©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2026; 32(4): 115040
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.115040
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.115040
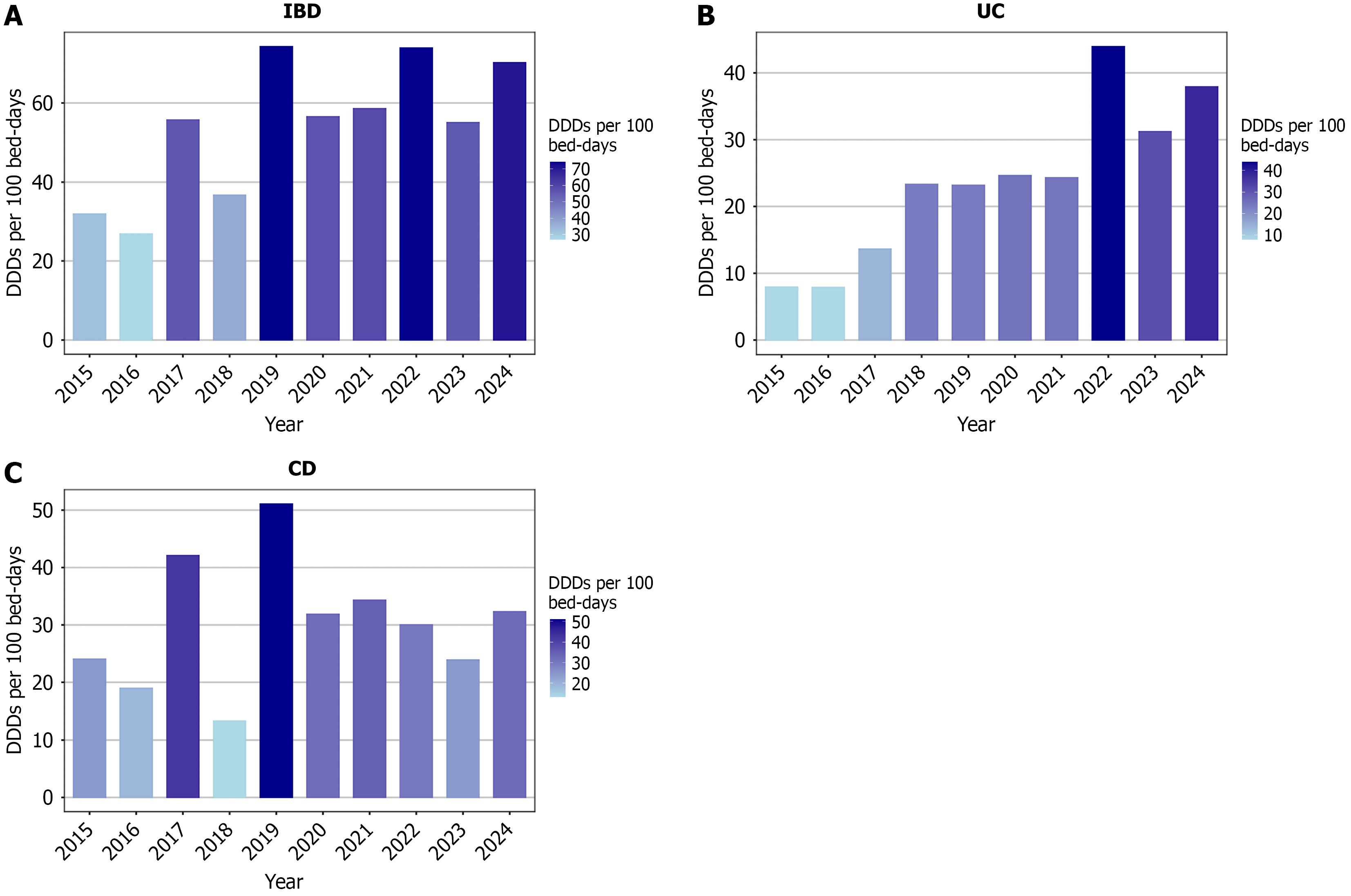
Figure 1 Change in antibiotic consumption from 2015 to 2024.
A: Inflammatory bowel disease; B: Ulcerative colitis; C: Crohn’s disease. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CD: Crohn’s disease; DDD: Defined daily dose.
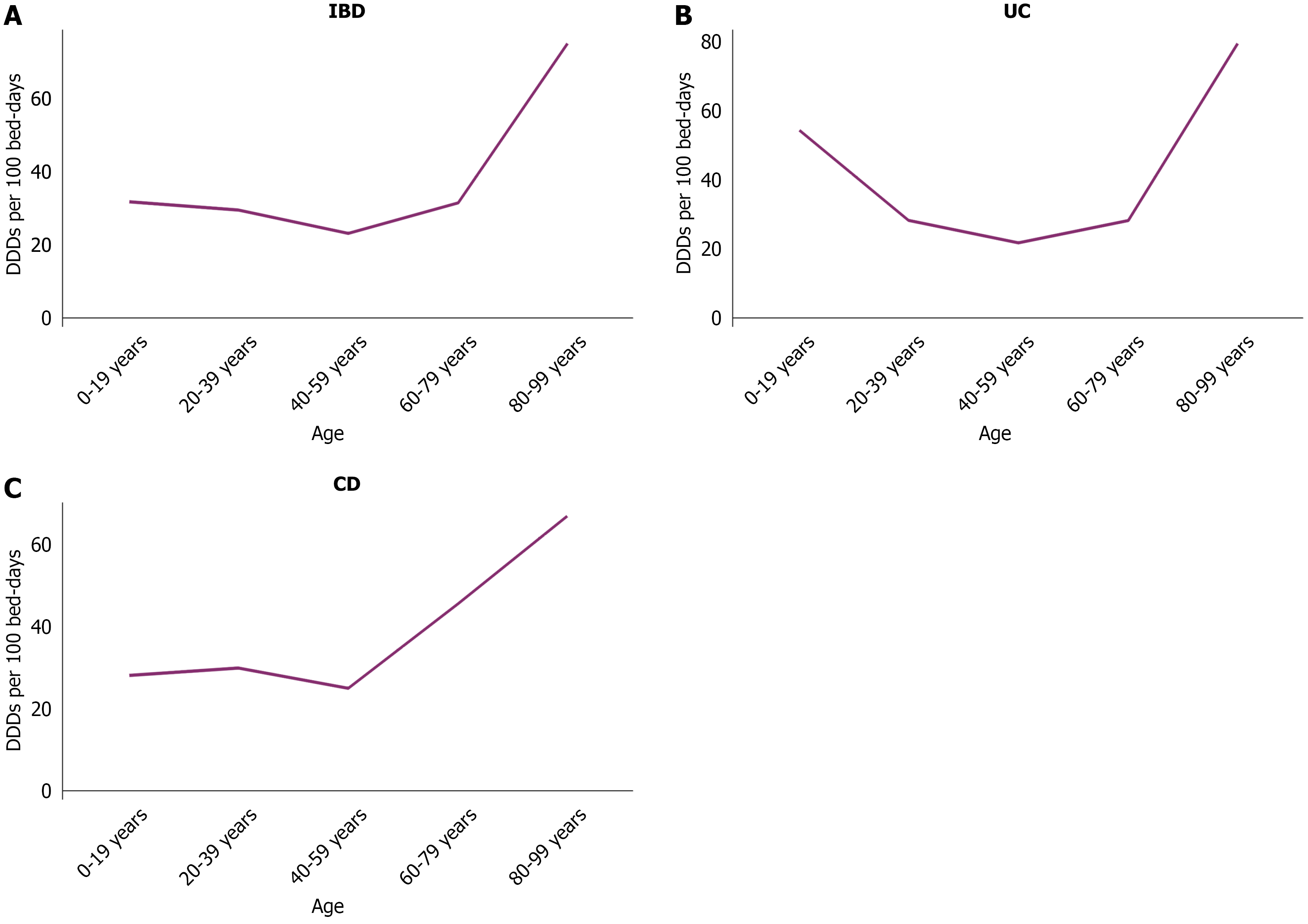
Figure 2 Change in antibiotic consumption by age group.
A: Inflammatory bowel disease; B: Ulcerative colitis; C: Crohn’s disease. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CD: Crohn’s disease; DDD: Defined daily dose.
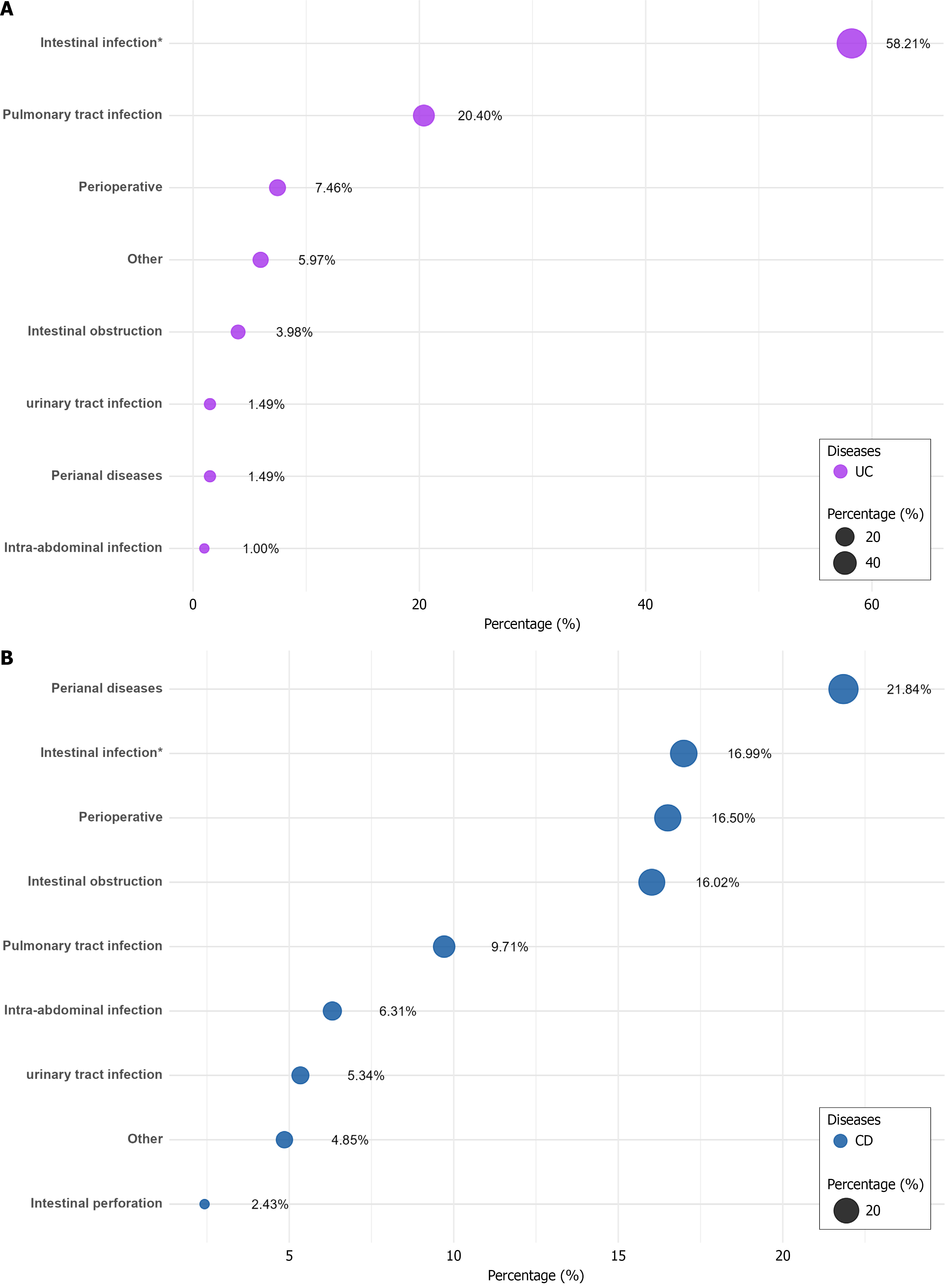
Figure 3 Causes of antibiotic treatments in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
A: Ulcerative colitis; B: Crohn’s disease. UC: Ulcerative colitis; CD: Crohn’s disease.
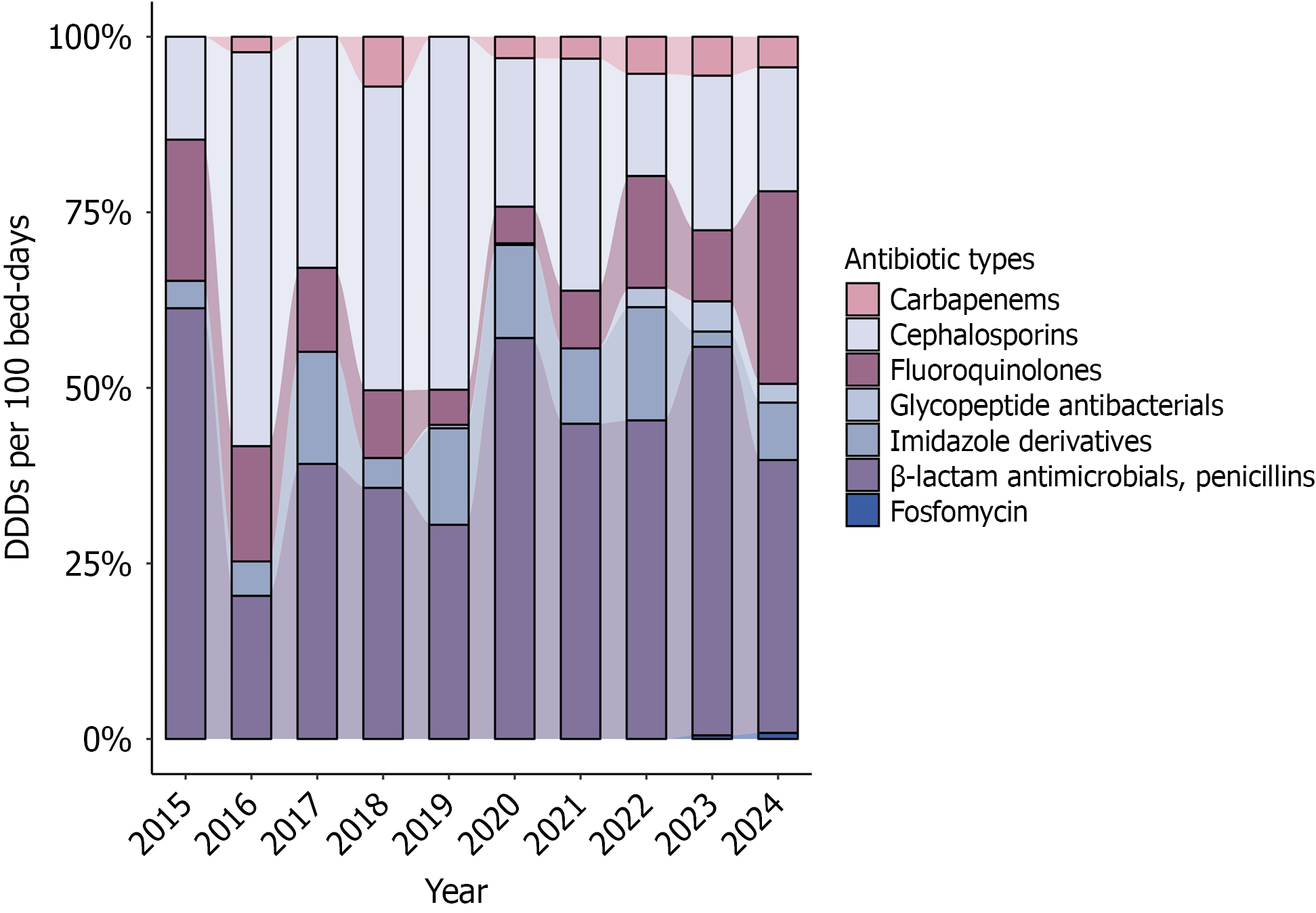
Figure 4 Each antibiotic consumption by antibiotic class.
DDD: Defined daily dose.
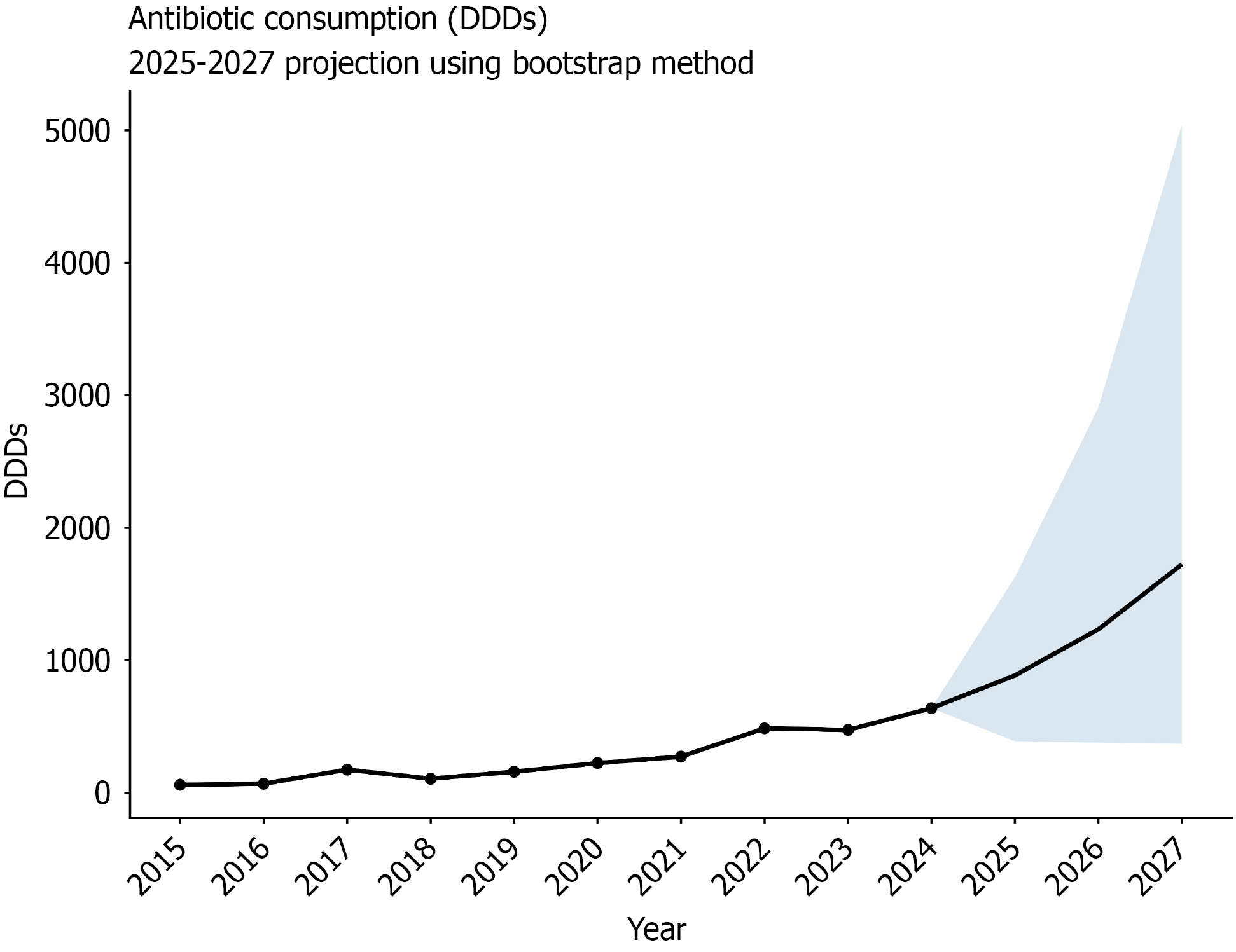
Figure 5 Estimated antibiotic consumption in defined daily doses.
DDD: Defined daily dose.
- Citation: Zeng W, Zhang WK, Xu D, He K, Huang YP, Liu YX, Yang HF. Antibiotic consumption of inpatients with inflammatory bowel disease during 2015-2024 and future prediction: Evidence from a general hospital. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(4): 115040
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i4/115040.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.115040