©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2025; 31(8): 100069
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.100069
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.100069
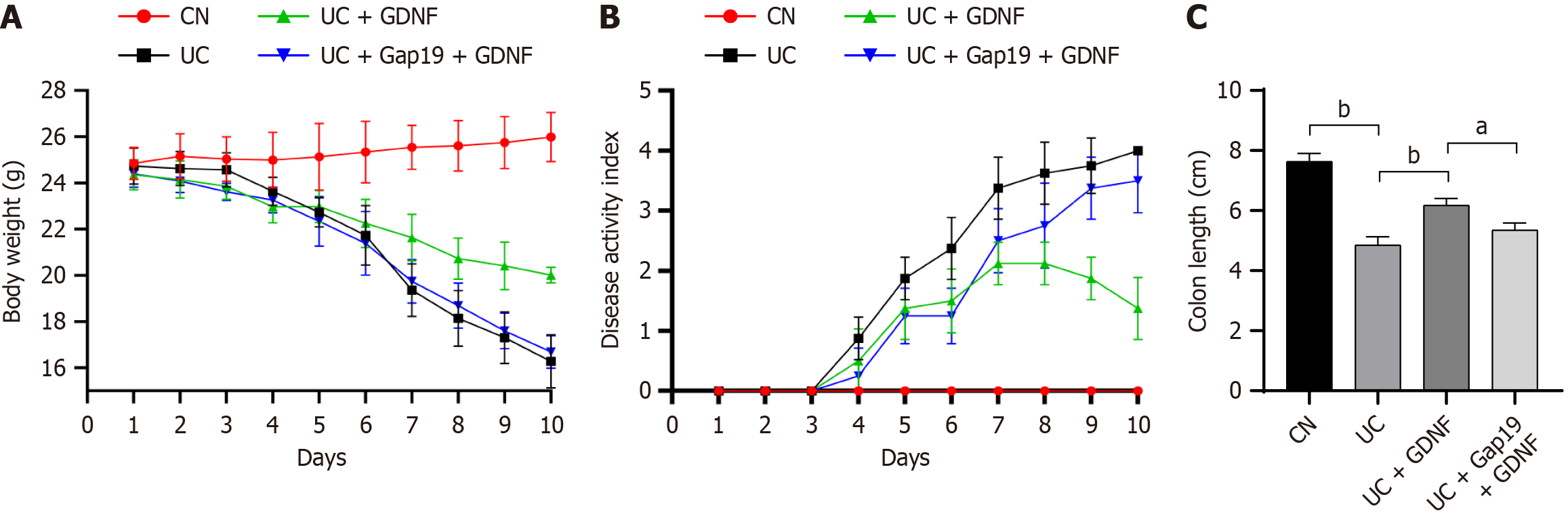
Figure 1 Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor alleviates colitis symptoms in dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis mice.
A: Monitoring of body weight changes from day 1 to day 10; B: Daily calculation of the disease activity index scores from day 1 to day 10; C: Measurement of colon length on day 11 after euthanasia. Data were expressed as mean ± SD (n = 8). aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. GDNF: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CN: Normal control.
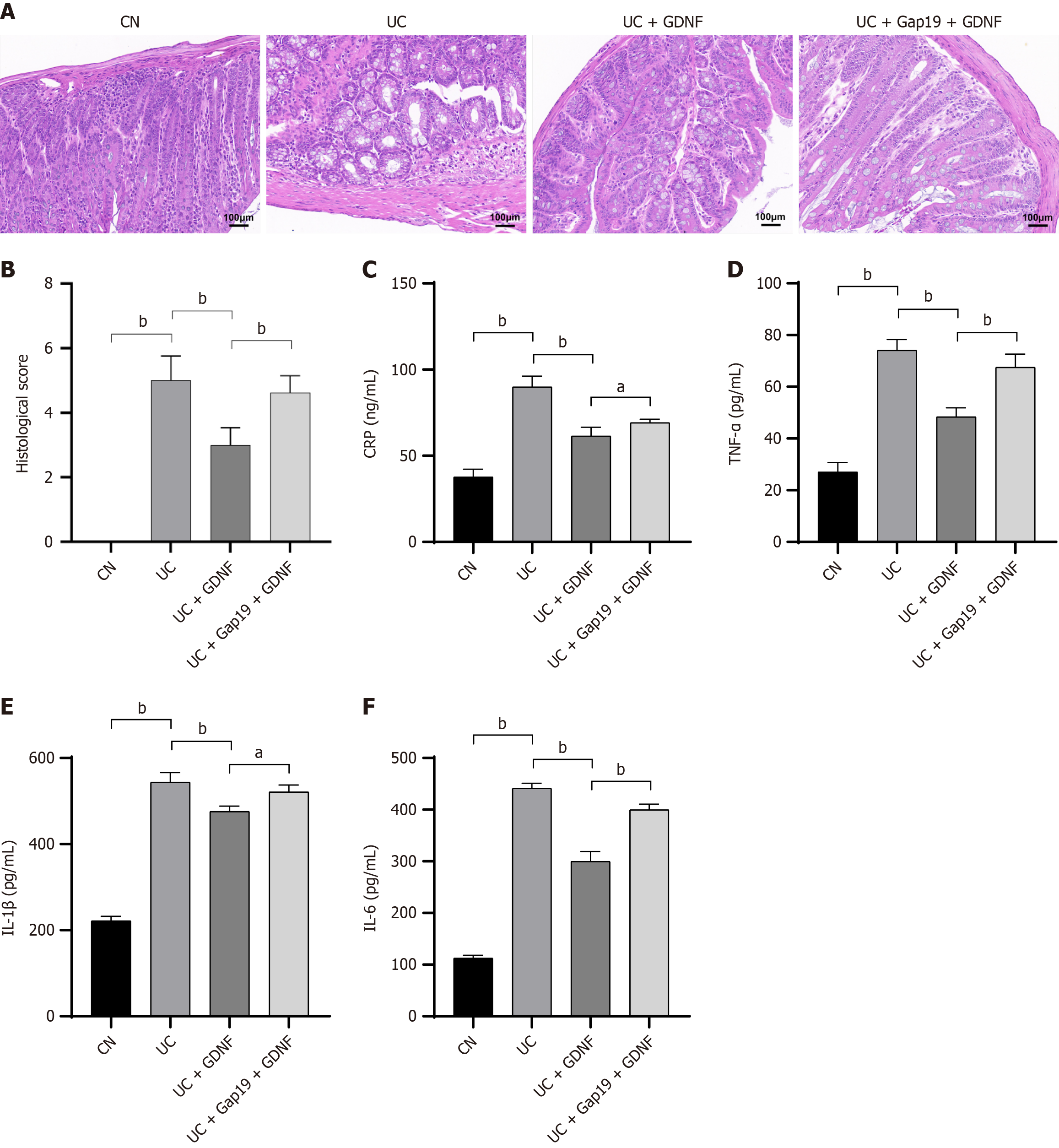
Figure 2 Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor protects against colonic histopathological damage and reduces inflammation in dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis mice.
A: Representative colon tissue sections stained by hematoxylin and eosin staining showing histopathological changes in each group (scale bar: 100 μm); B: Histological scores; Quantification of serum levels of C: C-reactive protein; D: Tumor necrosis factor-α; E: Interleukin-1β; F: Interleukin-6 using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data were presented as mean ± SD (n = 8). aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. GDNF: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CN: Normal control; CRP: C-reactive protein; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL: Interleukin.
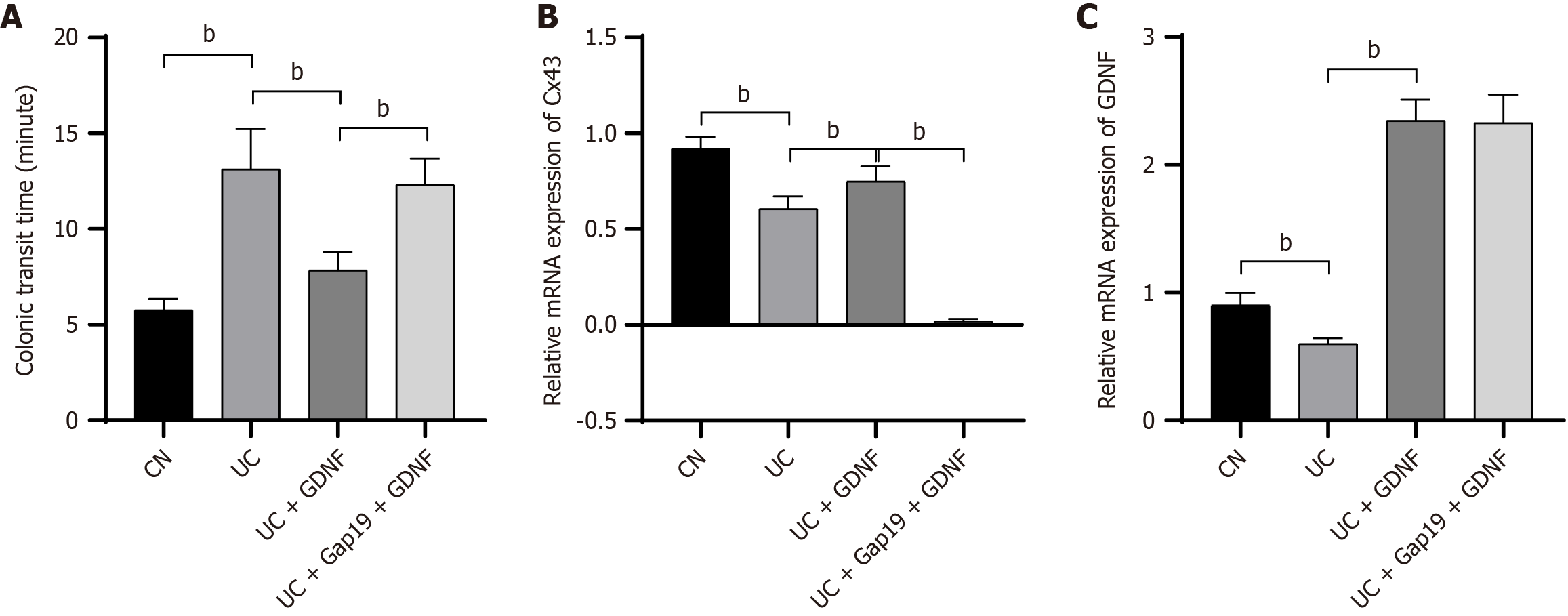
Figure 3 Dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis mice.
A: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor improves colonic transit time in dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis mice. The colonic transit time in mice across different groups; B: Relative mRNA expression of connexin 43 in the colon of dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis mice in different groups; C: Relative mRNA expression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the colon of dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis mice in different groups. bP < 0.01. GDNF: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CN: Normal control; Cx43: Connexin 43.
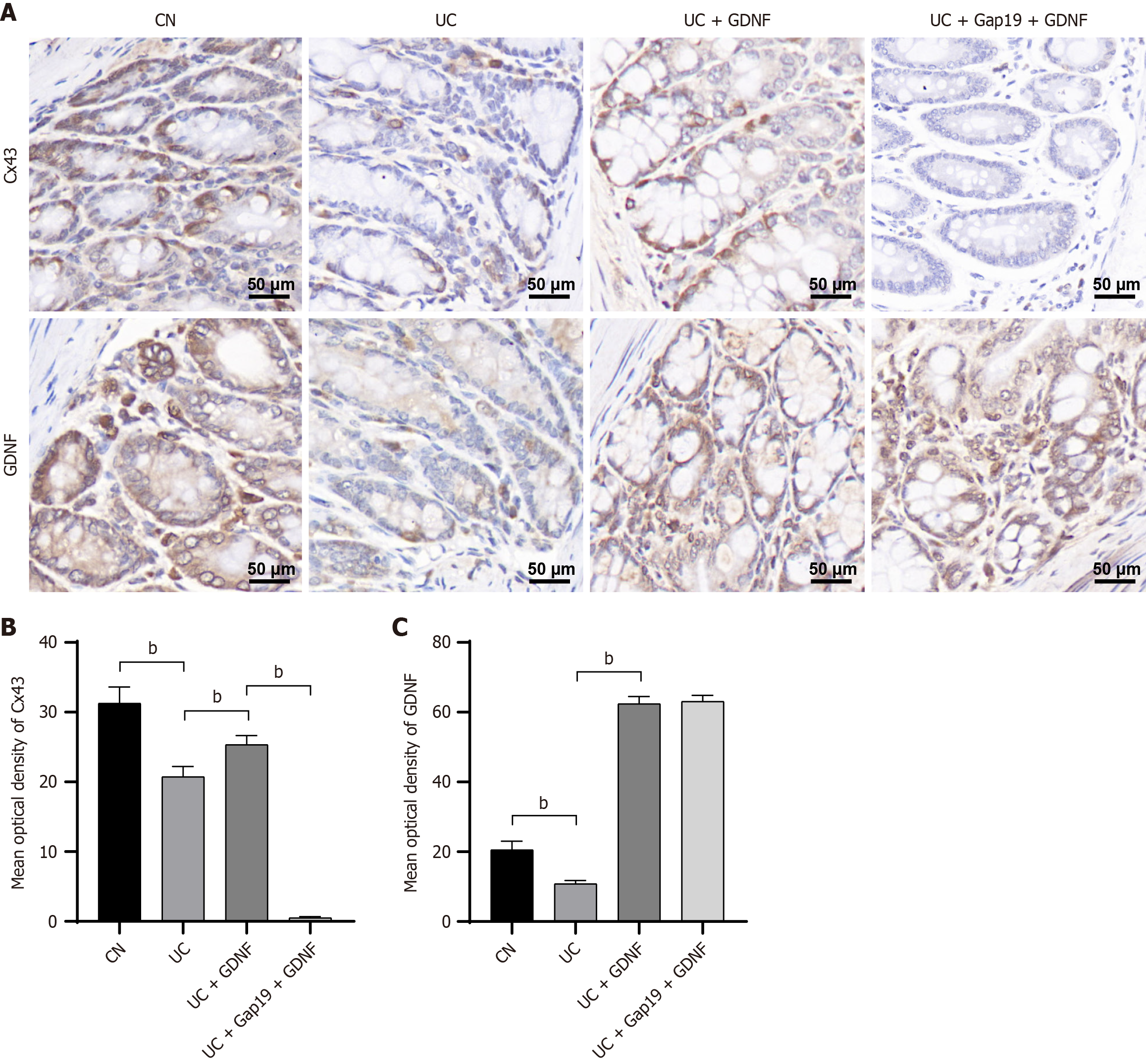
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical staining and quantification of connexin 43 and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in colonic tissues.
A: Representative immunohistochemical images of connexin 43 and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in colonic tissues (scale bar: 50 μm); B: Quantification of the mean optical density of connexin 43; C: Quantification of the mean optical density of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor staining. Data were presented as mean ± SD (n = 8). bP < 0.01. GDNF: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CN: Normal control; Cx43: Connexin 43.
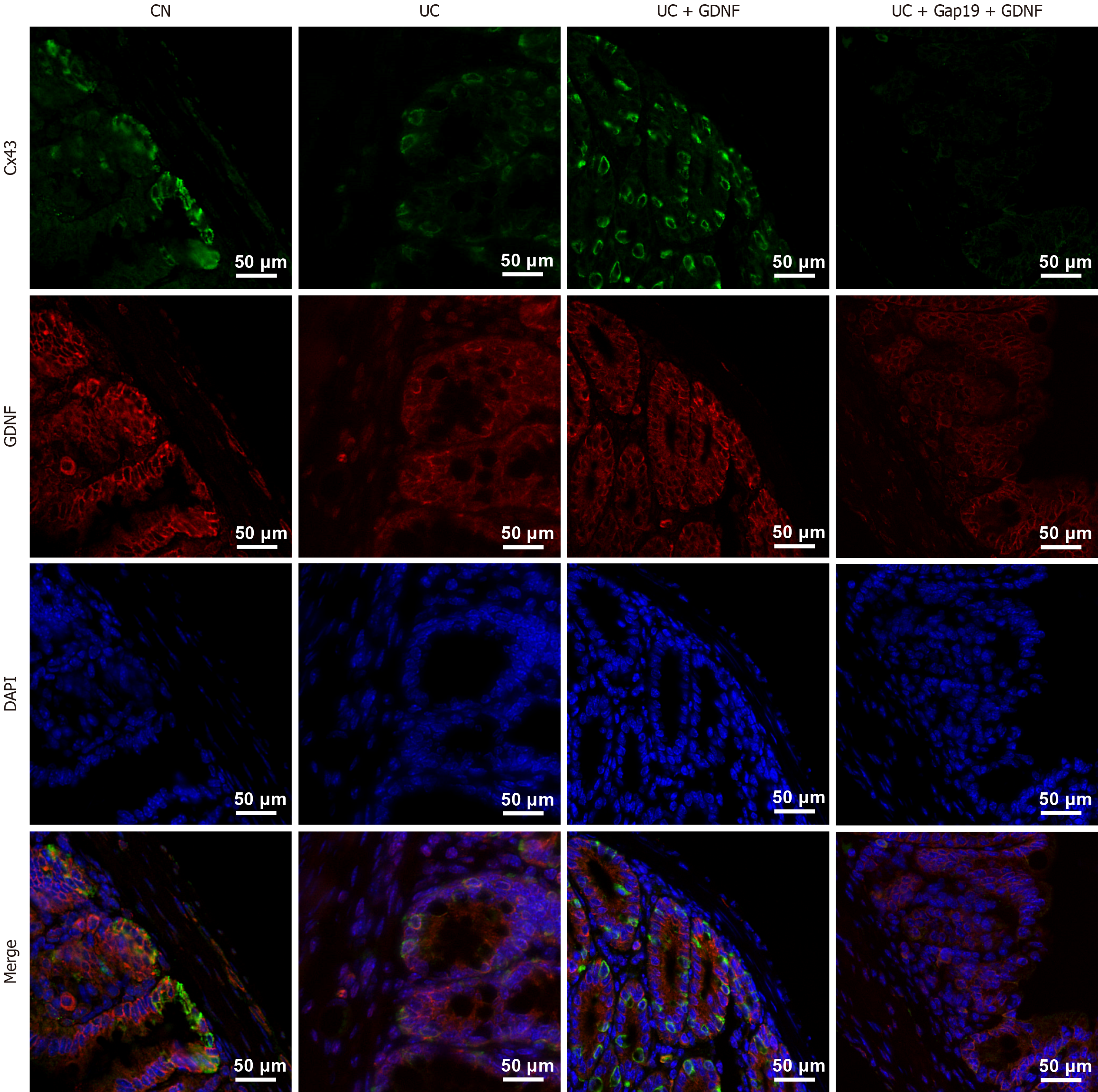
Figure 5 Dual-labelling immunofluorescence analysis of connexin 43 and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in colonic tissues.
Representative images of immunofluorescence staining for glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (red), connexin 43 (green), and 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue) in colonic tissues from different groups. Merged images showed the co-localization of connexin 43 and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. Scale bar: 50 μm. GDNF: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CN: Normal control; Cx43: Connexin 43; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
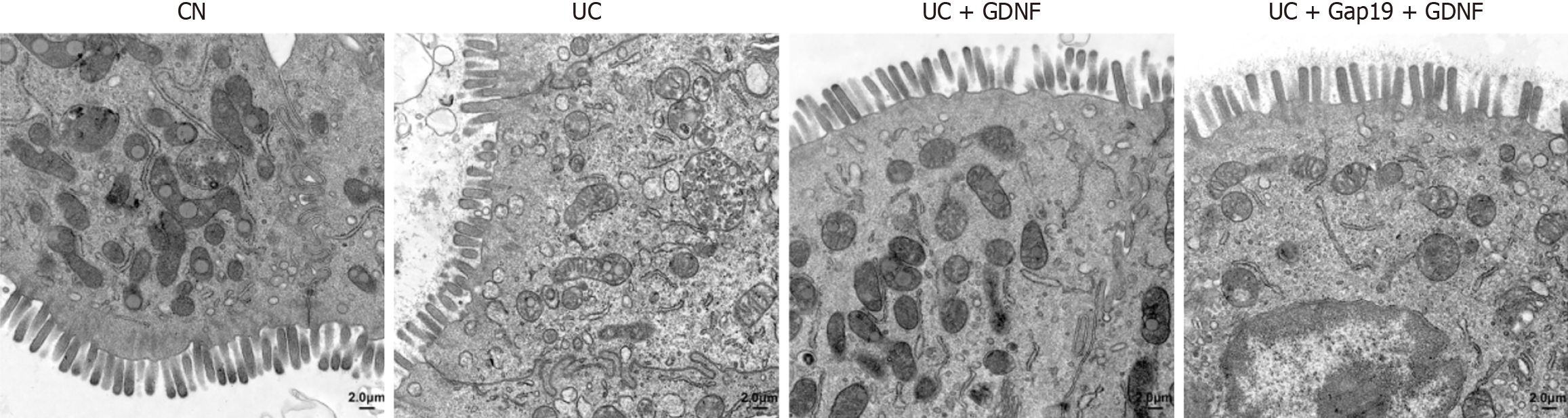
Figure 6 Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor mitigates ultrastructure damage in colonic tissues.
Representative transmission electron microscopy images showing ultrastructural alterations in colonic tissues from different groups. Original magnification: 5000 ×; Scale bar: 2.0 μm. GDNF: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CN: Normal control.
- Citation: Yang W, Liu R, Xu F. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor improves impaired colonic motility in experimental colitis mice through connexin 43. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(8): 100069
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i8/100069.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.100069