©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2025; 31(47): 114789
Published online Dec 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.114789
Published online Dec 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.114789
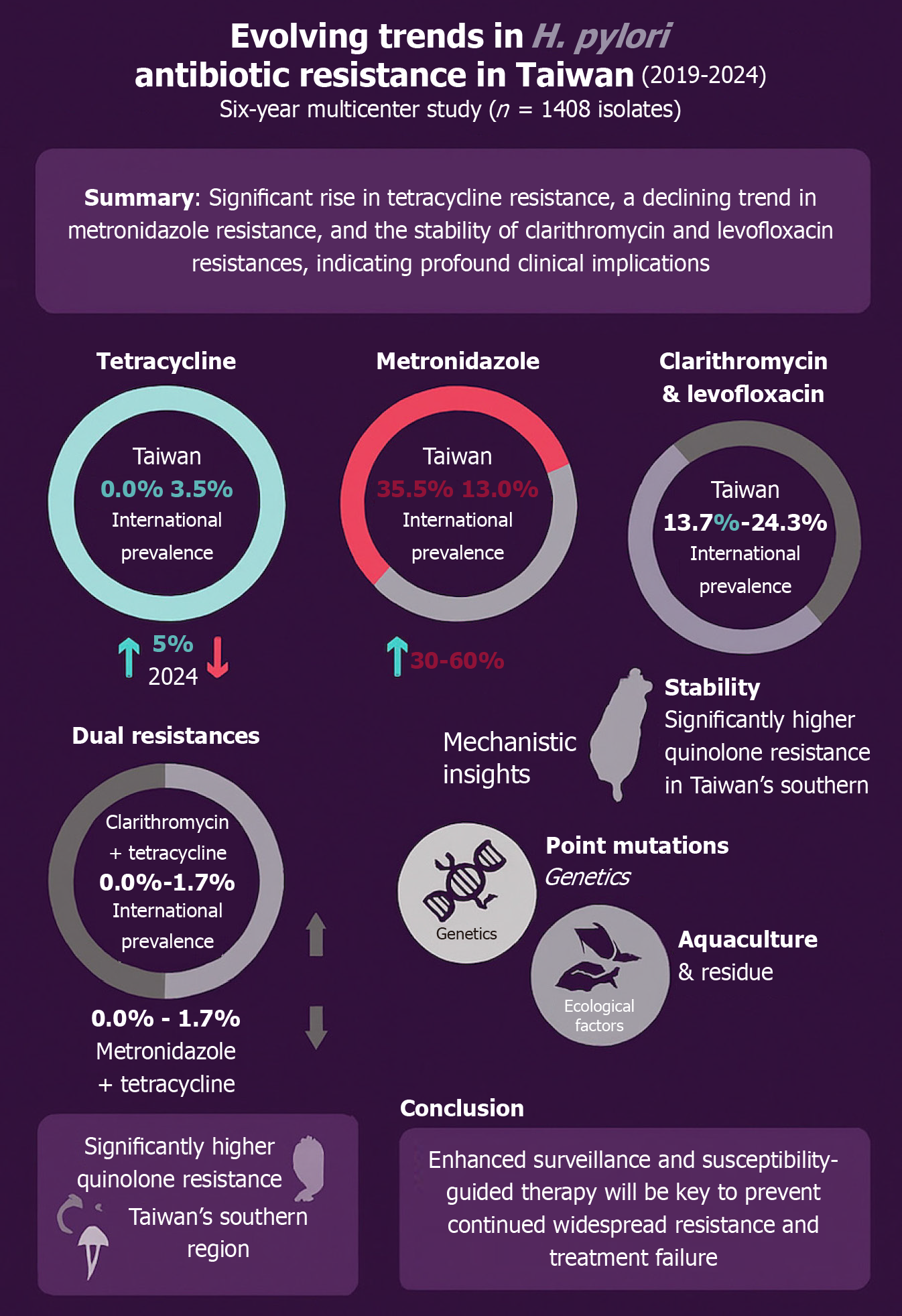
Figure 1 Evolving trends in Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance in Taiwan (2019-2024).
This infographic summarizes six-year surveillance data from 1408 treatment-naive patients across Taiwan. It highlights the rising prevalence of tetracycline resistance, the decline in metronidazole resistance, and the relative stability of clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance. Dual resistance involving tetracycline is emerging, and regional variation in levofloxacin resistance is noted. Mechanistic insights include genetic mutations and environmental exposure contributing to resistance evolution. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
- Citation: Issa T, Zalloua P, Issa IA. Resistance reversal: Taiwan’s Helicobacter pylori trends defy global norms. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(47): 114789
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i47/114789.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i47.114789