 1 Herb pair exerted therapeutic effects on colitis mice induced by dextran sulfate sodium.
A: Changes in relative body weight; B: Colon length changes in mice from each group; C: Representative images of the colon length; D: Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining in colon tissues; E: Histological scores of HE staining of colon tissues. For body weight and colon length measurement: n = 9, for HE staining: n = 3. bP < 0.01 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, cP < 0.001 vs dextran sulfate sodium group. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
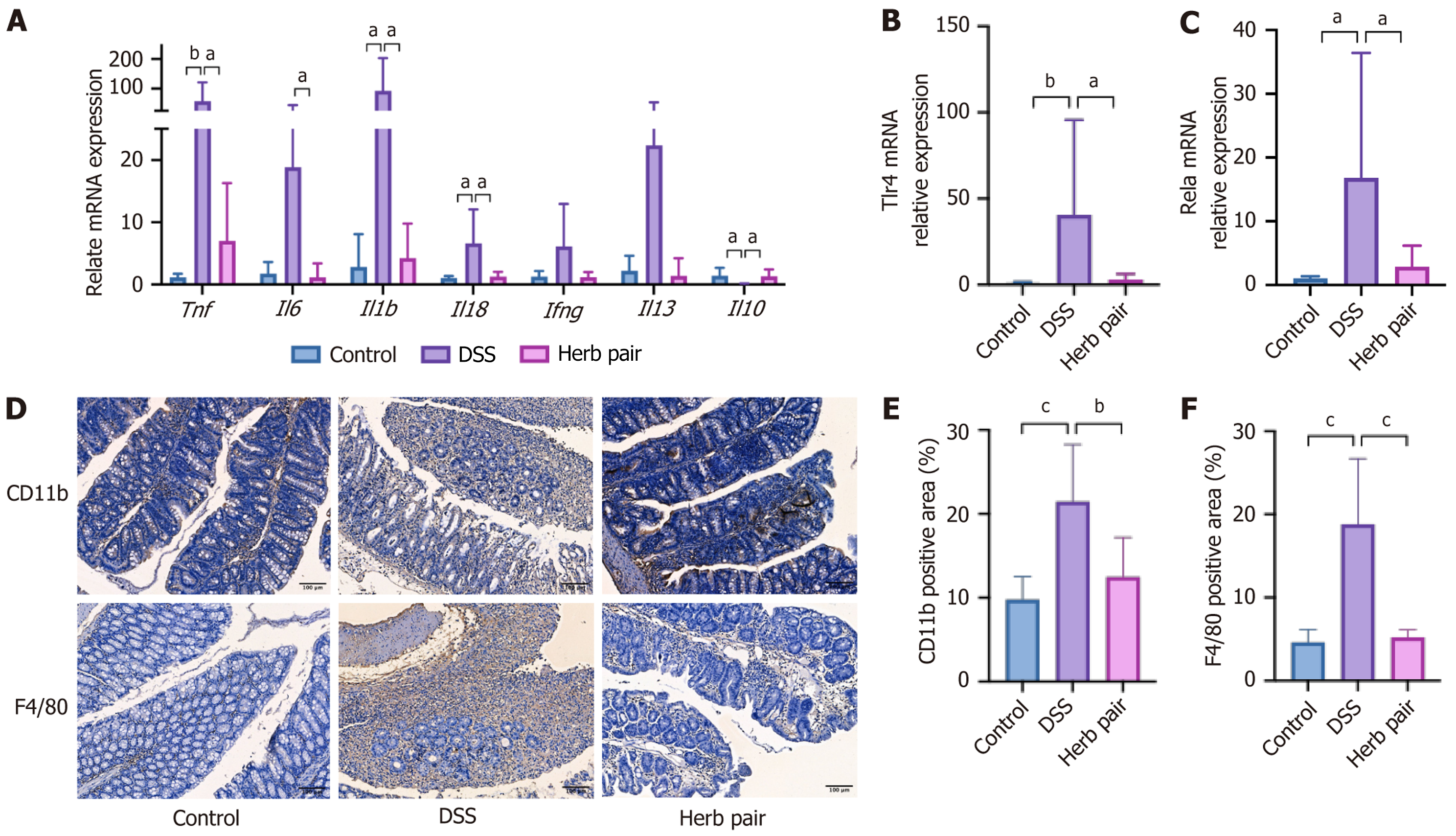
Figure 2 Herb pair inhibited intestinal inflammation in colitis mice.
A: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analysis of mRNA expression of tumor necrosis factor, interleukin 6, interleukin 1b, interleukin 18, interferon-gamma, interleukin 13, and interleukin 10 in colon tissues; B: QPCR analysis of mRNA expression of toll-like receptor 4 in colon tissues; C: QPCR analysis of mRNA expression of V-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A in colon tissues; D: Representative images of immunohistochemical (IHC) of CD11b and F4/80 in colon tissues; E and F: Quantitative analysis of IHC results of CD11b and F4/80. For qPCR analysis: n = 5-6, for IHC measurement: n = 3. aP < 0.05 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, bP < 0.01 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, cP < 0.001 vs dextran sulfate sodium group. Tnf: Tumor necrosis factor; Il6: Interleukin 6; Il1b: Interleukin 1b; Il18: Interleukin 18; Ifng: Interferon-gamma; Il13: Interleukin 13; Il10: Interleukin 10; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
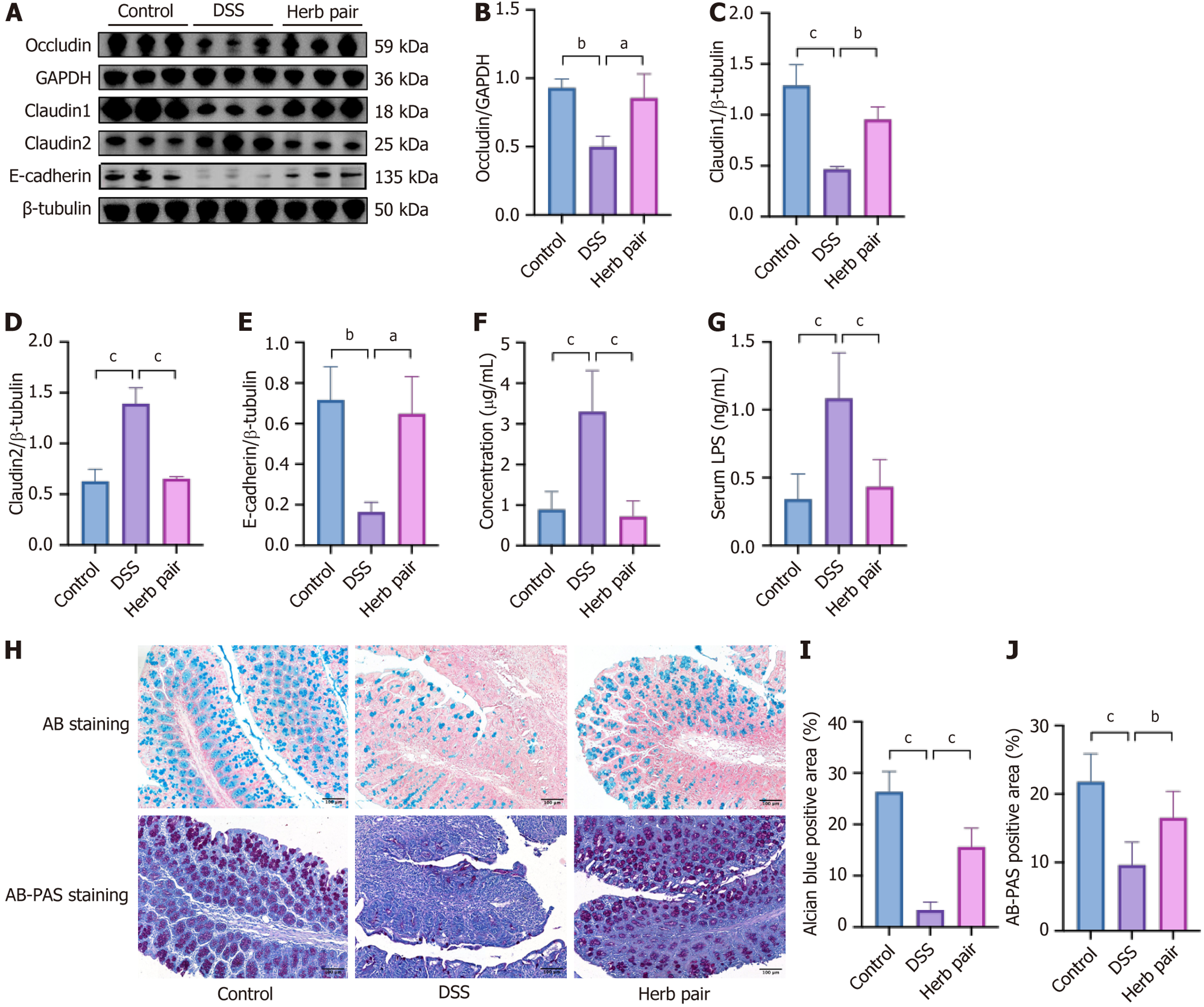
Figure 3 Herb pair reinforced intestinal barrier in colitis mice.
A-E: Western blotting analysis of protein expression of Occludin, Claudin1, Claudin2, and E-cadherin in colon tissues; F: Fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran fluorescence intensity in serum; G: Expression level of lipopolysaccharide in serum; H: Representative images of Alcian blue (AB) staining and AB-periodic acid schiff (PAS) staining of colon tissues; I and J: Quantitative analysis of AB staining and AB-PAS staining. For western blotting analysis: n = 3, for fluorescein isothiocyanate analysis: n = 5-7, for lipopolysaccharide measurement: n = 7, for AB staining and AB-PAS staining: n = 3. aP < 0.05 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, bP < 0.01 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, cP < 0.001 vs dextran sulfate sodium group. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; AB: Alcian blue; PAS: Periodic acid Schiff.
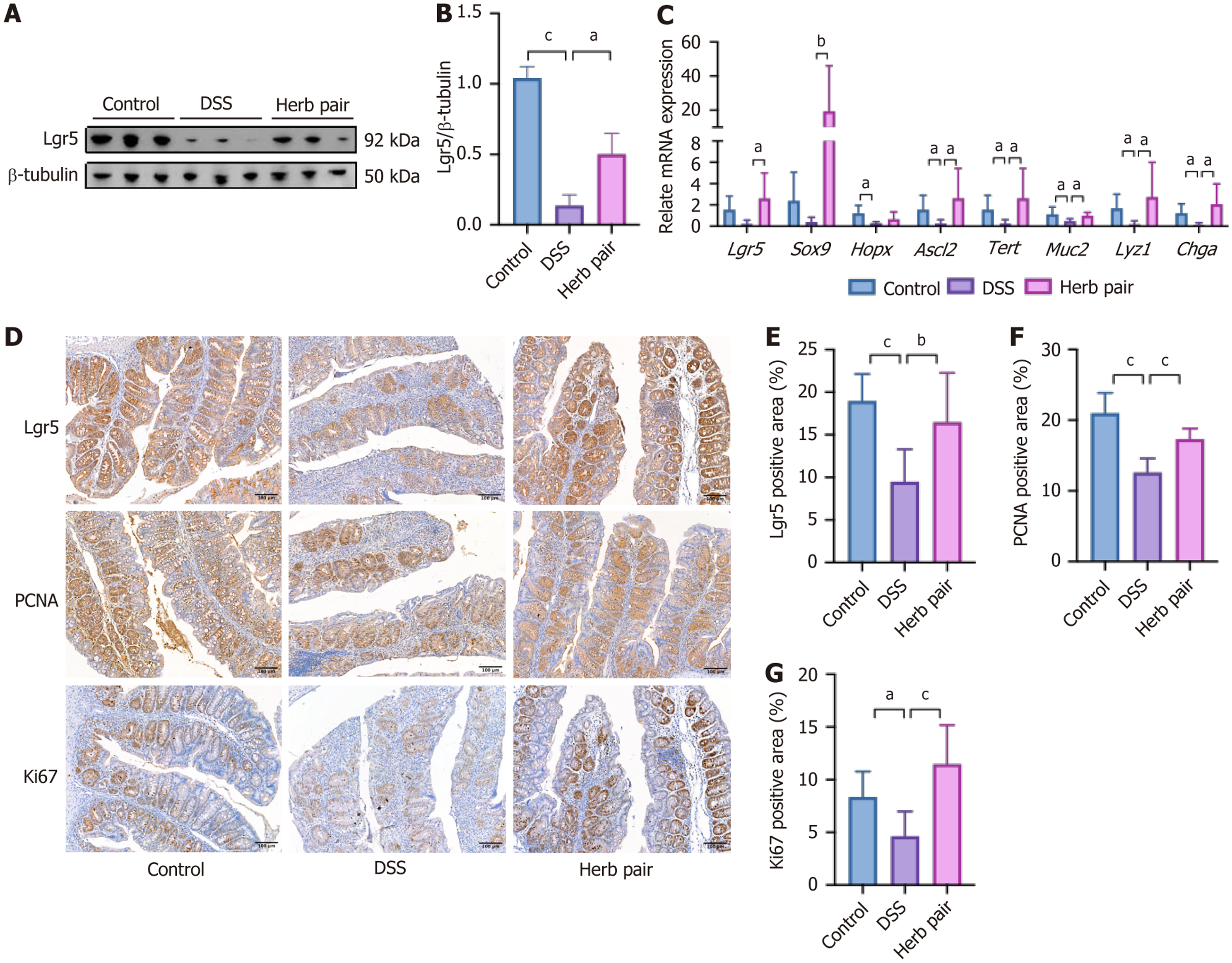
Figure 4 Herb pair restored abnormal epithelial proliferation in colitis mice.
A and B: Western blotting analysis of protein expression of leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5 (Lgr5) in colon tissues; C: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of mRNA expression of Lgr5, SRY-box transcription factor 9, homeodomain-only protein homeobox, achaete scute-like 2, telomerase reverse transcriptase, Mucin 2, lysozyme 1, and Chromogranin A in colon tissues; D: Representative images of immunohistochemical (IHC) of Lgr5, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, Ki67 in colon tissues; E-G: Quantitative analysis of IHC results of Lgr5, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, Ki67. For western blotting analysis: n = 3, for quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis: n = 5-6, for IHC measurement: n = 3. aP < 0.05 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, bP < 0.01 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, cP < 0.001 vs dextran sulfate sodium group. Lgr5: Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5; Sox9: SRY-box transcription factor 9; Hopx: Homeodomain-only protein homeobox; Ascl2: Achaete scute-like 2; Tert: Telomerase reverse transcriptase; Muc2: Mucin 2; Lyz1: Lysozyme 1; Chga: Chromogranin A; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen.
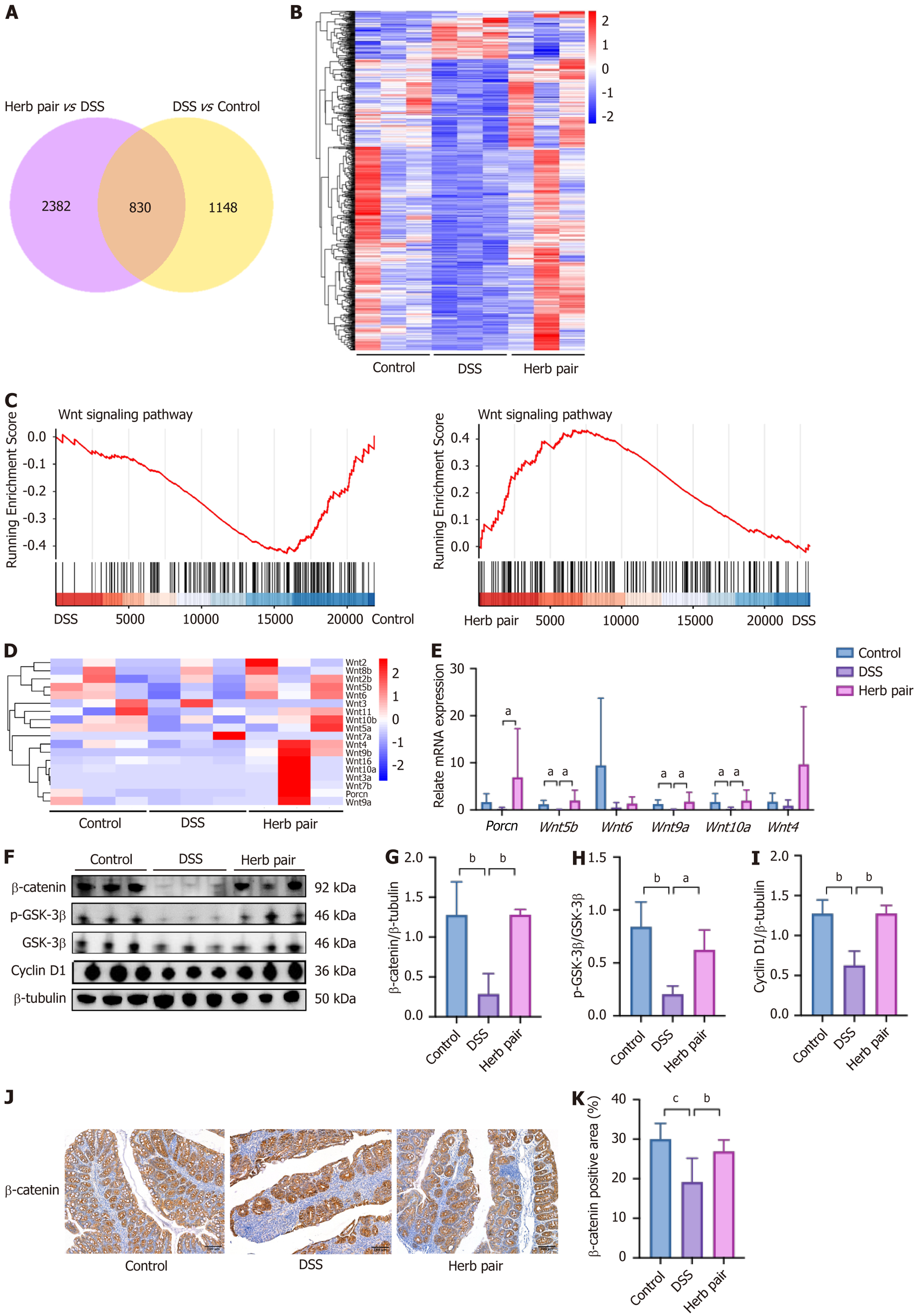
Figure 5 Herb pair promoted the Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation in colitis mice.
A: The overlap analysis visualized in the Venn diagram; B: The overlap analysis visualized in the heatmap; C: Gene set enrichment analysis; D: The overlap analysis visualized in the heatmap of the Wnt signal; E: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of mRNA expression of porcupine, Wnt5b, Wnt6, Wnt9a, Wnt10a, and Wnt4 in colon tissues; F-I: Western blotting analysis of protein expression of β-catenin, p- glycogen synthase kinase-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β, and Cyclin D1 in colon tissues; J: Representative images of immunohistochemical (IHC) of β-catenin in colon tissues; K: Quantitative analysis of IHC results. For RNA sequencing and western blotting analysis: n = 3, for quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis: n = 5-6, for IHC measurement: n = 3. aP < 0.05 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, bP < 0.01 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, cP < 0.001 vs dextran sulfate sodium group. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β; Porcn: Porcupine.
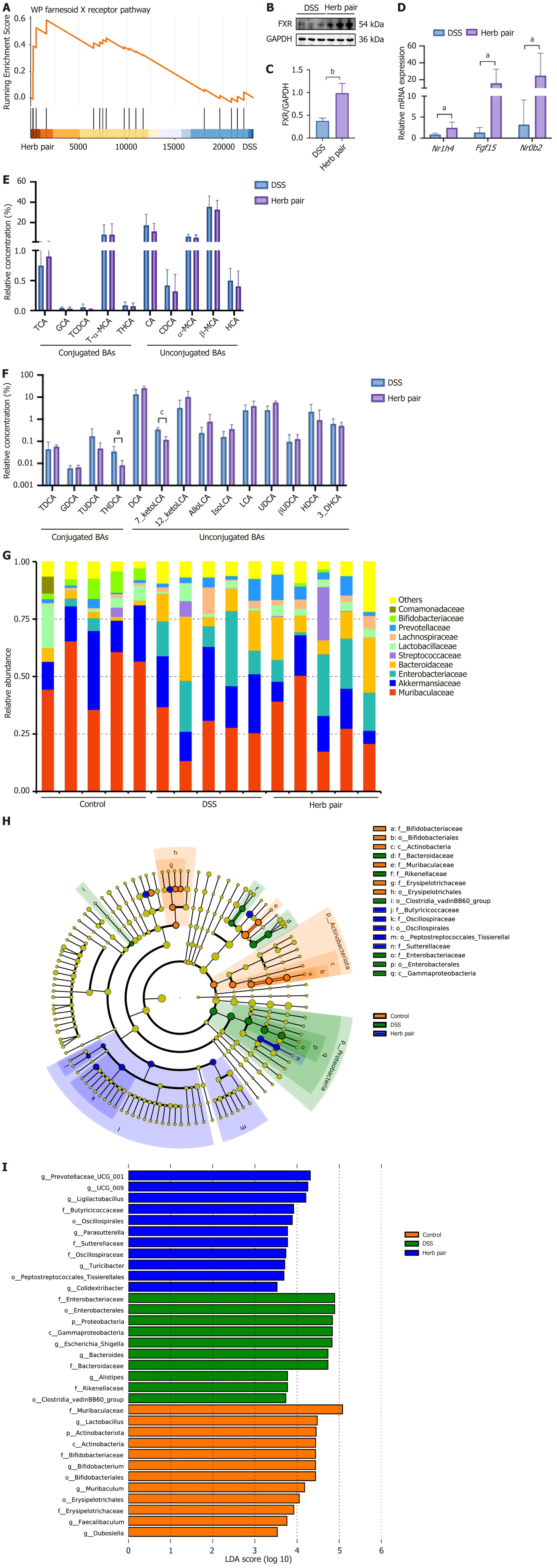
Figure 6 Herb pair altered the composition of bile acids metabolism and gut microbiota in colitis mice.
A: Gene set enrichment analysis; B and C: Western blotting analysis of protein expression of farnesoid X receptor in colon tissues; D: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of mRNA expression of nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 4, fibroblast growth factor 15, and nuclear receptor subfamily 0 group B member 2 in colon tissues; E and F: Influenced bile acids in colitis mice colon contents; G: Abundance of differential bacteria in colitis mice colon contents; H: Taxonomic cladogram analyzed by linear discriminant analysis coupled with effect size; I: Histogram of the linear discriminant analysis coupled with effect size analysis. For western blotting analysis: n = 3, for quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis: n = 6, for bile acids measurement: n = 7, for 16S rRNA sequencing: n = 5. aP < 0.05 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, bP < 0.01 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, cP < 0.001 vs dextran sulfate sodium group. FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Nr1h4: Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 4; Fgf15: Fibroblast growth factor 15; Nr0b2: Nuclear receptor subfamily 0 group B member 2; BAs: Bile acids.
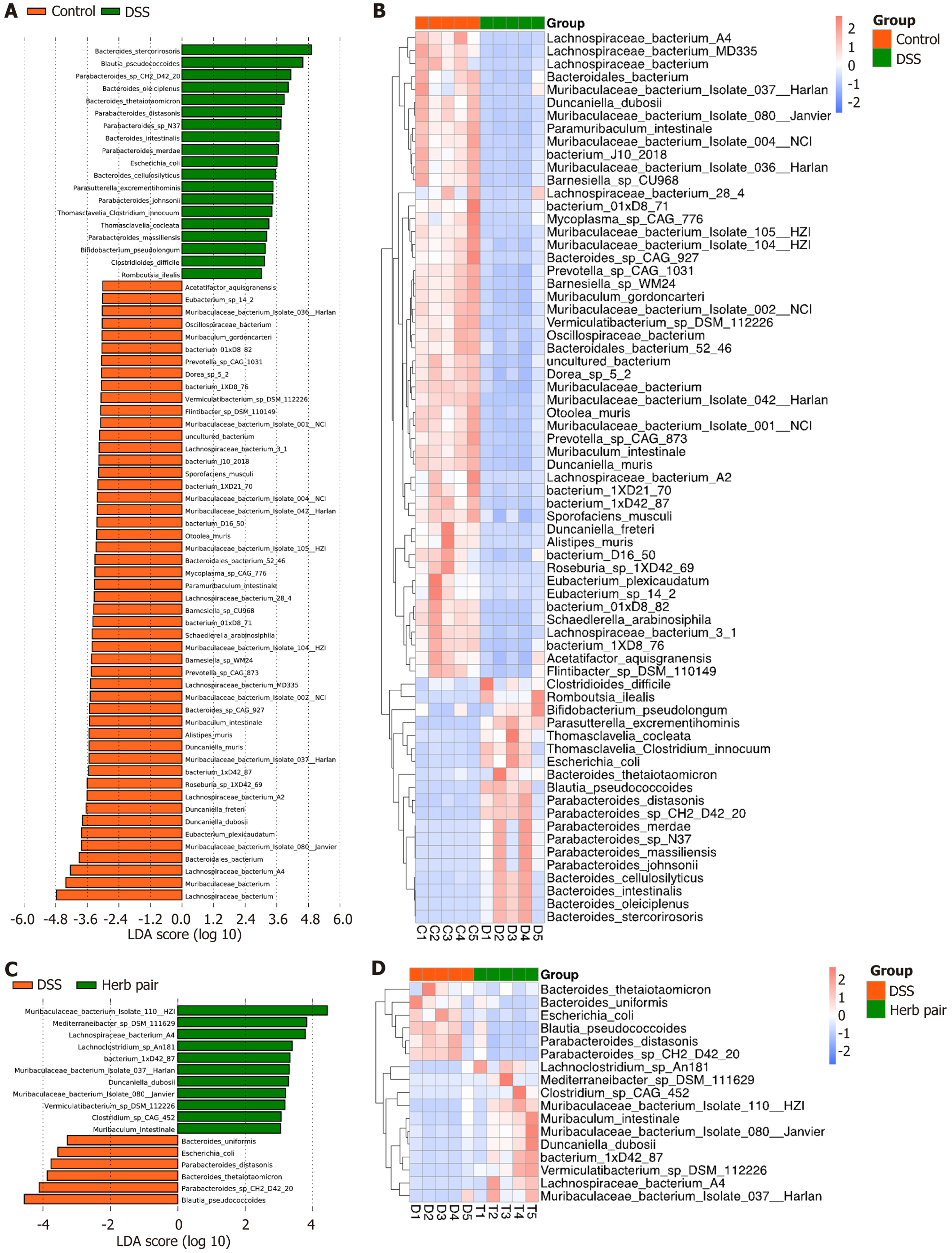
Figure 7 Herb pair ameliorated gut microbiota dysbiosis in colitis mice.
A: Linear discriminant analysis coupled with effect size analysis of latent Diri
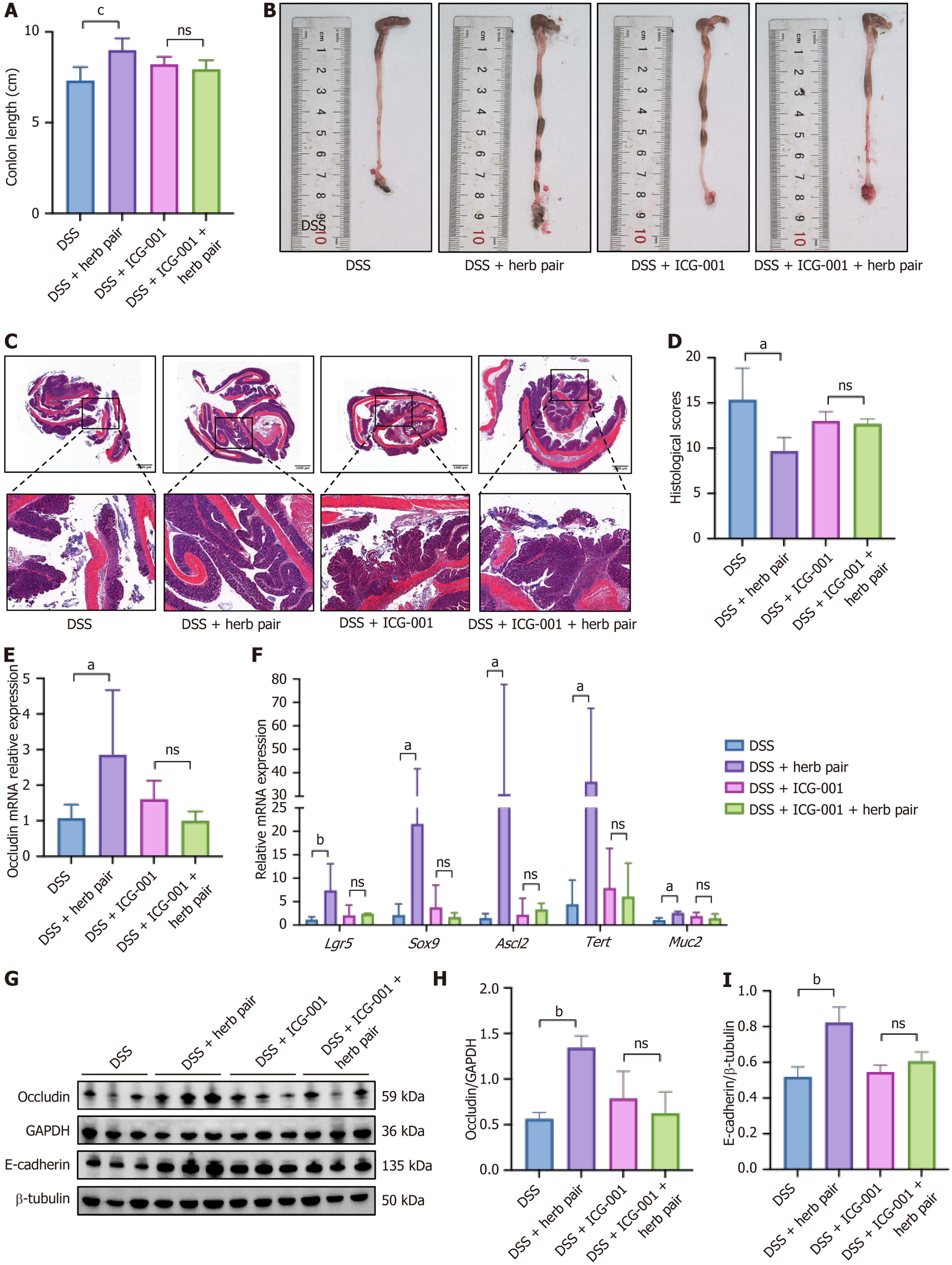
Figure 8 The β-catenin inhibitor abolished the protective effect of the herb pair on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.
A: Colon length changes in mice from each group; B: Representative images of the colon length; C: Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin staining of colon tissues; D: Histological scores of hematoxylin and eosin staining of colon tissues; E: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of mRNA expression of Occludin in colon tissues; F: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of mRNA expression of leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5, SRY-box transcription factor 9, achaete scute-like 2, telomerase reverse transcriptase, and Mucin 2 in colon tissues; G-I: Western blotting analysis of protein expression of Occludin and E-cadherin in colon tissues. For colon length measurement: n = 6, for western blotting analysis: n = 3, for quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis: n = 5-6. aP < 0.05 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, bP < 0.01 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, cP < 0.001 vs dextran sulfate sodium group. ns: No significance compared with the dextran sulfate sodium + ICG-001 group. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Lgr5: Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5; Sox9: SRY-box transcription factor 9; Ascl2: Achaete scute-like 2; Tert: Telomerase reverse transcriptase; Muc2: Mucin 2.
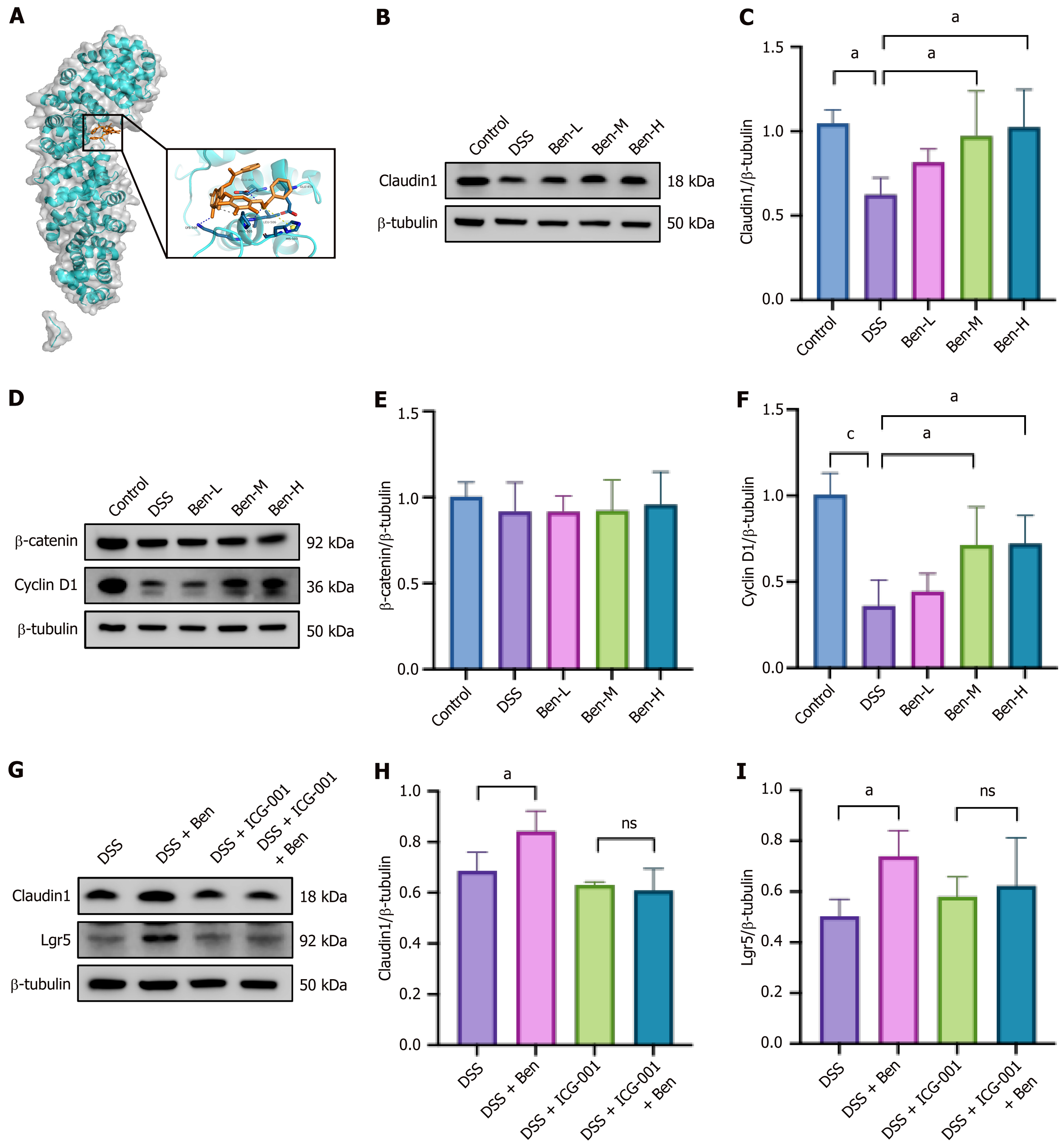
Figure 9 Benzoylpaeoniflorin protected against dextran sulfate sodium-induced injury through activating β-catenin in vitro.
A: Molecular docking of benzoylpaeoniflorin and β-catenin protein and their binding sites; B and C: Western blotting analysis of protein expression of Claudin1; D-F: Western blotting analysis of protein expression of β-catenin and Cyclin D1; G-I: Western blotting analysis of protein expression of Claudin1 and leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5. For all the experiments: n = 4. aP < 0.05 vs dextran sulfate sodium group, cP < 0.001 vs dextran sulfate sodium group. ns: No significance compared with dextran sulfate sodium + ICG-001 group; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; Lgr5: Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5; Ben: Benzoylpaeoniflorin.
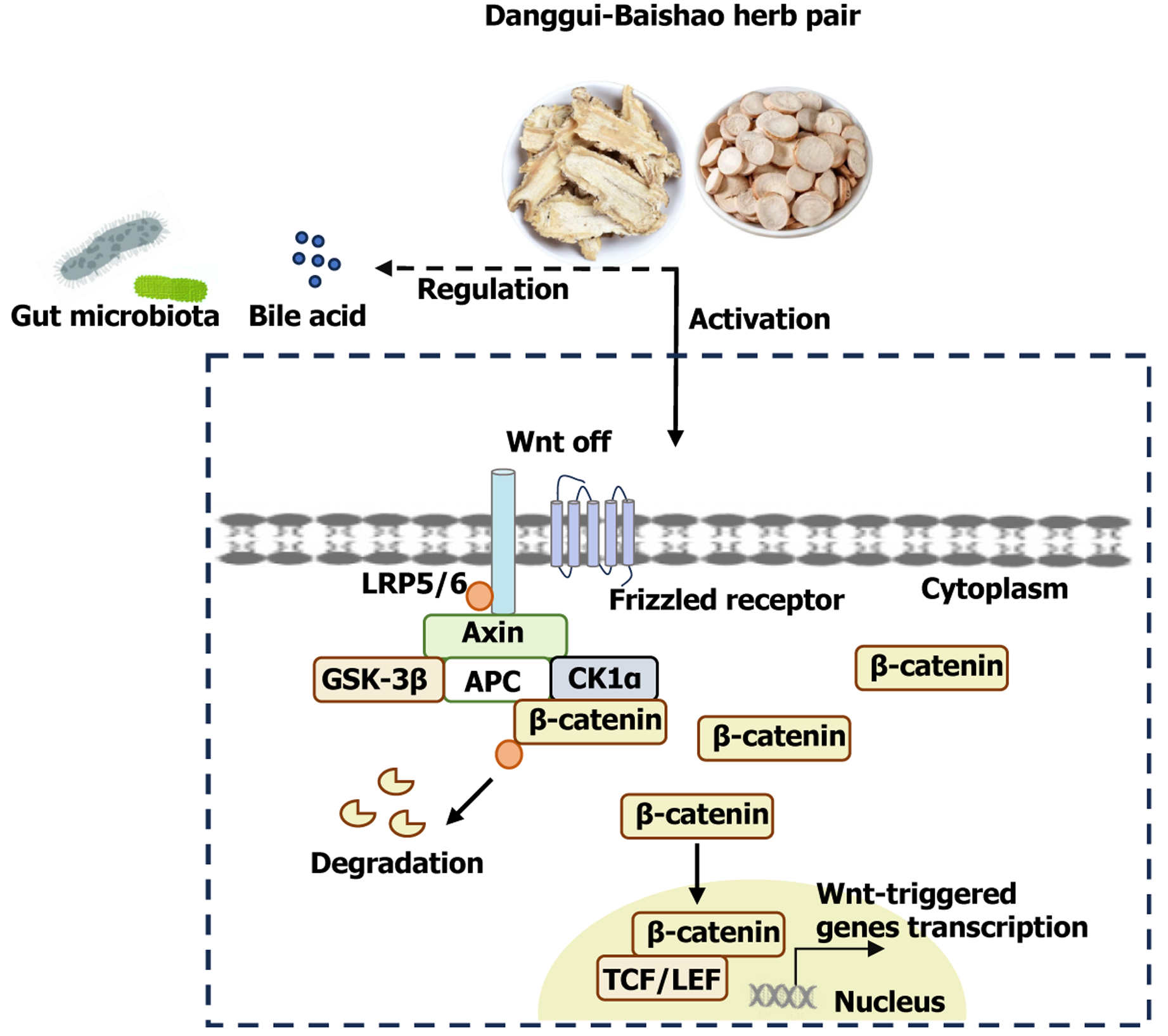
Figure 10 Schematic diagram of the anti-colitis mechanism of the herb pair.
Herb pair exerts its alleviates experimental colitis by the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. LRP5/6: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; CK1α: Casein kinase 1α; TCF: T-cell factor; LEF: Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor.
- Citation: Xu T, Hou WX, Yang ST, Shao YP, Wang J, Han TT, Li JN. Danggui-Baishao herb pair protects against dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by modulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(5): 113024
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i5/113024.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i5.113024