©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2025; 31(46): 111631
Published online Dec 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i46.111631
Published online Dec 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i46.111631
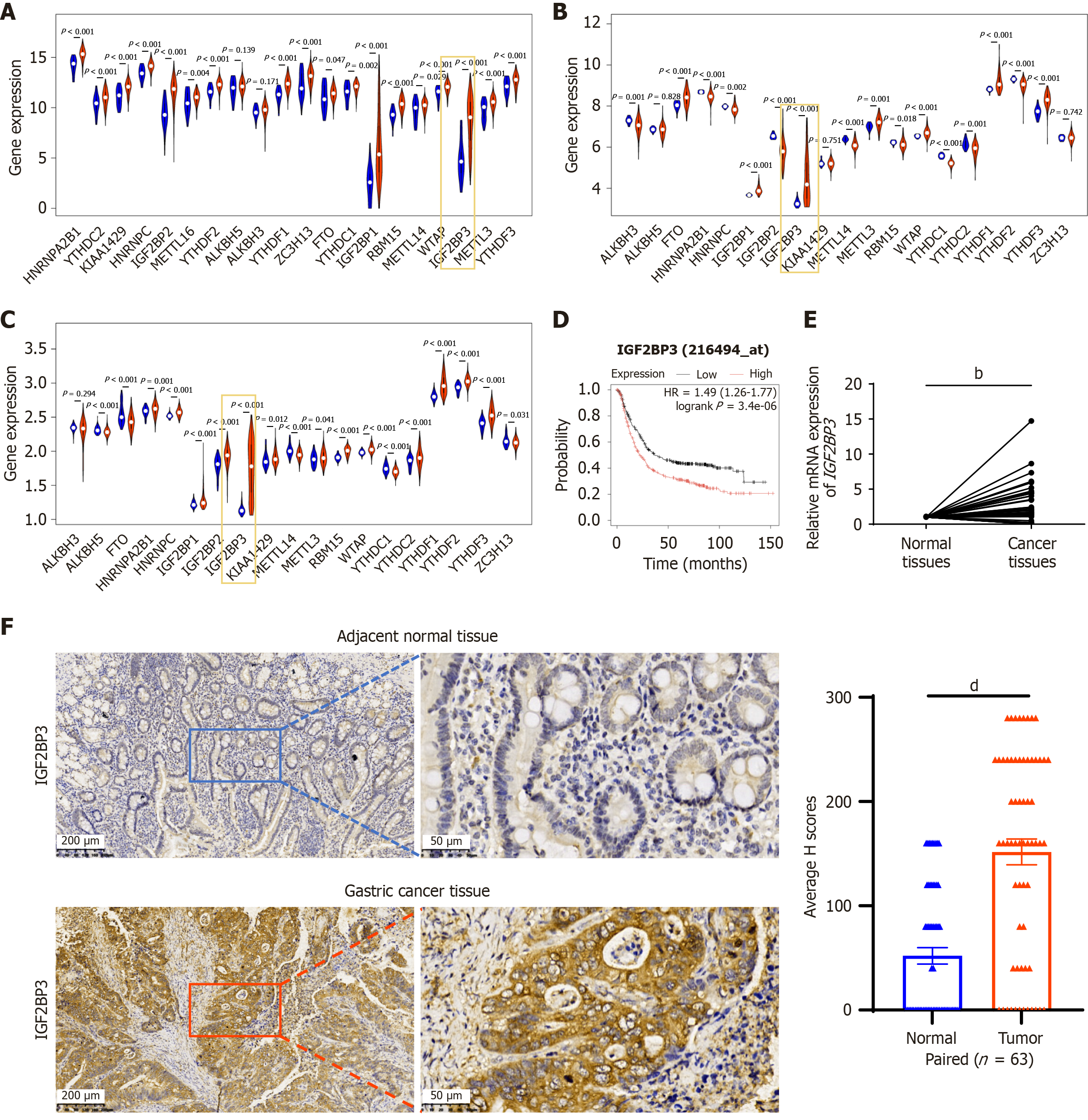
Figure 1 Increased IGF2BP3 expression is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients.
A-C: Expression of N6-methyladenosine-related genes in The Cancer Genome Atlas and the GSE54129 and GSE66229 datasets. Red and blue bars represent expression of IGF2BP3 messenger RNA (mRNA) in gastric cancer (GC) tissue and adjacent normal tissue, respectively; D: Kaplan-Meier analysis of IGF2BP3 expression levels and overall survival in GC patients (the cutoff for high vs low expression groups was defined by the median value of IGF2BP3 expression in the cohort); E: Expression levels of IGF2BP3 mRNA in 50 pairs of GC and adjacent normal tissue samples as detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; F: Representative images showing IGF2BP3 protein expression levels in 63 pairs of GC and adjacent normal tissue samples, as detected by immunohistochemical staining. Scale bars: 200 μm and 50 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01. dP < 0.0001. HR: Hazard ratio; mRNA: Messenger RNA.
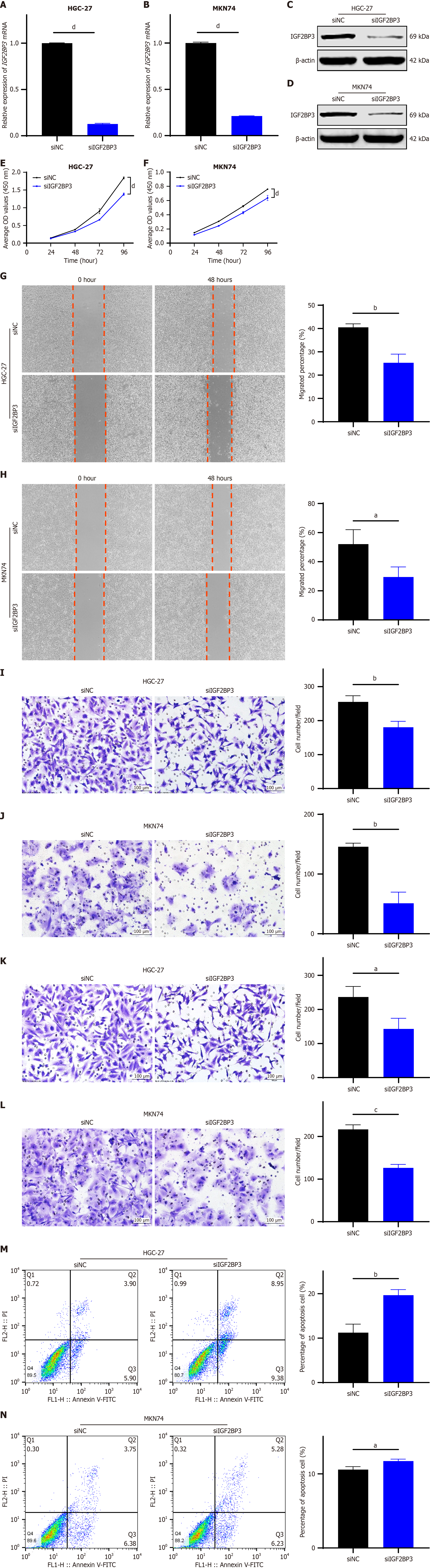
Figure 2 Knockdown of IGF2BP3 in gastric cancer cells suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro.
A and B: Expression of IGF2BP3 messenger RNA in HGC-27 and MKN74 cells as detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; C and D: Expression of IGF2BP3 protein in HGC-27 and MKN74 as detected by Western blot; E and F: Effects of IGF2BP3 knockdown on proliferation of HGC-27 and MKN74 cells as determined by cell counting kit-8 assay; G and H: Effects of IGF2BP3 knockdown on migration of HGC-27 and MKN74 cells as assessed by wound healing assay, scale bar: 200 μm; I and J: Effects of IGF2BP3 knockdown on migration of HGC-27 and MKN74 cells as evaluated using transwell migration assays, scale bar: 100 μm; K and L: Effects of IGF2BP3 knockdown on invasion of HGC-27 and MKN74 cells as assessed using transwell invasion assays, scale bar: 100 μm; M and N: Effects of IGF2BP3 knockdown on apoptosis of HGC-27 and MKN74 cells as determined by flow cytometry. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. mRNA: Messenger RNA; siNC: Small interfering RNA-negative control; siIGF2BP3: Small interfering RNA-IGF2BP3; OD: Optical density.
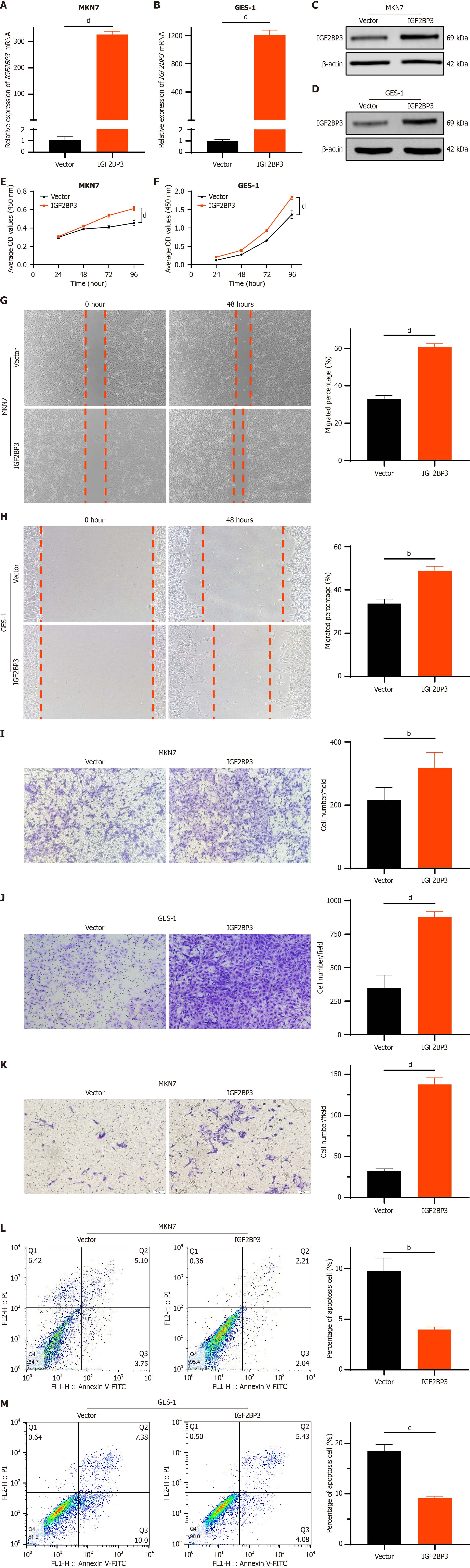
Figure 3 Overexpression of IGF2BP3 in gastric cancer cells and human gastric mucosa cells promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro.
A and B: Expression of IGF2BP3 messenger RNA in MKN7 and GES-1 cells as detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; C and D: Expression of IGF2BP3 protein in MKN7 and GES-1 cells as detected by Western blot; E and F: Effects of IGF2BP3 overexpression on proliferation of MKN7 and GES-1 cells as assessed using cell counting kit-8 assays; G and H: Effects of IGF2BP3 overexpression on migration of MKN7 and GES-1 cells as evaluated through wound healing assays, scale bar: 200 μm; I and J: Effects of IGF2BP3 overexpression on migration of MKN7 and GES-1 cells as determined utilizing transwell migration assays, scale bar: 100 μm; K: Effects of IGF2BP3 overexpression on invasion of MKN7 cells as assessed via transwell invasion assays, scale bar: 100 μm; L and M: Effects of IGF2BP3 overexpression on apoptosis of MKN7 and GES-1 cells as analyzed by flow cytometry. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. mRNA: Messenger RNA; OD: Optical density.
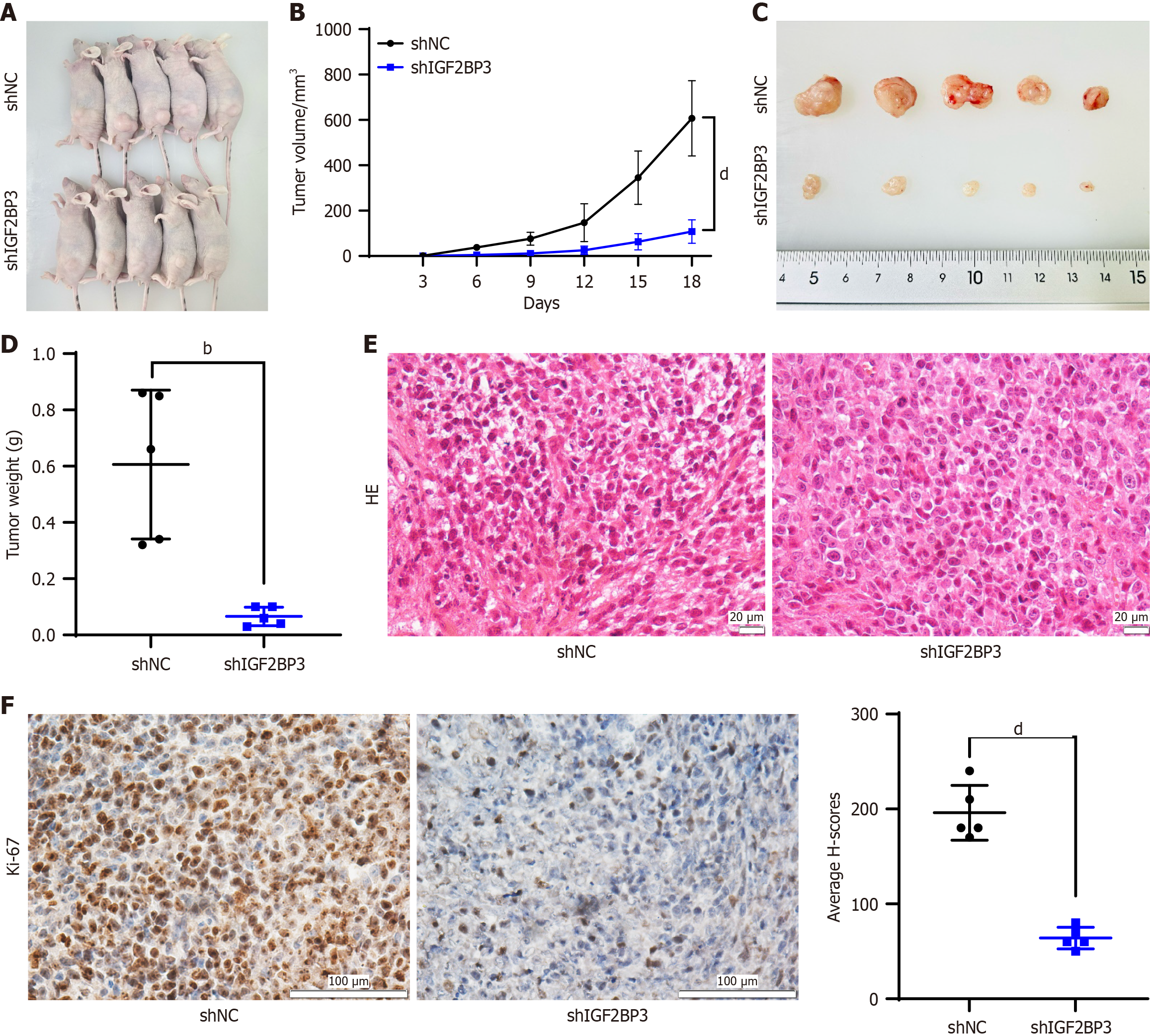
Figure 4 IGF2BP3 regulates the growth of gastric cancer in vivo.
A: Nude mouse tumor-bearing model; B: Tumor growth curve; C and D: Images (C) and weights (D) of xenografted tumors; E: Representative images of tumor tissue sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin, scale bar: 20 μm; F: Representative image of Ki67 immunohistochemical staining in tumor tissue sections. Scale bar: 100 μm. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01. dP < 0.0001. shNC: Short hairpin RNA-negative control; shIGF2BP3: Short hairpin RNA-IGF2BP3; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin.
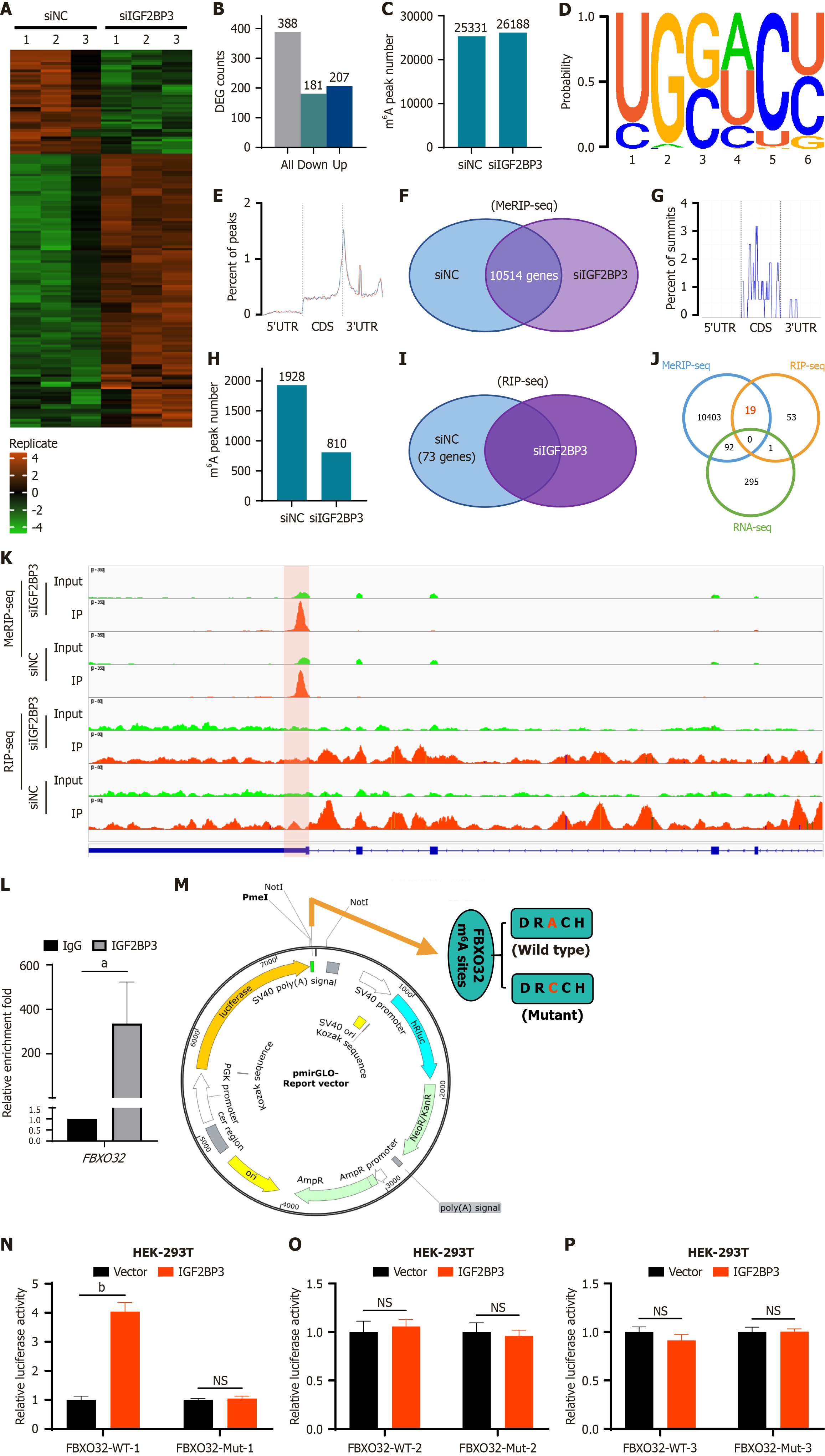
Figure 5 FBXO32 is the N6-methyladenosine modification target of IGF2BP3.
A: Heat map of differentially expressed genes identified by RNA sequencing (RNA-seq); B: Numbers of differentially expressed genes identified by RNA-seq; C: Numbers of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) peaks identified by methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeRIP-seq); D: M6A motifs identified by MeRIP-seq; E: Enriched regions of m6A peaks on messenger RNA (mRNA) identified by MeRIP-seq; F: Common genes between the small interfering RNA-negative control group and the small interfering RNA-IGF2BP3 group according to MeRIP-seq; G: Enriched regions of m6A peaks on mRNA identified by RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (RIP-seq); H: Numbers of m6A peaks identified by RIP-seq; I: Genes identified by RIP-seq; J: Overlap analysis of genes identified by MeRIP-seq, RIP-seq, and RNA-seq; K: Analysis of the m6A site and its abundance on FBXO32 transcripts using Integrative Genomics Viewer software; L: Interaction between IGF2BP3 and FBXO32 as detected by RIP-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; M: Schematic of the wild-type FBXO32 sequence and the m6A site-mutated FBXO32 sequence fused to the luciferase reporter vector; N: Relative luciferase activity of wild-type and mutant (site 1427) FBXO32 upon IGF2BP3 overexpression; O: Relative luciferase activity of wild-type and mutant (site 1399) FBXO32 upon IGF2BP3 overexpression; P: Relative luciferase activity of wild-type and mutant (site 1493) FBXO32 upon IGF2BP3 overexpression. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. siNC: Small interfering RNA-negative control; siIGF2BP3: Small interfering RNA-IGF2BP3; DEG: Differentially expressed gene; m6A: N6-methyladenosine; CDS: Coding sequence; UTR: Untranslated regions; RIP-seq: RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing; MeRIP-seq: Methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing; RNA-seq: RNA sequencing; WT: Wild type; Mut: Mutant; NS: Not significant.
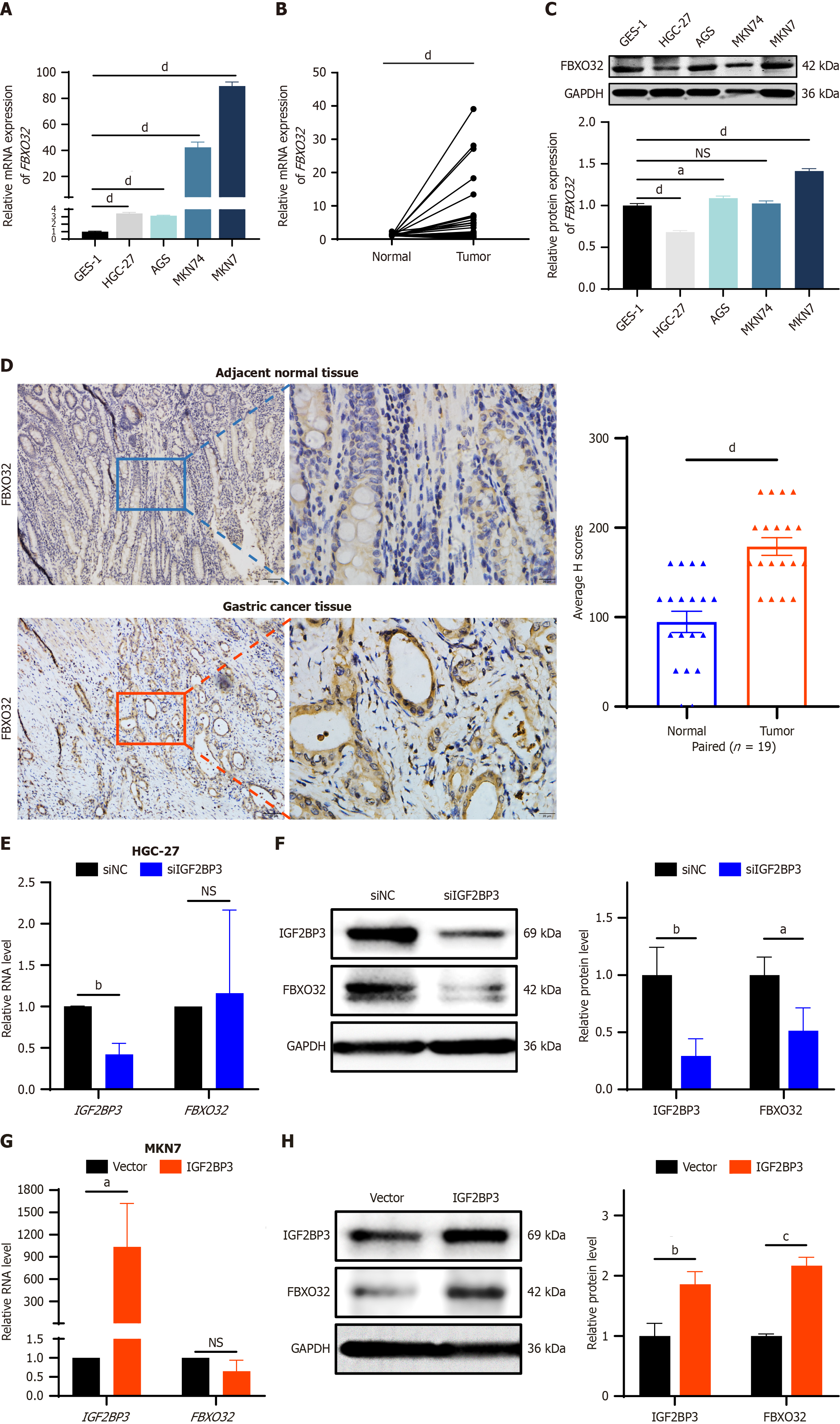
Figure 6 Expression of FBXO32 and its interaction with IGF2BP3 in gastric cancer.
A: Expression of FBXO32 messenger RNA (mRNA) in gastric cancer (GC) cell lines and GES-1 as detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR); B: Expression of FBXO32 mRNA in 34 pairs of GC paired tissues as detected by qRT-PCR; C: Basal expression of FBXO32 protein in cell lines as detected by western blot (WB); D: Expression of FBXO32 protein in 19 pairs of GC paired tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry, scale bar: 50 μm; E: QRT-PCR was used to detect FBXO32 mRNA expression after IGF2BP3 knockdown in HGC-27 cells; F: WB was used to detect FBXO32 protein expression after IGF2BP3 knockdown in HGC-27 cells; G: QRT-PCR was used to detect FBXO32 mRNA expression after IGF2BP3 overexpression in MKN7 cells; H: WB was used to detect FBXO32 protein expression after IGF2BP3 overexpression in MKN7 cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. mRNA: Messenger RNA; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; siNC: Small interfering RNA-negative control; siIGF2BP3: Small interfering RNA-IGF2BP3; NS: Not significant.
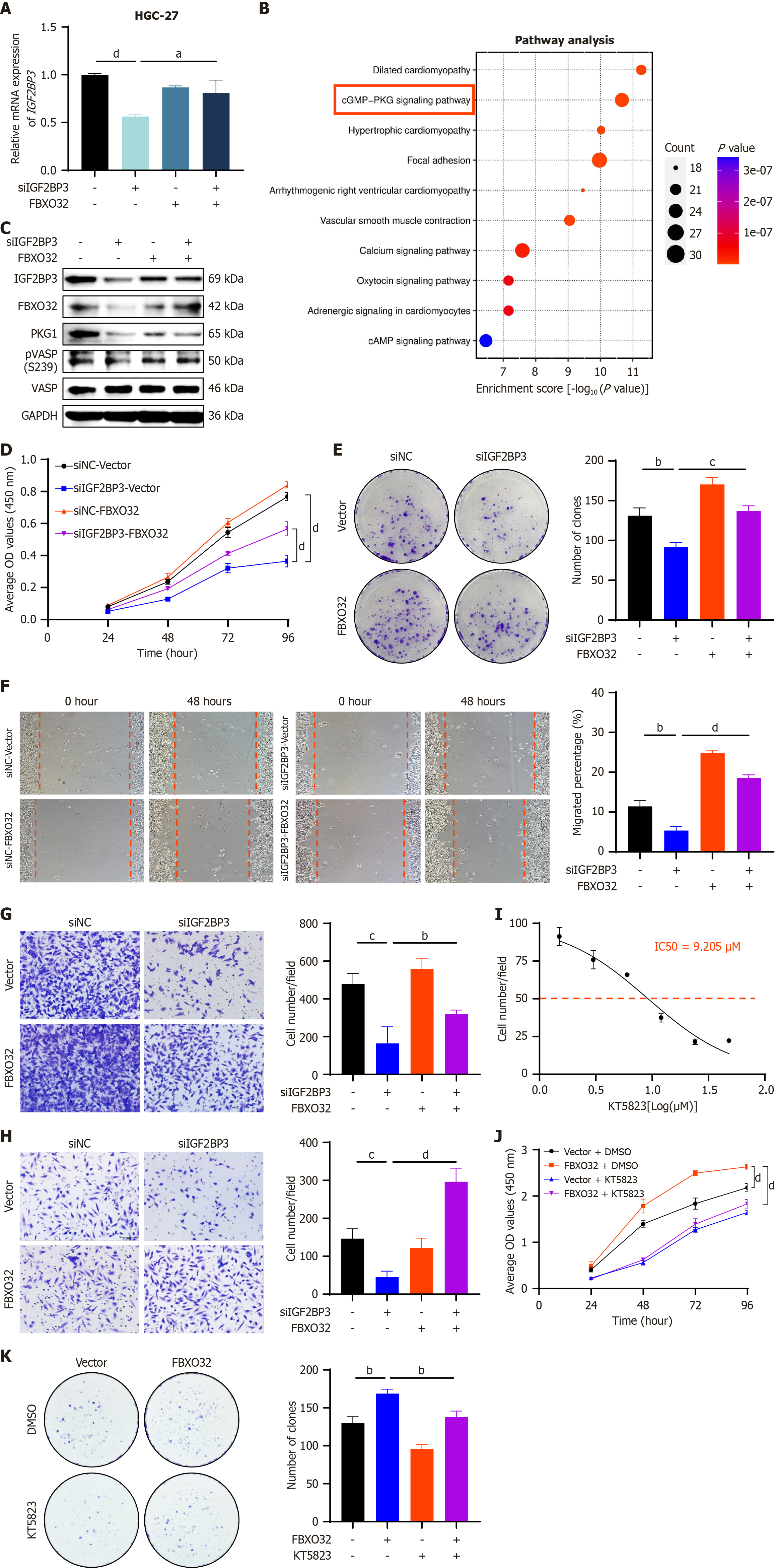
Figure 7 Oncogenic function of IGF2BP3 depends on FBXO32 and cyclic guanosine monophosphate-protein kinase G signaling pathway.
A: Expression of IGF2BP3 messenger RNA in HGC-27 cells as measured by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction after co-transfection of small interfering RNA (siRNA)-negative control (siNC) or siRNA-IGF2BP3 (siIGF2BP3), and pcDNA3.1 (vector) or pcDNA3.1-FBXO32 (FBXO32) plasmids; B: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment results for the top 1000 genes co-expressed with FBXO32 in gastric adenocarcinoma in the Cancer Genome Atlas; C: Expression levels of proteins related to the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-protein kinase G signaling pathway as detected by western blot after instantaneous co-transfection of siNC/siIGF2BP3 and vector/FBXO32 in HGC-27 cells; D-H: Effects of FBXO32 on IGF2BP3 in HGC-27 cells as detected by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay (D), colony formation assay (E), and wound healing assay (F) (scale bar: 200 μm), transwell migration assay (G), and transwell invasion assay (H) (scale bar: 100 μm); I: Half-maximal inhibitory concentration of KT5823 as determined in HGC-27 cells using CCK-8 assay; J: Measurement of HGC-27 cell proliferation by CCK-8 assay following different treatments; K: Measurement of HGC-27 cell proliferation by colony formation assay following different treatments. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. mRNA: Messenger RNA; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; siNC: Small interfering RNA-negative control; siIGF2BP3: Small interfering RNA-IGF2BP3; cGMP: Cyclic guanosine monophosphate; PKG: Protein kinase G; p-VASP: Phospho-VASP; OD: Optical density; IC50: The half maximal inhibitory concentration.
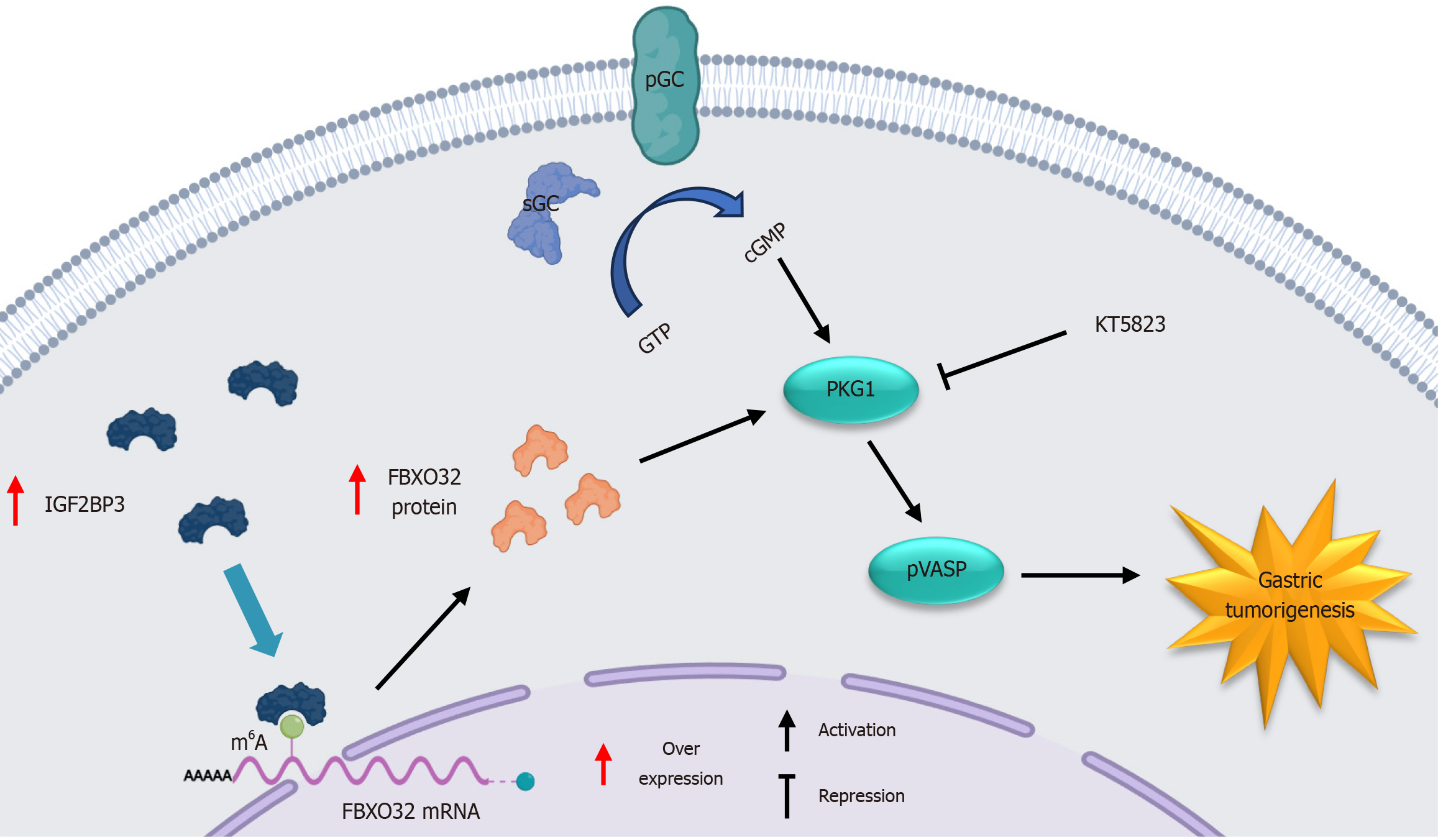
Figure 8 Schematic illustration of the molecular mechanism of IGF2BP3 in gastric cancer.
pGC: Particulate guanylyl cyclase; sGC: Soluble guanylyl cyclase; GTP: Guanosine triphosphate; cGMP: Cyclic guanosine monophosphate; PKG: Protein kinase G; p-VASP: Phospho-VASP; mRNA: Messenger RNA; m6A: N6-methyladenosine.
- Citation: Si Y, Tian B, Zhang R, Xuan MD, Liu KY, Jiao J, Han SS, Li HF, Hu YH, Zhao HY, He WJ, Wang J, Liu T, Yu WF. IGF2BP3 binds to FBXO32 to activate the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-protein kinase G pathway, promoting gastric cancer progression. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(46): 111631
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i46/111631.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i46.111631