Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2025; 31(43): 111609
Published online Nov 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i43.111609
Published online Nov 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i43.111609
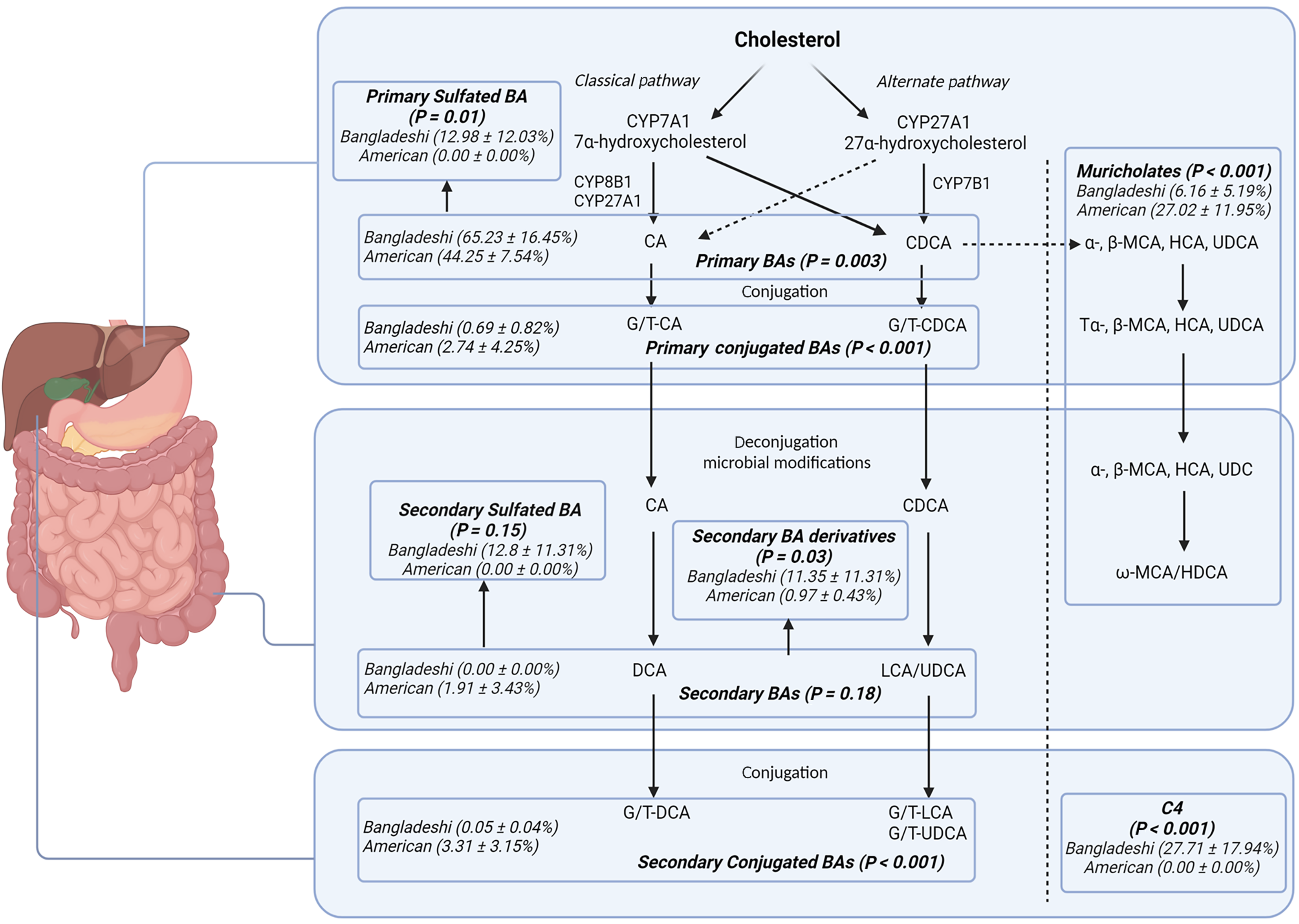
Figure 1 Percent distributions comparing the younger Bangladeshi infants' serum bile acids and C4 Levels to the American children are displayed with mean and standard deviation.
Secondary bile acid derivatives include 7-Keto DCA, 7-Keto LCA, 3-Keto LCA, isoDCA, isoLCA, and allo isoLCA. Bangladeshi infants demonstrate a deficiency in primary bile acid conjugation as compared to American children with compensatory increase in hydrophilic primary sulfated bile acids. C4 is also increased.
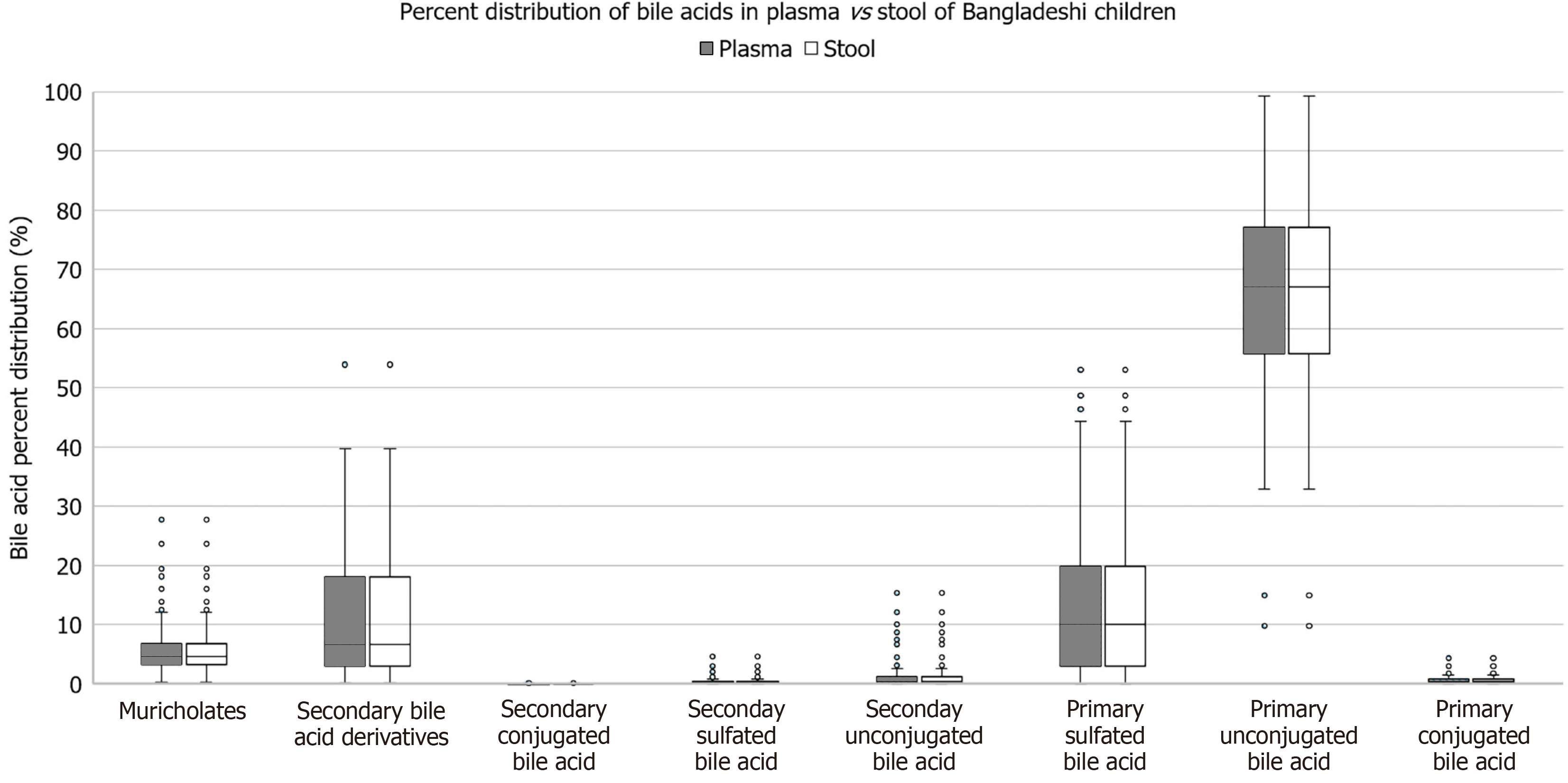
Figure 2 Stool and plasma bile acid pools were compared in Bangladeshi 6-9-month-old.
Plasma distribution is shown as shaded box-and-whisker plots while stool distribution is illustrated with clear box-and-whisker plots. The central line in each box represents the median, while the box spans the interquartile range (IQR). Whiskers extend to 1.5 times the IQR, with individual points representing outliers. There were no significant differences between the groups in regard to bile acid percent distributions.
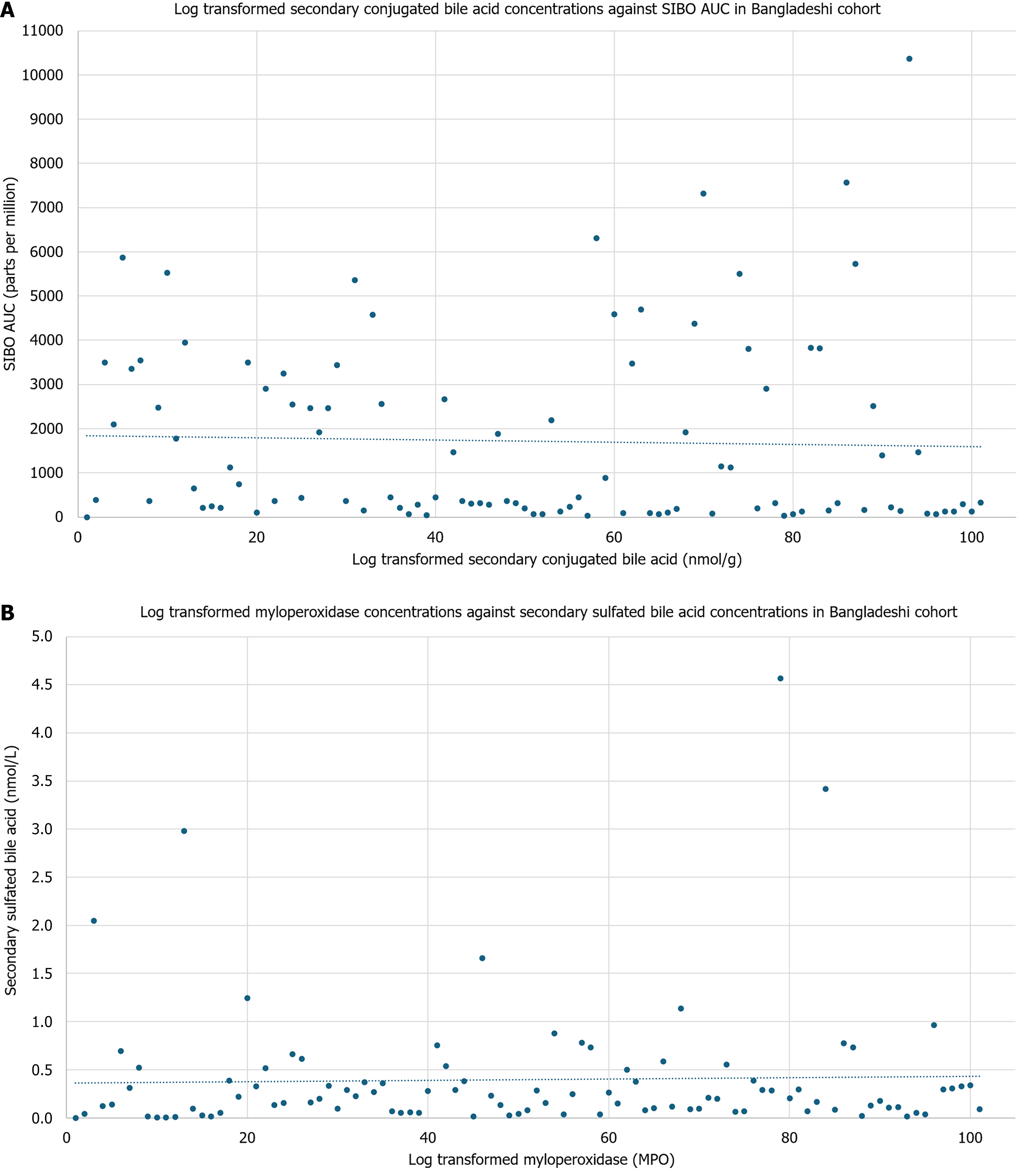
Figure 3 Compared in the Bangladeshi infants.
A: Log transformed secondary conjugated bile acid concentrations were plotted against small intestine bacterial overgrowth area under the curve in the Bangladeshi infants. Small intestine bacterial overgrowth area under the curve is associated with a decrease in secondary conjugated bile acids (β = -1096.68, P = 0.05); B: Log transformed myeloperoxidase were regressed on secondary sulfated bile acid concentrations in the Bangladeshi infants. As myeloperoxidase increases, there is a decrease in the concentration of secondary sulfated bile acids (β = -0.40, P = 0.04). AUC: Area under the curve; SIBO: Small intestine bacterial overgrowth; MPO: Myeloperoxidase.
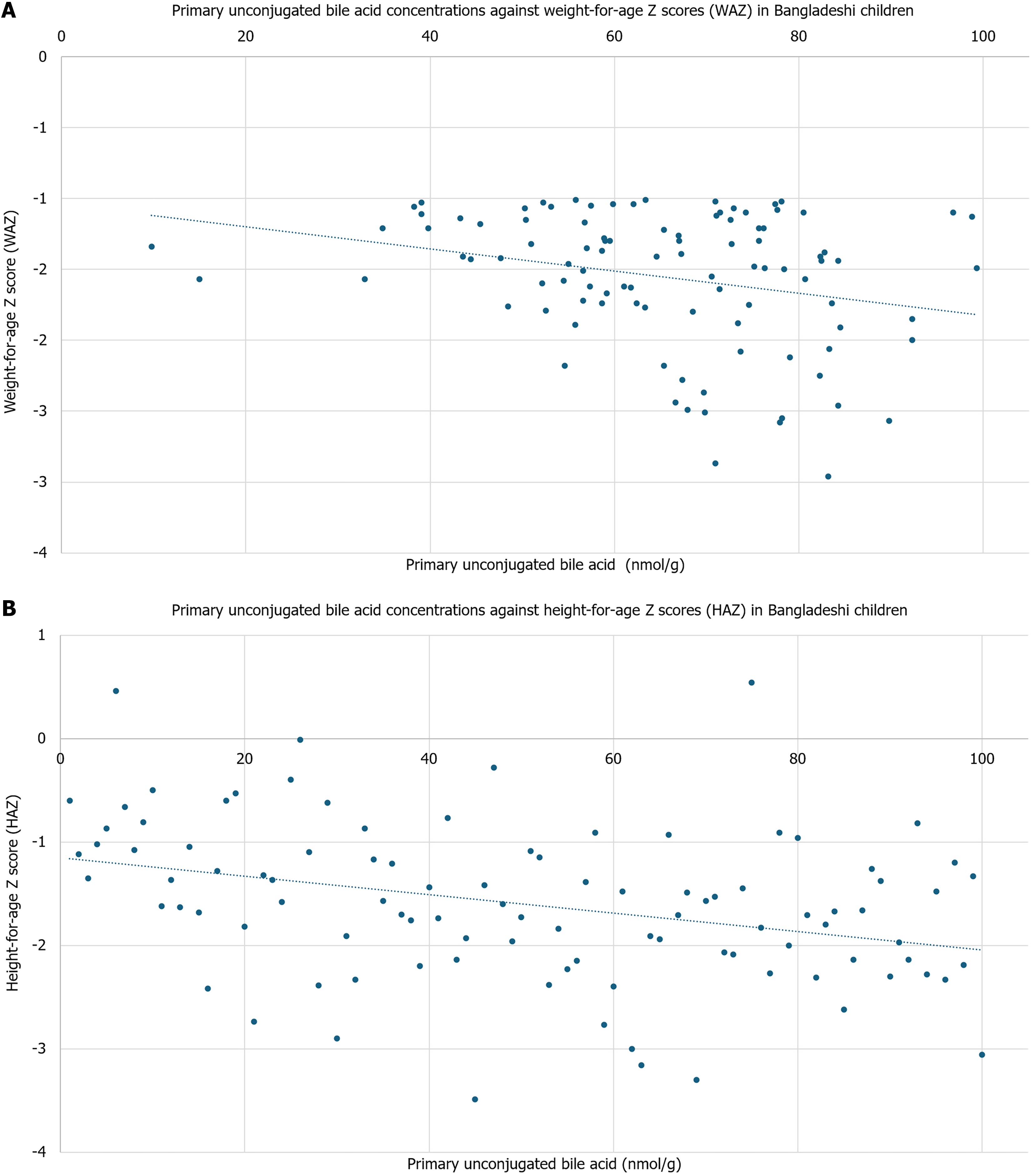
Figure 4 Compared in the Bangladeshi infants.
A: Primary unconjugated bile acid concentrations are plotted against weight-for-age Z scores in the Bangladeshi infants. There is a significant correlation with drop in weight-for-age Z score as primary unconjugated bile acid concentrations increase (β = -0.01, P = 0.01); B: Primary unconjugated bile acid concentrations are plotted against height-for-age Z scores in the Bangladeshi infants. There is a significant correlation with drop in height-for-age Z score as primary unconjugated bile acid concentrations increase (β = -0.01, P = 0.03). HAZ: Height-for-age Z scores; WAZ: Weight-for-height Z scores.
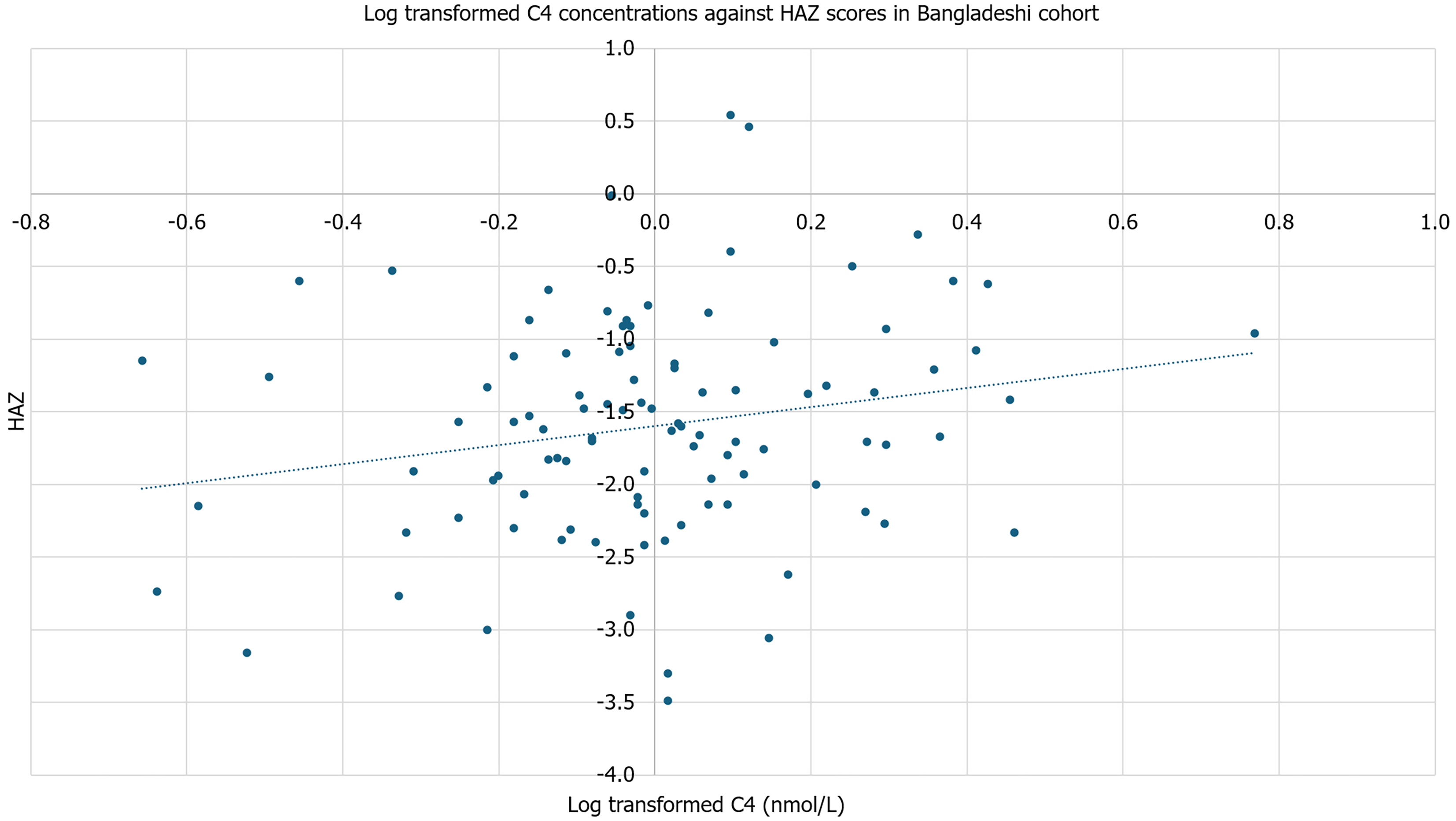
Figure 5 Log transformed C4 concentrations were regressed on height-for-age Z scores in the Bangladeshi infants.
Regression shows that there is an increase in height-for-age Z scores with increased C4 Levels (β = 0.65, P = 0.04).
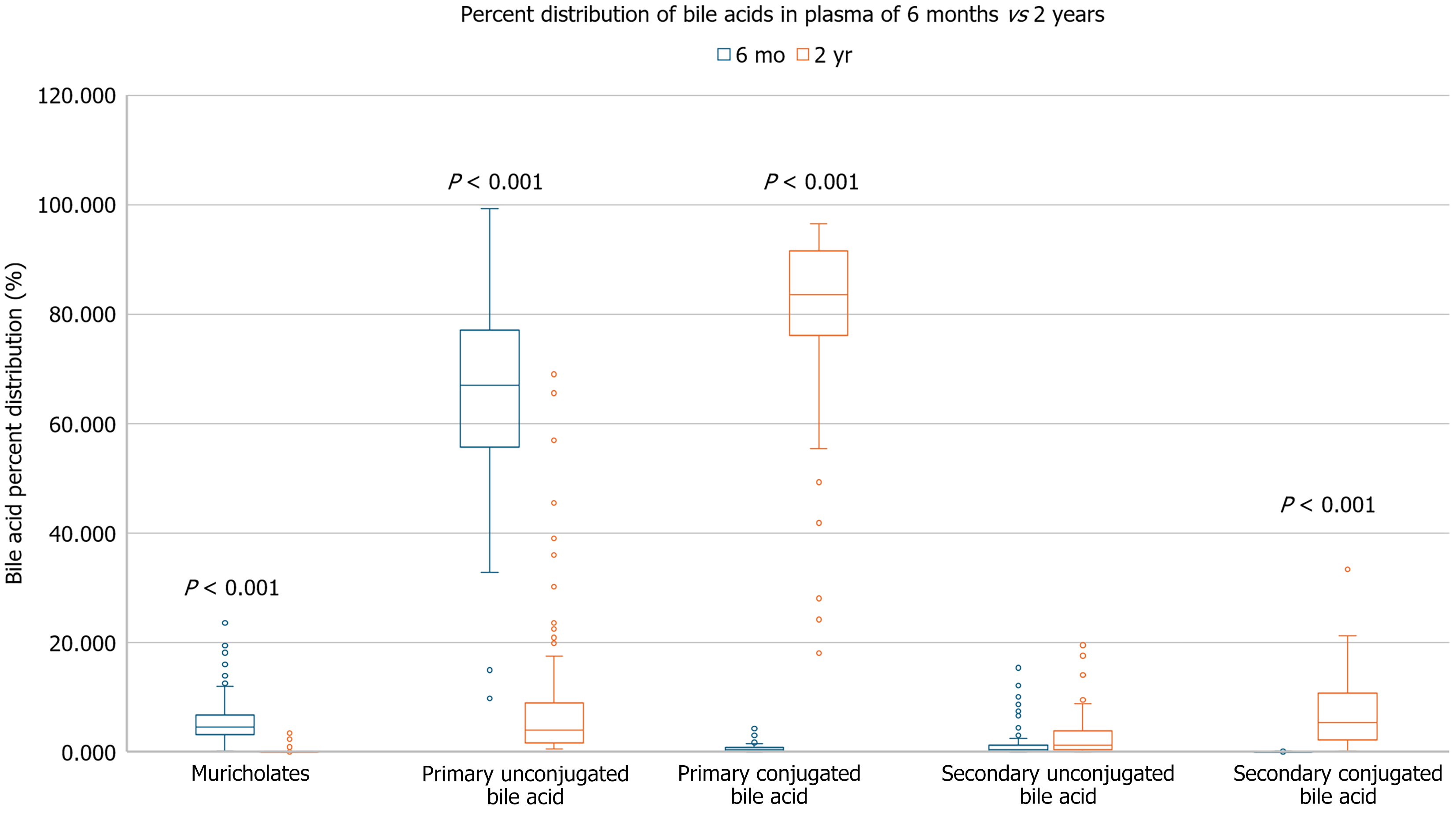
Figure 6 Box-and-whiskers plot showing percent distribution of bile acids in plasma between the Bangladeshi infants (aged 6-9 months) and the Bangladeshi children (aged 2-years-old).
The younger Bangladeshi infants' distributions are shown in blue and the older Bangladeshi children are shown in orange. If P value was not denoted, there was no significant difference between the two groups. The central line in each box represents the median, while the box spans the interquartile range (IQR). Whiskers extend to 1.5 times the IQR, with individual points representing outliers. The younger infants showed higher levels of unconjugated bile acids compared to their older counterparts.
- Citation: Hasan F, Hylemon PB, Haque R, Petri WA, Faruque ASG, Kirkpatrick BD, Alam M, Ferdous T, Shama T, Moreau B, Ramakrishnan G, Zhou H, Chesney A, Medrano Garcia F, Smirnova E, Prem P, Huang Y, Bojja R, Thapaliya A, Donowitz JR. Bile acid dysmetabolism in Bangladeshi infants associated with poor linear growth, enteric inflammation, and small intestine bacterial overgrowth. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(43): 111609
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i43/111609.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i43.111609