©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2025; 31(42): 110717
Published online Nov 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i42.110717
Published online Nov 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i42.110717
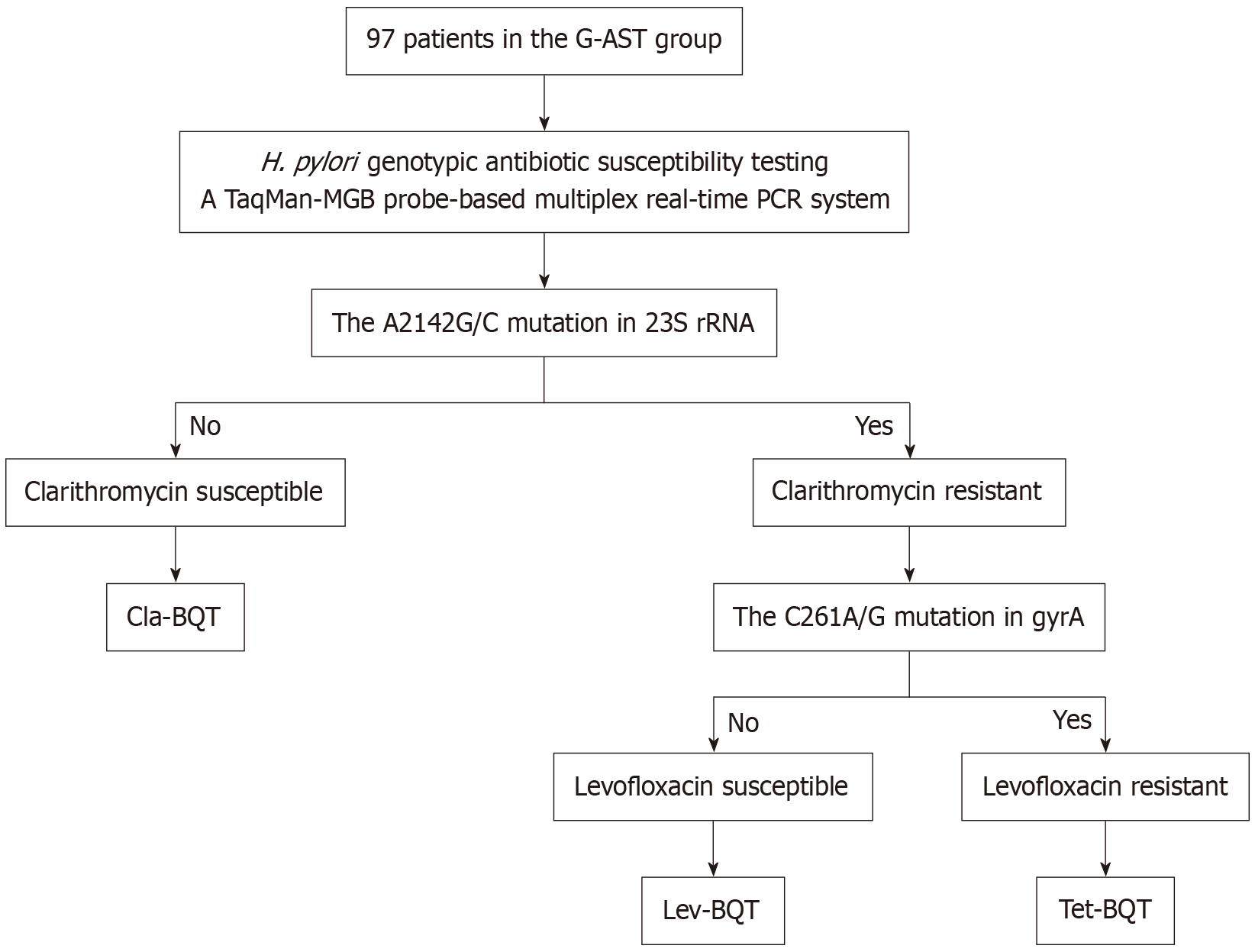
Figure 1 Flowchart of therapeutic decision-making in the genotypic antibiotic susceptibility testing group based on resistance mutations detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Treatment was tailored as clarithromycin-containing bismuth quadruple therapy (BQT), levofloxacin-containing BQT, or tetracycline-containing BQT according to clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; Cla-BQT: Clarithromycin-containing bismuth quadruple therapy; Lev-BQT: Levofloxacin-containing bismuth quadruple therapy; Tet-BQT: Tetracycline-containing bismuth quadruple therapy.
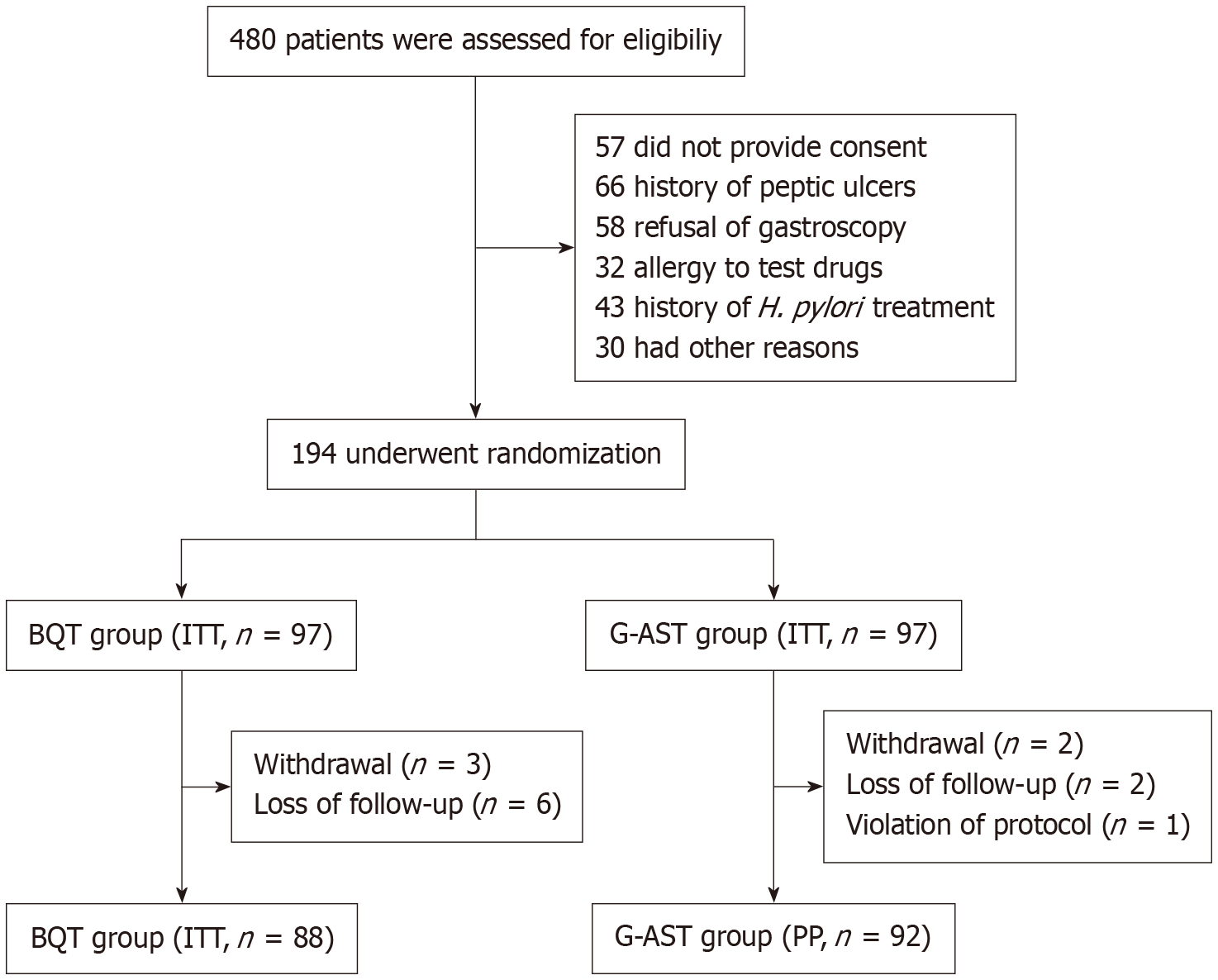
Figure 2 Flowchart of the recruitment of study subjects.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; ITT: Intention-to-treat analysis; PP: Per-protocol analysis; G-AST: Genotypic antibiotic susceptibility testing; BQT: Bismuth quadruple therapy.
- Citation: Xu Y, Hao JW, Min CC, Yang L, Ma CP, Shi C, Mao T, Tian ZB, Wang T, Yu YN. Precision therapy guided by genotypic antibiotic resistance for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A prospective, randomized controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(42): 110717
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i42/110717.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i42.110717