©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2026; 32(2): 111737
Published online Jan 14, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i2.111737
Published online Jan 14, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i2.111737
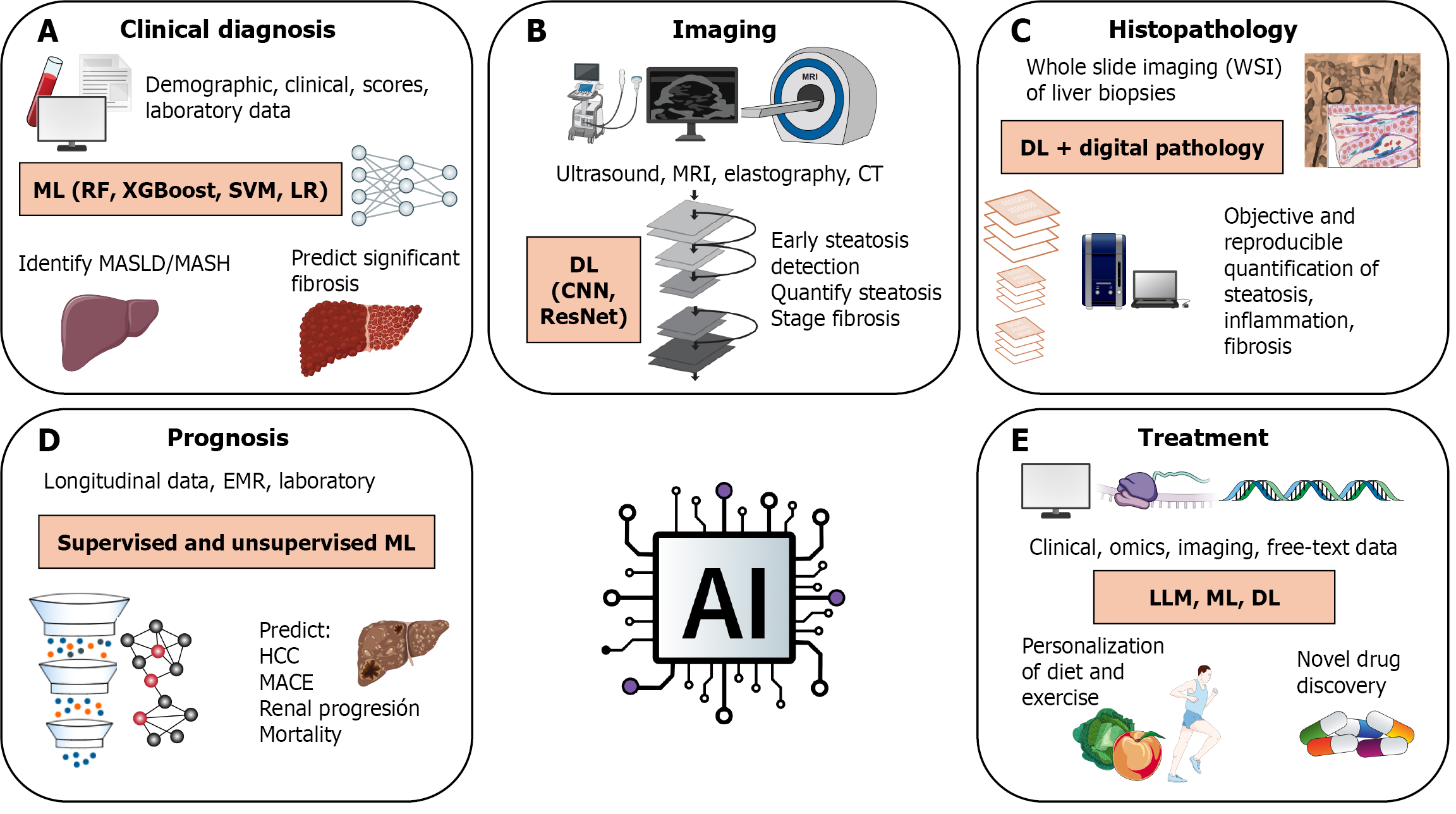
Figure 1 Artificial intelligence applications across the clinical spectrum of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
The figure illustrates how artificial intelligence tools are integrated at key stages of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) management. A: In clinical diagnosis, supervised machine learning (ML) models (e.g., Random Forest, XGBoost, support vector machine, logistic regression) predict MASLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, and significant fibrosis using clinical and laboratory data; B: Imaging-based deep learning (DL) methods, such as convolutional neural network and ResNet, support the detection of steatosis and the staging of fibrosis; C: In histopathology, DL combined with digital pathology enables the reproducible quantification of hepatic features using whole-slide imaging; D: Prognostic models based on supervised and unsupervised ML predict hepatocellular carcinoma, major adverse cardiovascular events, renal progression, and mortality; E: In treatment Large Language Model personalize lifestyle interventions. ML and DL facilitate novel drug discovery by integrating clinical, omics, imaging, and free-text data. Figure created by the authors using royalty-free and open-license content. Components were obtained from Servier Medical Art (CC BY 4.0), NIAID BioArt Source (free for educational and scientific use), and SciDraw (CC BY 4.0), with original creators credited in the source files.
- Citation: Hernández-Almonacid PG, Marín-Quintero X. Artificial intelligence in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Transforming diagnosis and therapeutic approaches. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(2): 111737
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i2/111737.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i2.111737