©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2025; 31(41): 111745
Published online Nov 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i41.111745
Published online Nov 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i41.111745
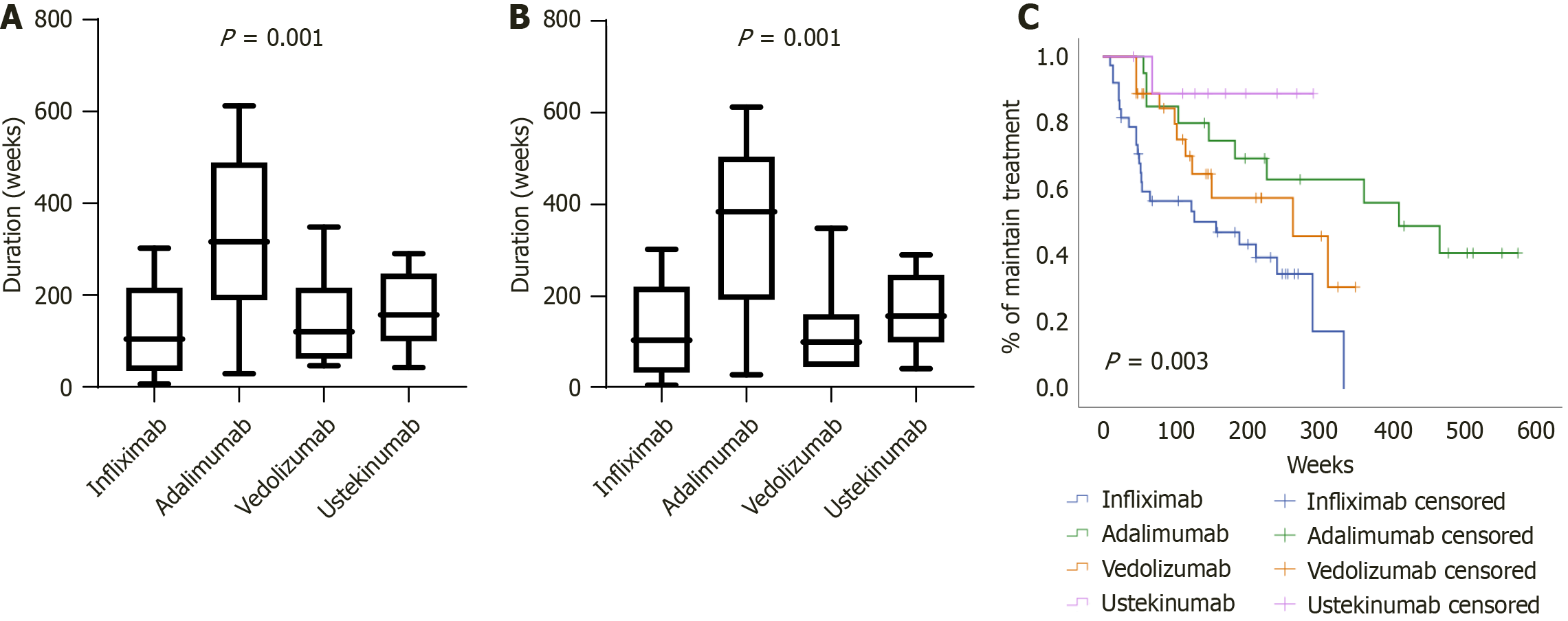
Figure 1 Drug persistence of biologic agents.
A: Overall inflammatory bowel disease cohort; B: Crohn’s disease cohort. Both determined according to a Kruskal-Wallis test; C: Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank test comparing drug persistence among biologic agents in the inflammatory bowel disease cohort.
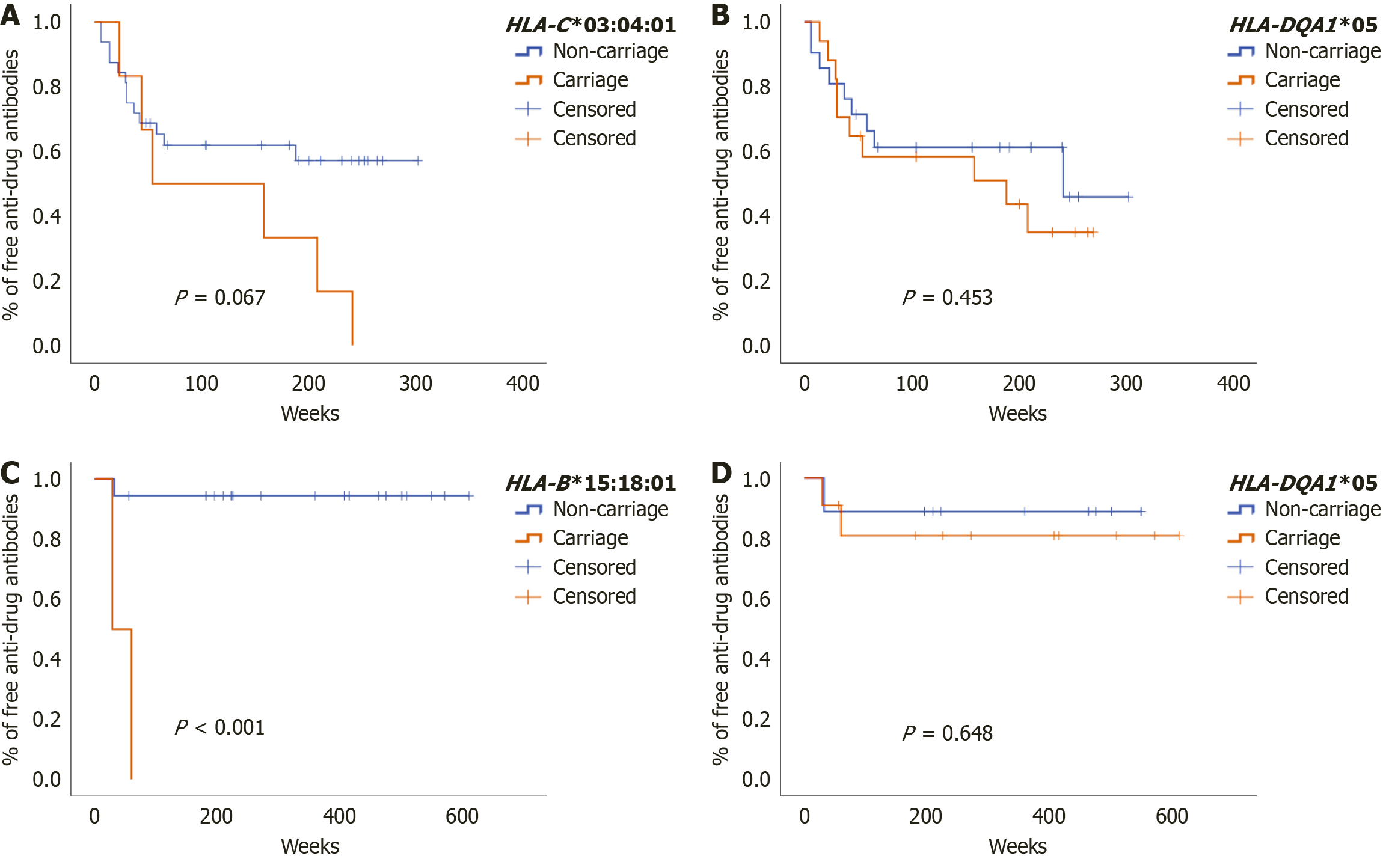
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier estimation of the rate of anti-drug antibodies development.
A: Infliximab-treated group, stratified according to human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-C*03:04:01 carrier status; B: Infliximab-treated group, stratified according to HLA-DQA1*05 carrier status; C: Adalimumab-treated group, stratified according to HLA-B*15:18:01 carrier status; D: Adalimumab-treated group, stratified according to HLA-DQA1*05 carrier status. HLA: Human leukocyte antigen.
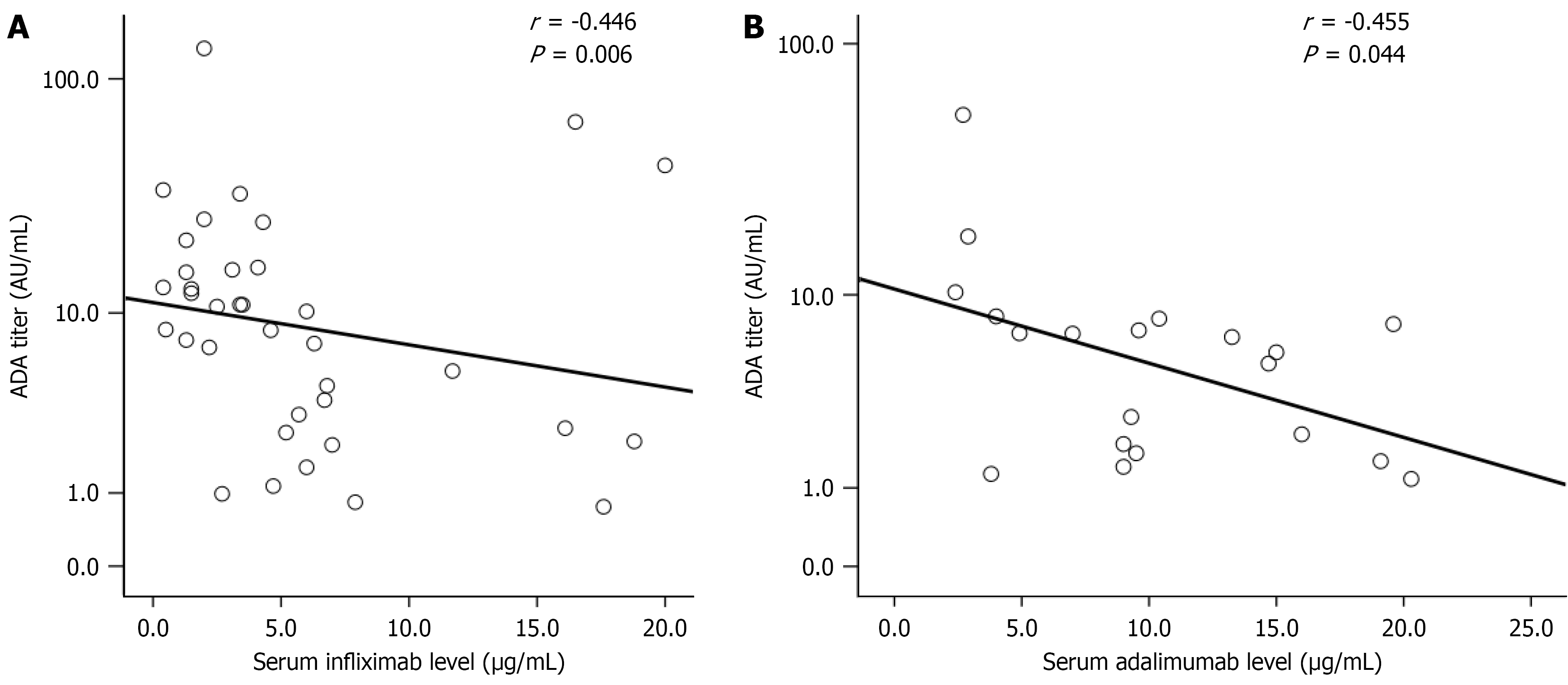
Figure 3 Spearman’s correlation between serum anti-drug antibodies titers and serum drug trough levels.
A: Infliximab-treated group; B: Adalimumab-treated group. ADA: Anti-drug antibody.
- Citation: Weng MT, Yao CY, Lin WC, Lai SK, Tung CC, Wang CY, Wong JM, Chen PL, Wei SC. HLA-C*03:04:01 and HLA-B*15:18:01 but not HLA-DQA1*05 associated with anti- tumor necrosis factor antibody formation in Taiwanese inflammatory bowel disease patients. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(41): 111745
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i41/111745.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i41.111745