©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2026; 32(4): 113647
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.113647
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.113647
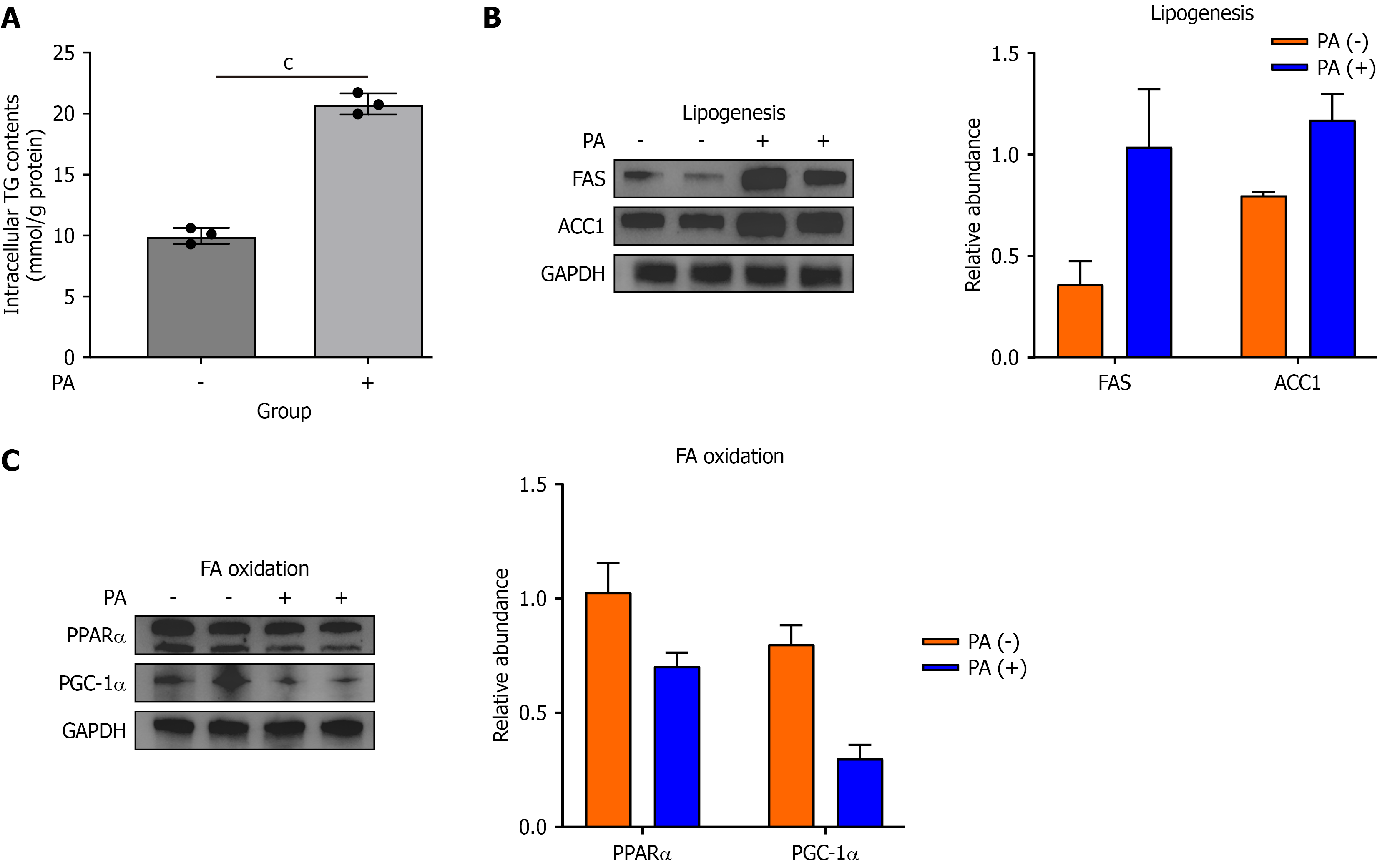
Figure 1 Palmitate acid induces lipid accumulation by promoting hepatic lipogenesis and inhibiting fatty acid β-oxidation in hepatocytes.
AML-12 cells were treated with 300 μM palmitate acid (PA) for 24 hours to establish an in vitro model of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. A: Intracellular triglyceride content in PA-stimulated AML-12 cells (n = 3/group); B: The protein expressions of lipogenesis target genes, fatty acid synthase, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1, were detected via Western blotting; C: The protein expressions of genes involved in fatty acid β-oxidation, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α, were detected via Western blotting. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. cP < 0.001. P value calculated between groups. TG: Triglyceride; PA: Palmitate acid; FA: Fatty acid; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; ACC1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α.
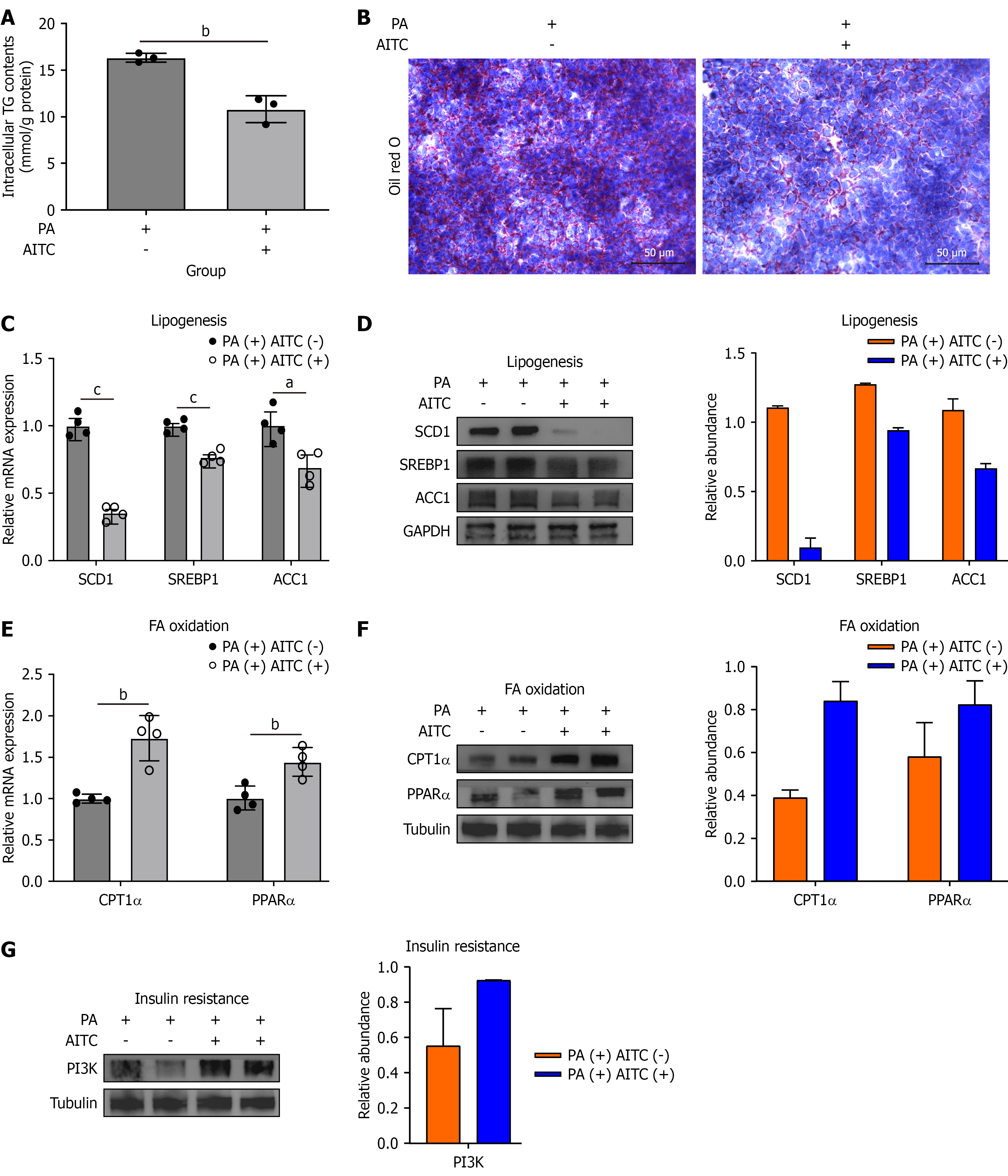
Figure 2 Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates hepatosteatosis by modulating lipid metabolism and insulin resistance in an in vitro metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease model.
AML-12 cells were treated with 20 μmol/L allyl isothiocyanate or vehicle for 24 hours to stimulate palmitate acid. A: Intracellular triglyceride content in AML-12 cells (n = 3/group); B: Representative image of oil red O staining of AML-12 cells in the two groups; C: The messenger RNA (mRNA) levels of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1), sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP1), and acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1) were detected (n = 4/group); D: The protein expressions of SCD1, SREBP1, and ACC1 were determined by Western blot analysis; E: The mRNA levels of the fatty acid β-oxidation-related genes carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 alpha (CPT1α) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) were detected (n = 4/group); F: The protein expressions of CPT1α and PPARα were determined by Western blot analysis; G: The protein expression of the insulin resistance-related gene phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase was determined by Western blot analysis. The scale bar in the panel represents 50 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. P calculated between groups. TG: Triglyceride; PA: Palmitate acid; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; ACC1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; mRNA: Messenger RNA; SCD1: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; SREBP1: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; CPT1α: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 alpha; FA: Fatty acid; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.
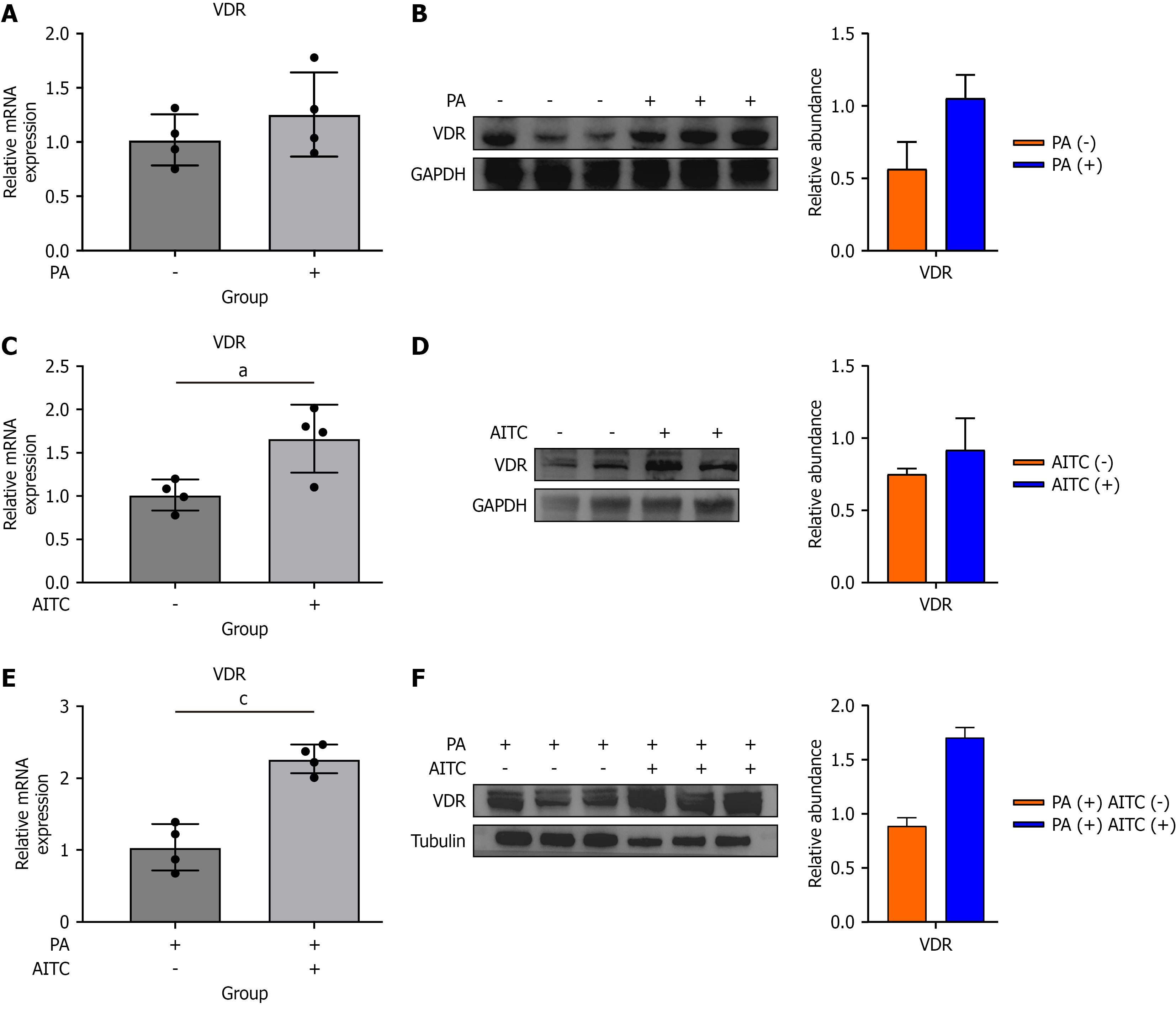
Figure 3 Allyl isothiocyanate activates vitamin D receptors in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in vitro.
A: The messenger RNA (mRNA) level of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) was detected in palmitate acid-stimulated AML-12 cells (n = 4/group); B: The protein expression of VDR was determined by Western blot analysis; C: The mRNA level of VDR was detected in allyl isothiocyanate (AITC)-stimulated AML-12 cells (n = 4/group); D: The protein expression of VDR in AITC-stimulated AML-12 cells; E: The mRNA level of VDR was detected in an AITC-stimulated in vitro metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease model; F: The protein expression of VDR was determined by Western blot analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. cP < 0.001. P calculated between groups. PA: Palmitate acid; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; VDR: Vitamin D receptor; mRNA: Messenger RNA; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
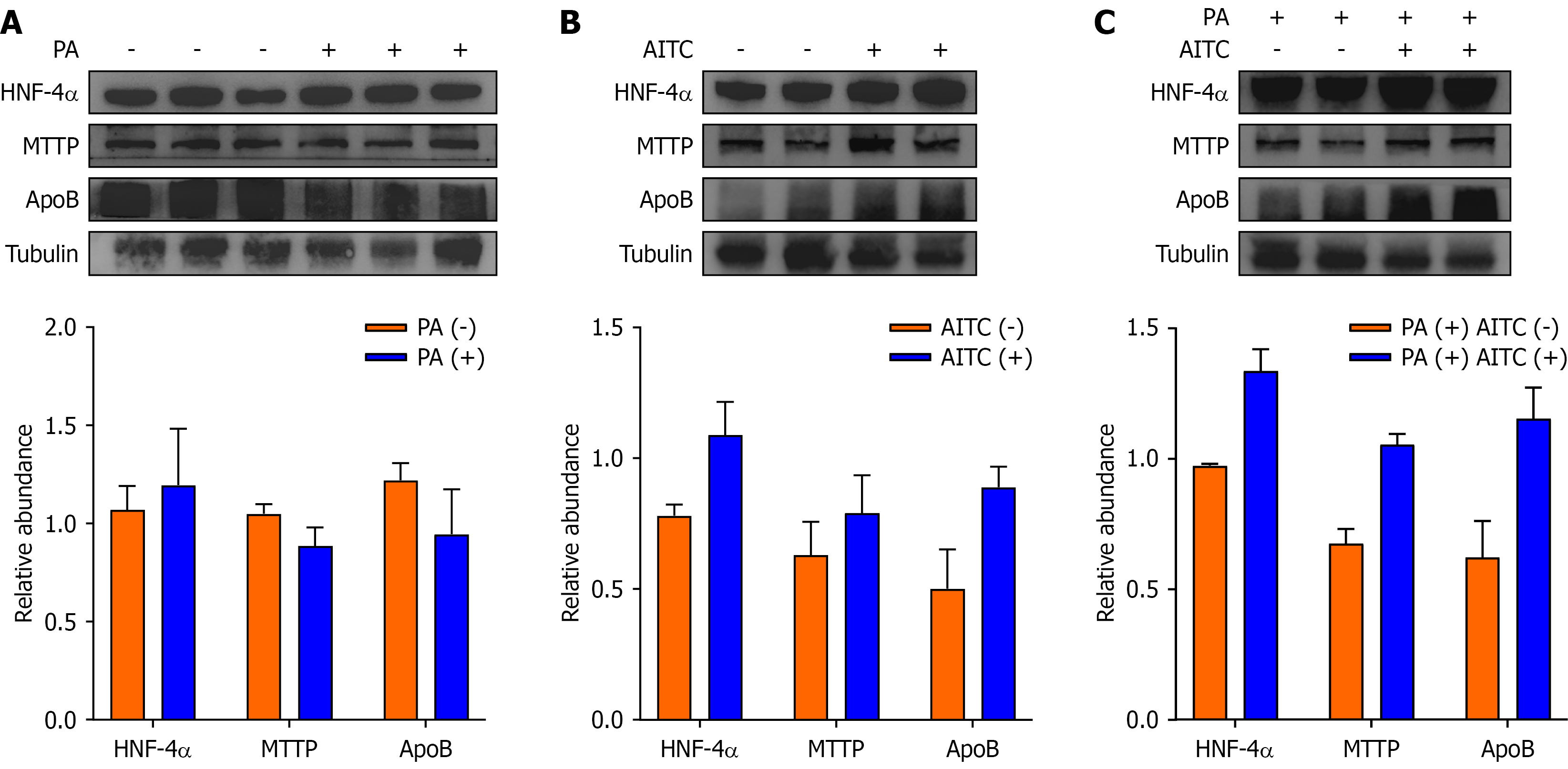
Figure 4 Allyl isothiocyanate attenuates lipid accumulation by activating the hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha/microsomal triglyceride transfer protein/apolipoprotein B signaling pathway.
A: The protein expressions of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF-4α), microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP) and apolipoprotein B (ApoB) in palmitate acid-stimulated AML-12 cells were determined by Western blot analysis; B: The protein expressions of HNF-4α, MTTP, and ApoB in allyl isothiocyanate (AITC)-stimulated AML-12 cells were detected by Western blot analysis; C: The protein expressions of HNF-4α, MTTP, and ApoB in the AITC-stimulated in vitro metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease model were determined by Western blot analysis. PA: Palmitate acid; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; HNF-4α: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha; MTTP: Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; ApoB: Apolipoprotein B.
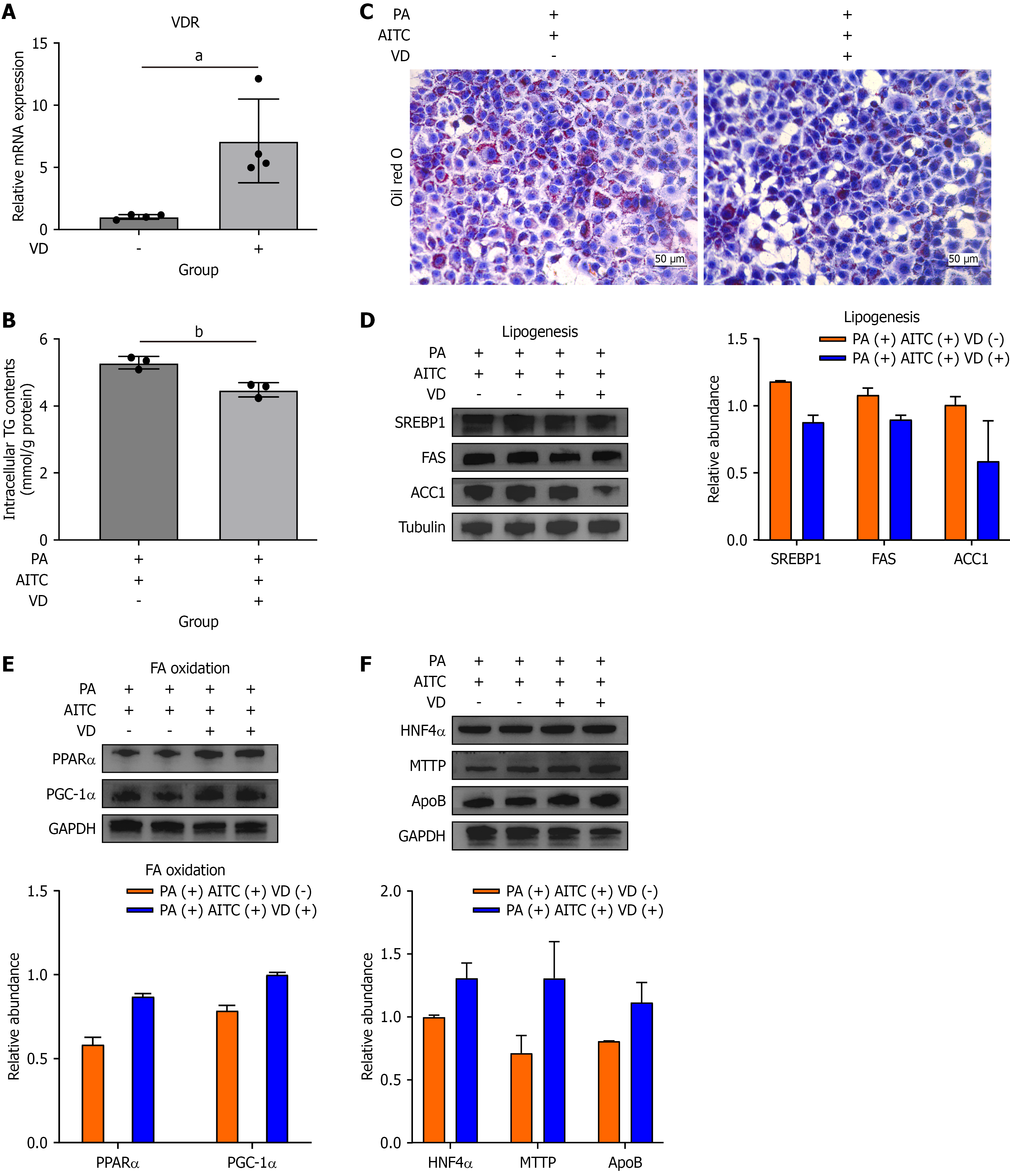
Figure 5 Activating vitamin D receptors promotes the ability of allyl isothiocyanate to alleviate metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease through the hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha/microsomal triglyceride transfer protein/apolipoprotein B signaling pathway.
AML-12 cells were treated with 600 nM vitamin D for 24 hours. A: The messenger RNA level of the vitamin D receptor was detected in AML-12 cells after vitamin D stimulation (n = 4/group); B: Intracellular triglyceride content in AML-12 cells was detected (n = 3/group); C: Oil red O staining of the vitamin D-stimulated in vitro metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease model; D: The protein expressions of lipogenesis-related genes, including sterol regulatory element binding protein 1, fatty acid synthase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1, were detected via Western blotting; E: The protein expressions of fatty acid β-oxidation-related genes, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α, were detected via Western blotting; F: The protein expressions of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha, microsomal triglyceride transfer protein, and apolipoprotein B were determined by Western blot analysis. The scale bar in the panel represents 50 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. P calculated between groups. VDR: Vitamin D receptor; VD: Vitamin D; mRNA: Messenger RNA; TG: Triglyceride; PA: Palmitate acid; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; ACC1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; SREBP1: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α; HNF-4α: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha; MTTP: Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; ApoB: Apolipoprotein B.
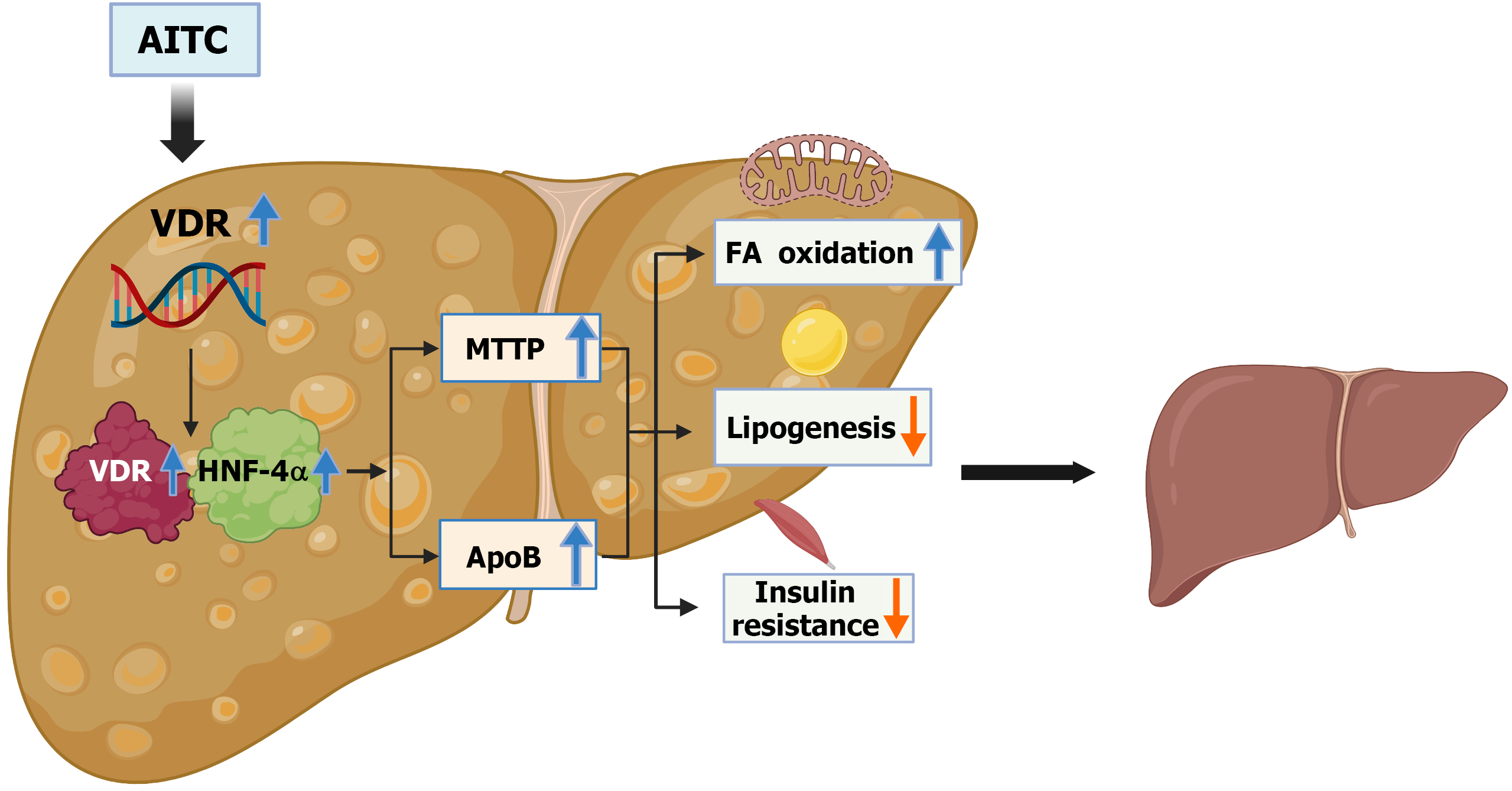
Figure 6 Model by which allyl isothiocyanate alleviates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
Allyl isothiocyanate activates vitamin D receptor to activate the hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha/microsomal triglyceride transfer protein/apolipoprotein B signaling pathway, inhibits lipogenesis, promotes fatty acid β-oxidation, and improves insulin resistance, alleviating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; HNF-4α: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha; FA: Fatty acid; VDR: Vitamin D receptor; MTTP: Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; ApoB: Apolipoprotein B.
- Citation: Gao T, Zhong KP, Wang JZ, Chen Y, Li CX. Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease via vitamin D receptors in hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(4): 113647
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i4/113647.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.113647