©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2026; 32(3): 115527
Published online Jan 21, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i3.115527
Published online Jan 21, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i3.115527
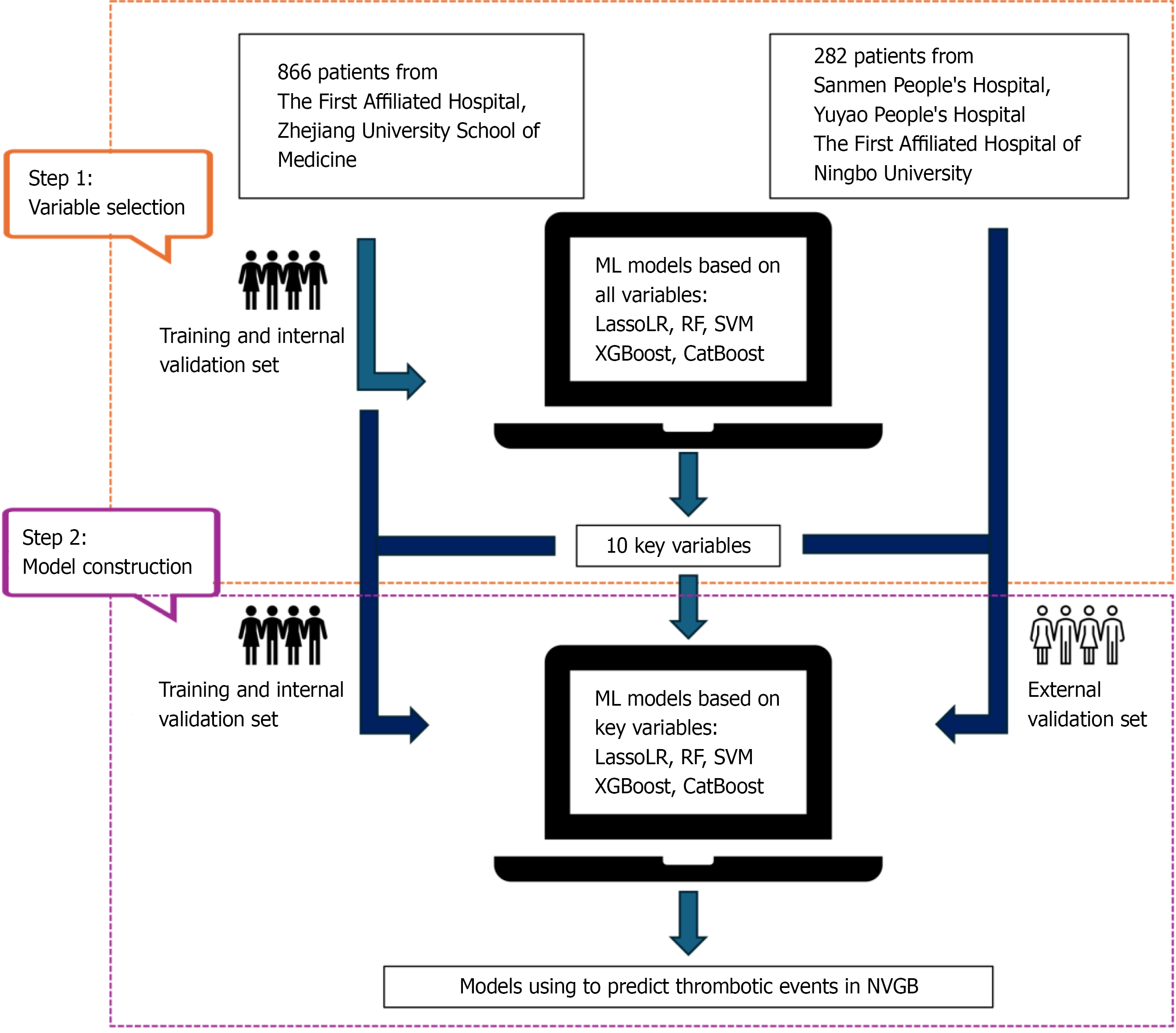
Figure 1 Study flow for the machine learning of internal and external validation set.
CatBoost: Categorical boosting; LassoLR: L1 regularized logistic regression; ML: Machine learning; NVGB: Nonvariceal gastrointestinal bleeding; RF: Random forest; SVM: Support vector machines; XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting.
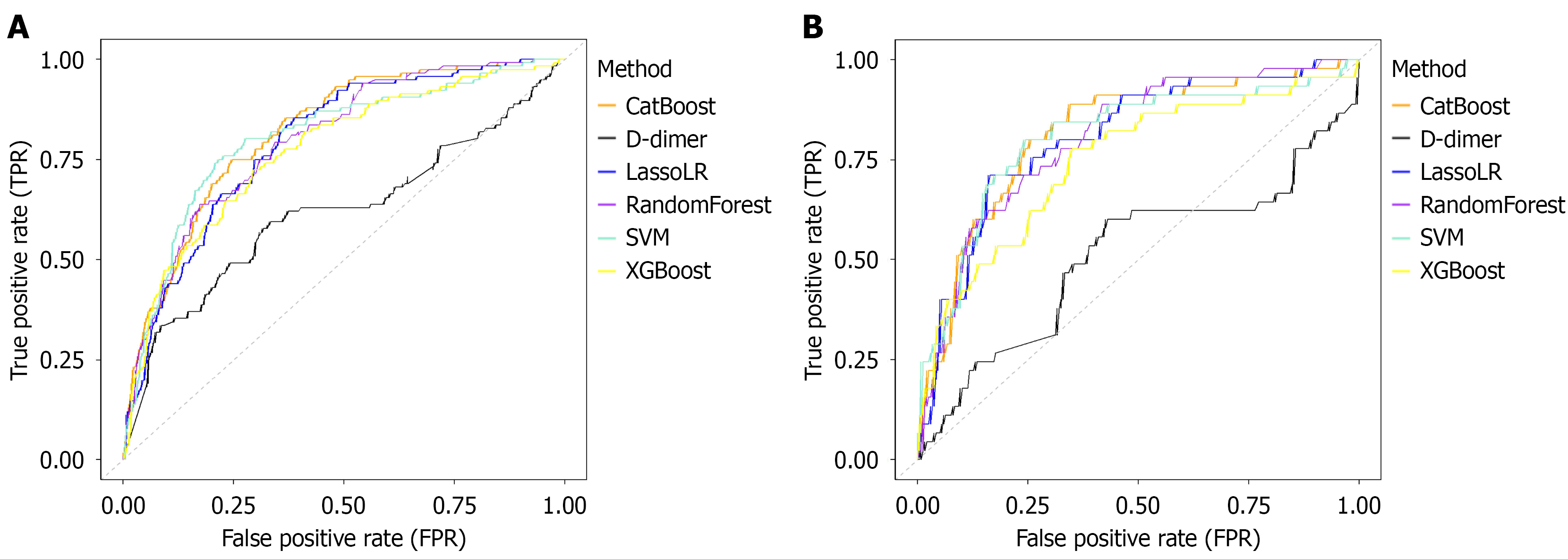
Figure 2 The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of different machine learning models with the internal validation set and the external validation set.
A: The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of different machine learning models with the internal validation set; B: The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of different machine learning L models with the external validation set. CatBoost: Categorical boosting; LassoLR: L1 regularized logistic regression; SVM: Support vector machines; XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting.
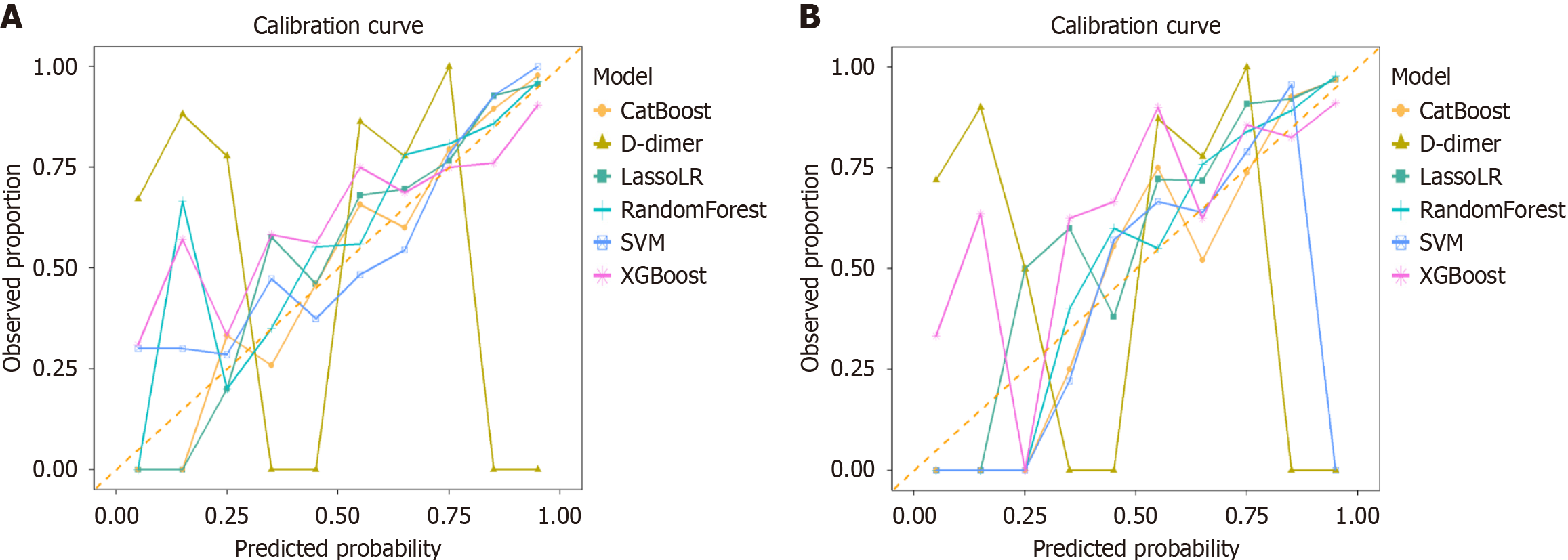
Figure 3 The calibration curve of different machine learning models.
A: Categorical boosting, L1 regularized logistic regression; B: Random forest for predicting thromboembolic events showed good performance. CatBoost: Categorical boosting; LassoLR: L1 regularized logistic regression; SVM: Support vector machines; XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting.
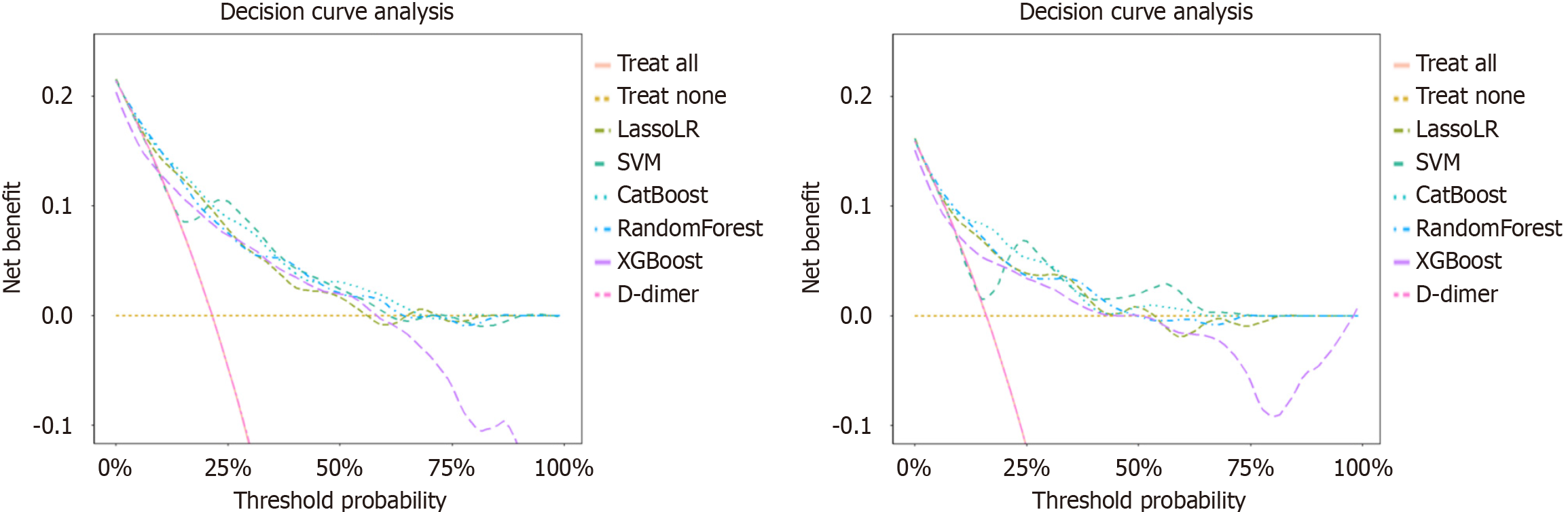
Figure 4 The decision curve analysis of different machine learning models.
The results showed that compared with the D-dimer, all machine learning models demonstrated higher net benefits across most threshold probability ranges. CatBoost: Categorical boosting; LassoLR: L1 regularized logistic regression; SVM: Support vector machines; XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting.
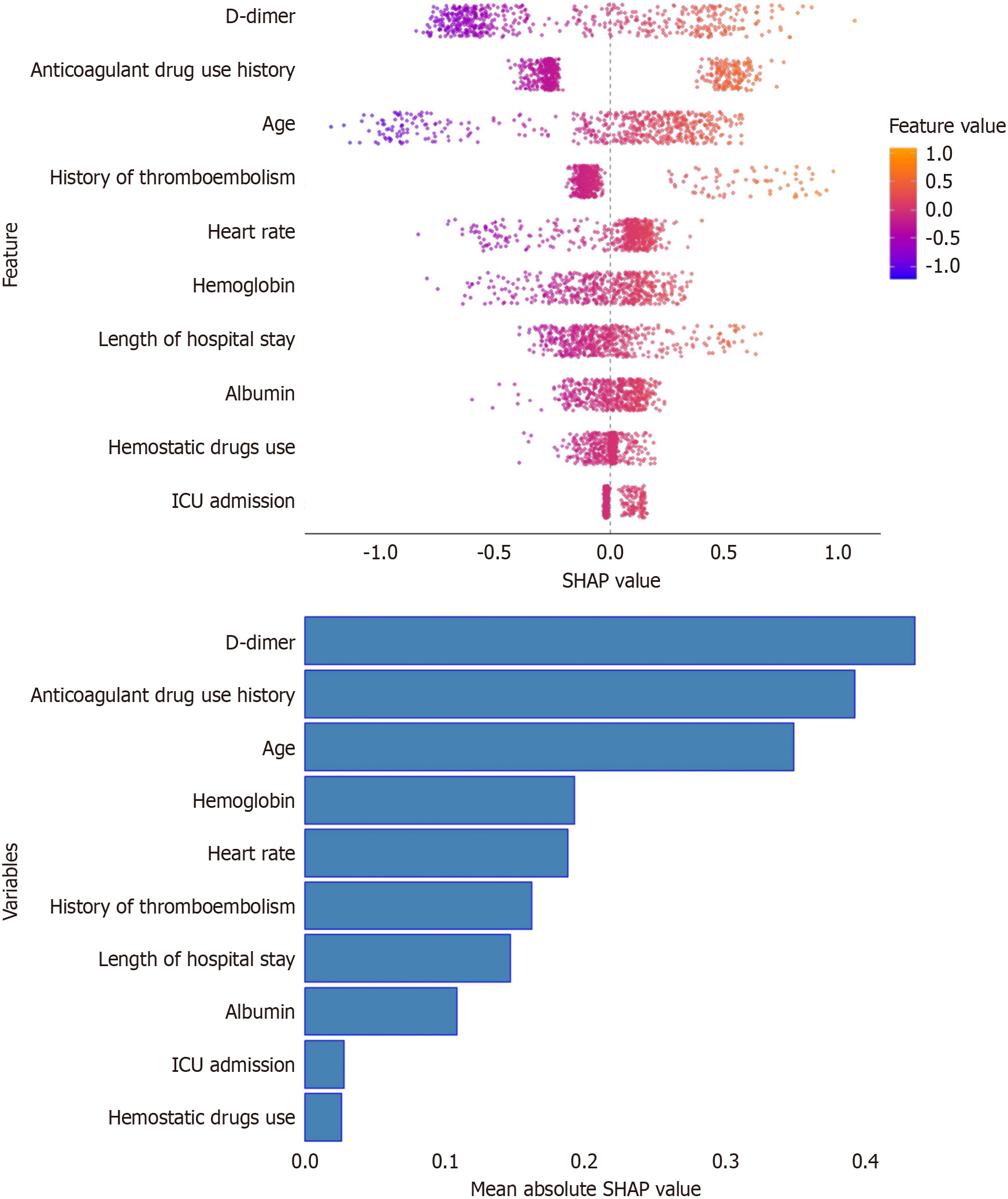
Figure 5 The SHapley Additive exPlanations summary plot.
The mean SHapley Additive exPlanations values of 10 important features and the influence of input features on the model's output. ICU: Intensive care unit.
- Citation: Lu C, Cheng HY, Zhu RK, Zhou YD, Sun KF, Xu L, Sang JZ, Chen JE, Yu CH, Qin YL, Li L. Application of machine learning models in predicting the risk of thromboembolic events in patients with nonvariceal gastrointestinal bleeding. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(3): 115527
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i3/115527.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i3.115527