©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2026; 32(3): 113935
Published online Jan 21, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i3.113935
Published online Jan 21, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i3.113935
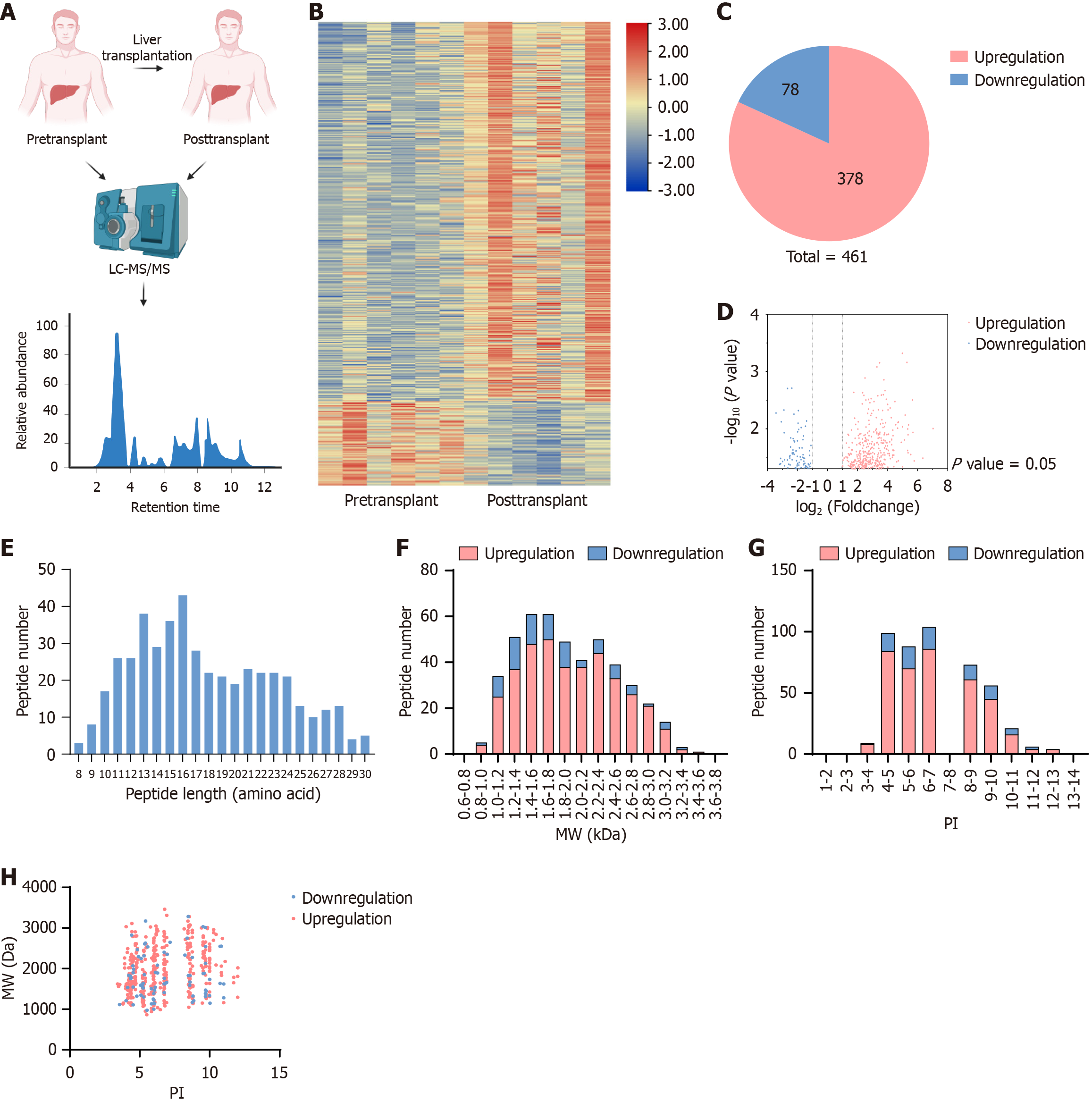
Figure 1 Human liver transplantation peptides expression profile.
A: Schematic diagram of liver specimens sent to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry before and after transplantation in liver transplant patients; B: The heat map indicates the peptide profiles with significant differences between the indicated groups; C: The number of upregulation and downregulation differentially expressed endogenous peptides from liver transplant patients compared with pretransplant; D: This volcano plot represents the distribution of upregulation and downregulation peptides; E-G: Distribution of the length, molecular weight and isoelectric point of peptides; H: Correlation between molecular weight and isoelectric point distribution of peptides. MW: Molecular weight; pI: Isoelectric point; LC/MS-MS: Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
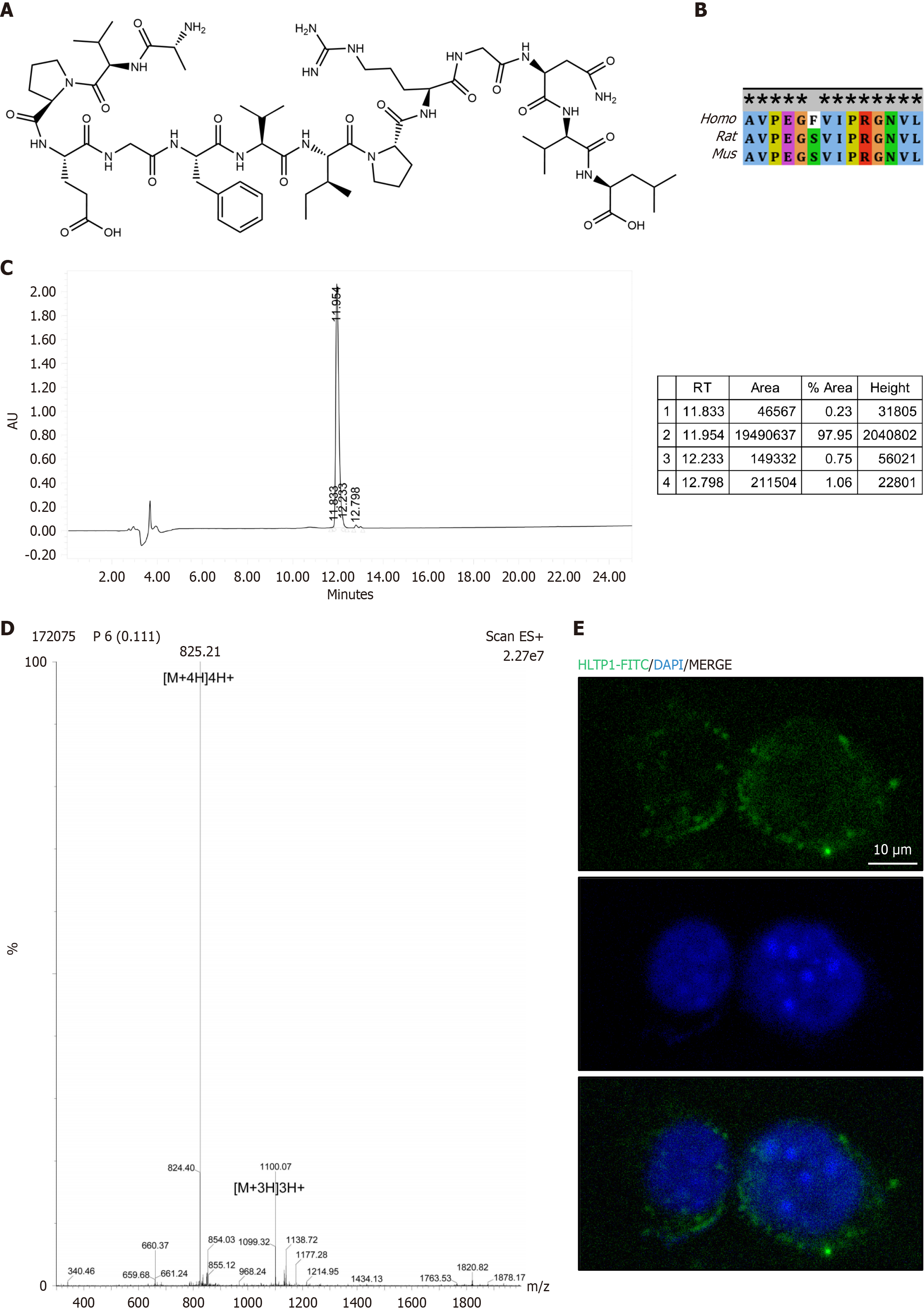
Figure 2 Screening for polypeptides with potential hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury-alleviating effects.
A: Chemical structure of ‘AVPEGFVIPRGNVL’; B: Conservativeness analysis of the ‘AVPEGFVIPRGNVL’ sequence; C: Mass spectrometry identification of the purity of ‘AVPEGFVIPRGNVL’; D: Mass spectrometry analysis of ‘AVPEGFVIPRGNVL’; E: Representative confocal microscopy images of AML12 cells under normal conditions. Cells were stained with the synthetic human liver transplantation peptide 1-fluorescein isothiocyanate peptide (green) and the nuclear dye DAPI (blue), scale bar = 10 μm. HLTP1: Human liver transplantation peptide 1; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; RT: Retention time.
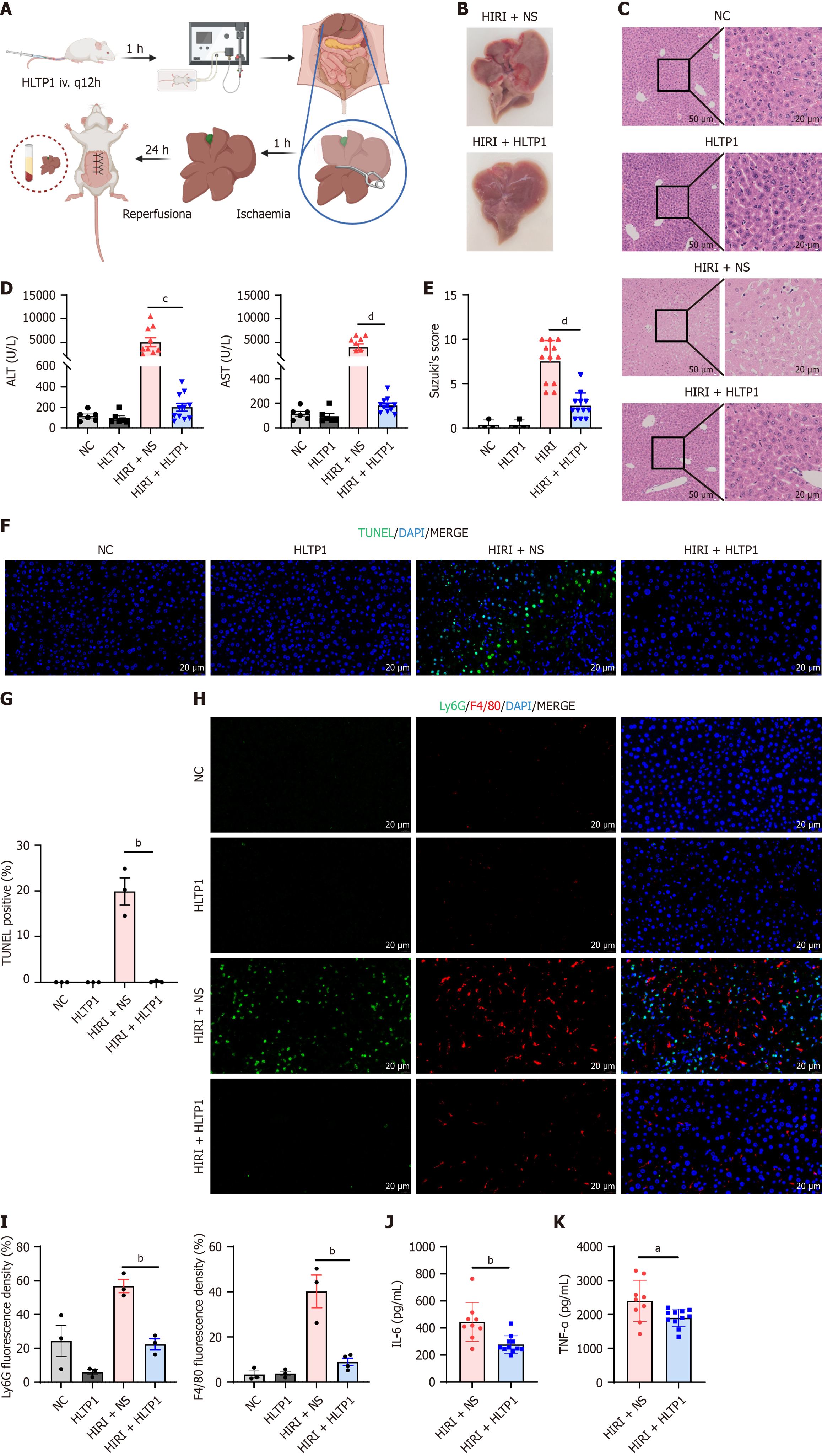
Figure 3 Human liver transplantation peptide 1 alleviates liver damage during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.
A: Schematic diagram of mouse liver ischemia-reperfusion injury modelling; B: Gross view of liver after ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice; C: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of liver sections. Scale bar = 20 μm; D: Serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase level; E: Suzuki’s score of Hematoxylin and eosin staining of liver sections; F: Representative images of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling staining (green) performed on liver sections. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 20 μm; G: Quantitative analysis of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling staining; H: Representative tissue immunofluorescence images of liver sections stained for neutrophils (Ly6G, green) and macrophages (F4/80, red). Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 20 μm; I: Quantitative analysis of Ly6G and F4/80; J: Serum interleukin-6 level; K: Serum tumor necrosis factor-α level. HLTP1: Human liver transplantation peptide 1; iv. Q12h: Intravenous injection every 12 hours; HIRI: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury; NS: Normal saline; NC: Negative control; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, and dP < 0.0001.
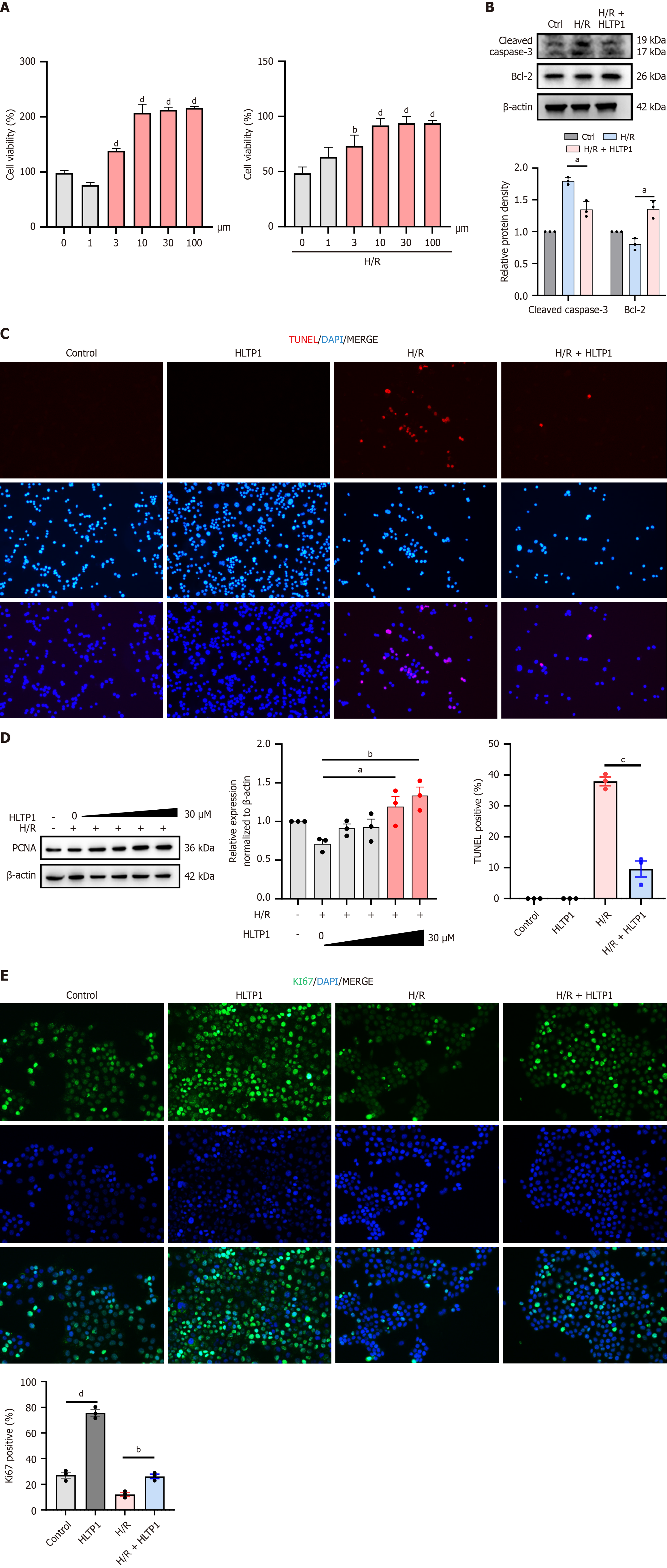
Figure 4 Human liver transplantation peptide 1 attenuates AML12 cells injury under hypoxia/reoxygenation treatment.
A: Cell viability after human liver transplantation peptide 1 treatment; B: Cleaved caspase-3 and Bcl-2 protein expression by western blotting; C: Representative images of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling staining (red) performed on AML12 cells. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue); D: PCNA protein expression by western blotting; E: Representative immunofluorescence images of AML12 cells stained for the proliferation marker Ki67 (green). Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). H/R: Hypoxia/reoxygenation; HLTP1: Human liver transplantation peptide 1; TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, and dP < 0.0001.
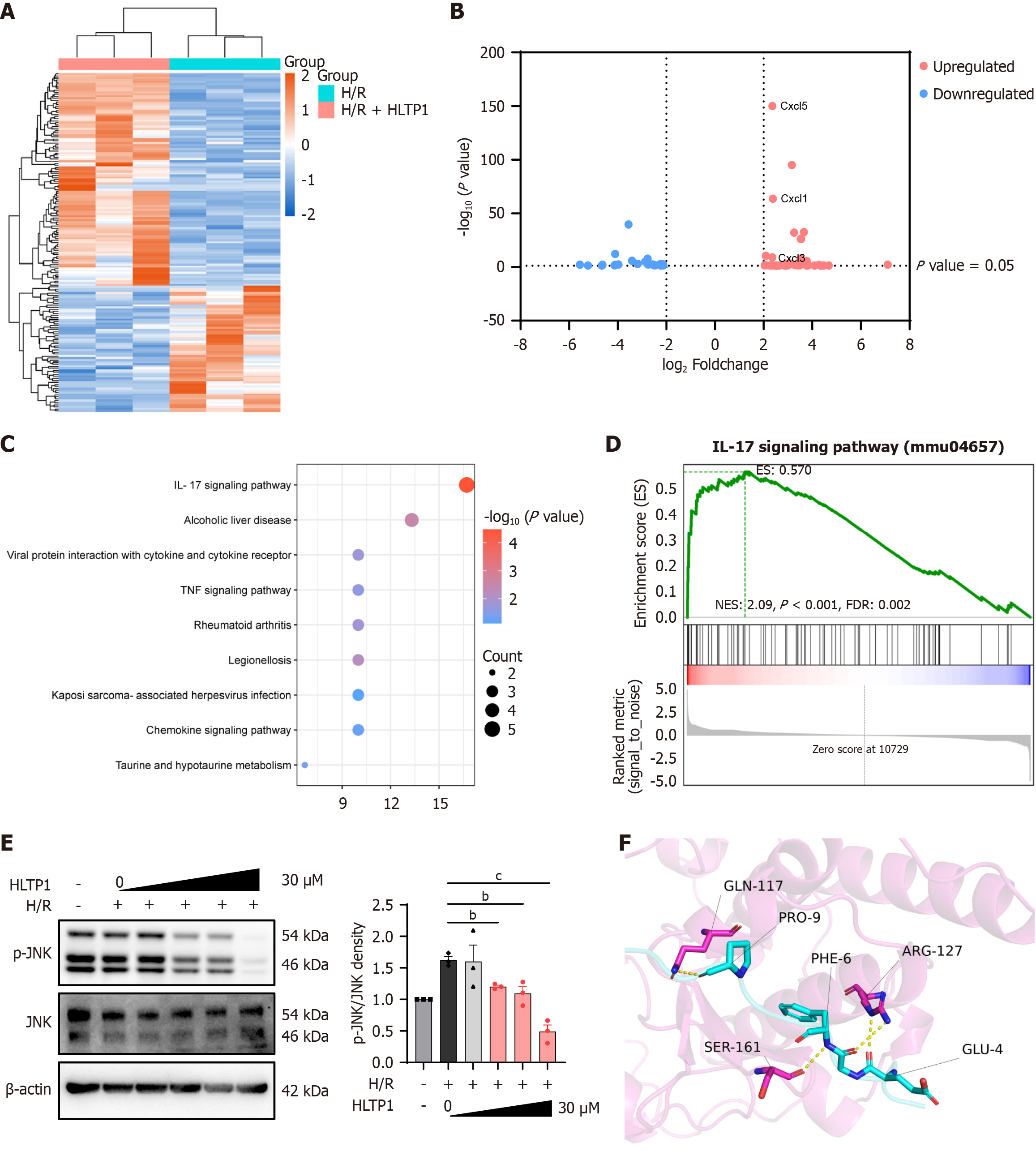
Figure 5 RNA-seq analysis indicate that human liver transplantation peptide 1 is involved in the mitogen-activated protein kinases pathway.
A: The heat map of significant differences genes; B: This volcano plot represents the distribution of significant differences genes; C: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis; D: Randomized controlled trial analysis of interleukin-17 signaling pathway; E: Protein levels of Jun N-terminal kinase and phosphorylated-Jun N-terminal kinase in hypoxia/reoxygenation treated AML12 cells with human liver transplantation peptide 1 (0 μM, 1 μM, 3 μM, 10 μM, 30 μM); F: 3D interaction diagram of human liver transplantation peptide 1 with Jun N-terminal kinase. H/R: Hypoxia/reoxygenation; HLTP1: Human liver transplantation peptide 1; IL-17: Interleukin-17; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; JNK: Jun N-terminal kinase; p-JNK: Phosphorylated-Jun N-terminal kinase. bP < 0.01, and cP < 0.001.
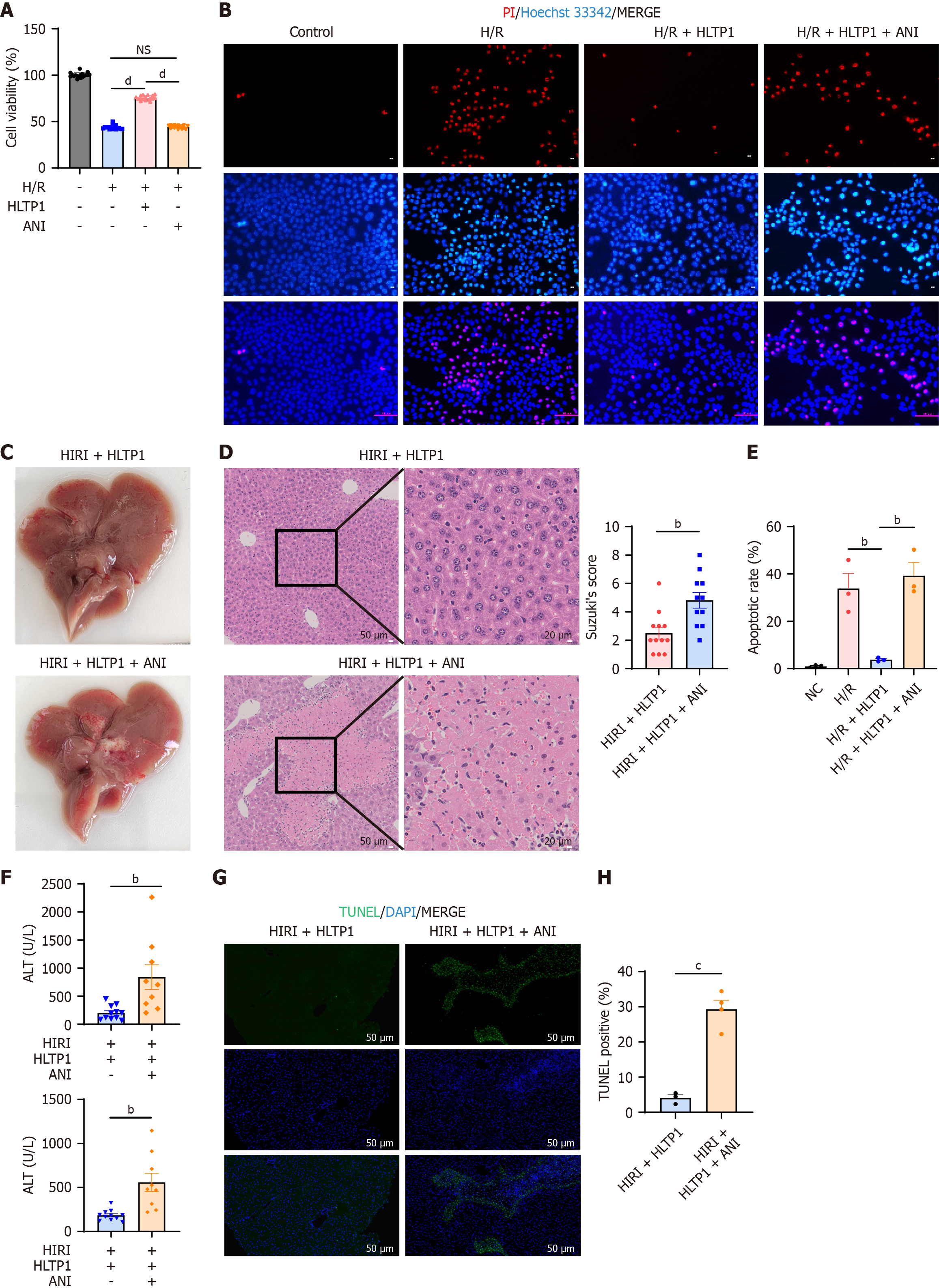
Figure 6 Human liver transplantation peptide 1 inhibits Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylation to reduce apoptosis.
A: Cell viability of AML12 with the administration of anisomycin; B: Representative fluorescence microscopy images of AML12 cells co-stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue, all nuclei) and propidium iodide (red, late apoptotic/dead cells). Scale bar = 100 μm; C: Gross view of liver after ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice; D: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of liver sections. Scale bar = 20 μm; E: Quantitative analysis of the apoptotic rate, which determined by propidium iodide/Hoechst 33342 co-staining; F: Serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase level; G: Representative images of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling staining (green) performed on liver sections. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 50 μm; H: Quantitative analysis of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling staining. H/R: Hypoxia/reoxygenation; HLTP1: Human liver transplantation peptide 1; ANI: Anisomycin; NS: Not significant; HIRI: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury; NC: Negative control; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling; PI: Propidium iodide. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, and dP < 0.0001.
- Citation: Xie HW, Bao Q, Chen ZX, Zhang XM, Liu XY, Wang R, Cai YS, Sun P. Targeting Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylation: A human-derived hepatoprotective peptide human liver transplantation peptide 1 attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(3): 113935
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i3/113935.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i3.113935