©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2025; 31(40): 111951
Published online Oct 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i40.111951
Published online Oct 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i40.111951
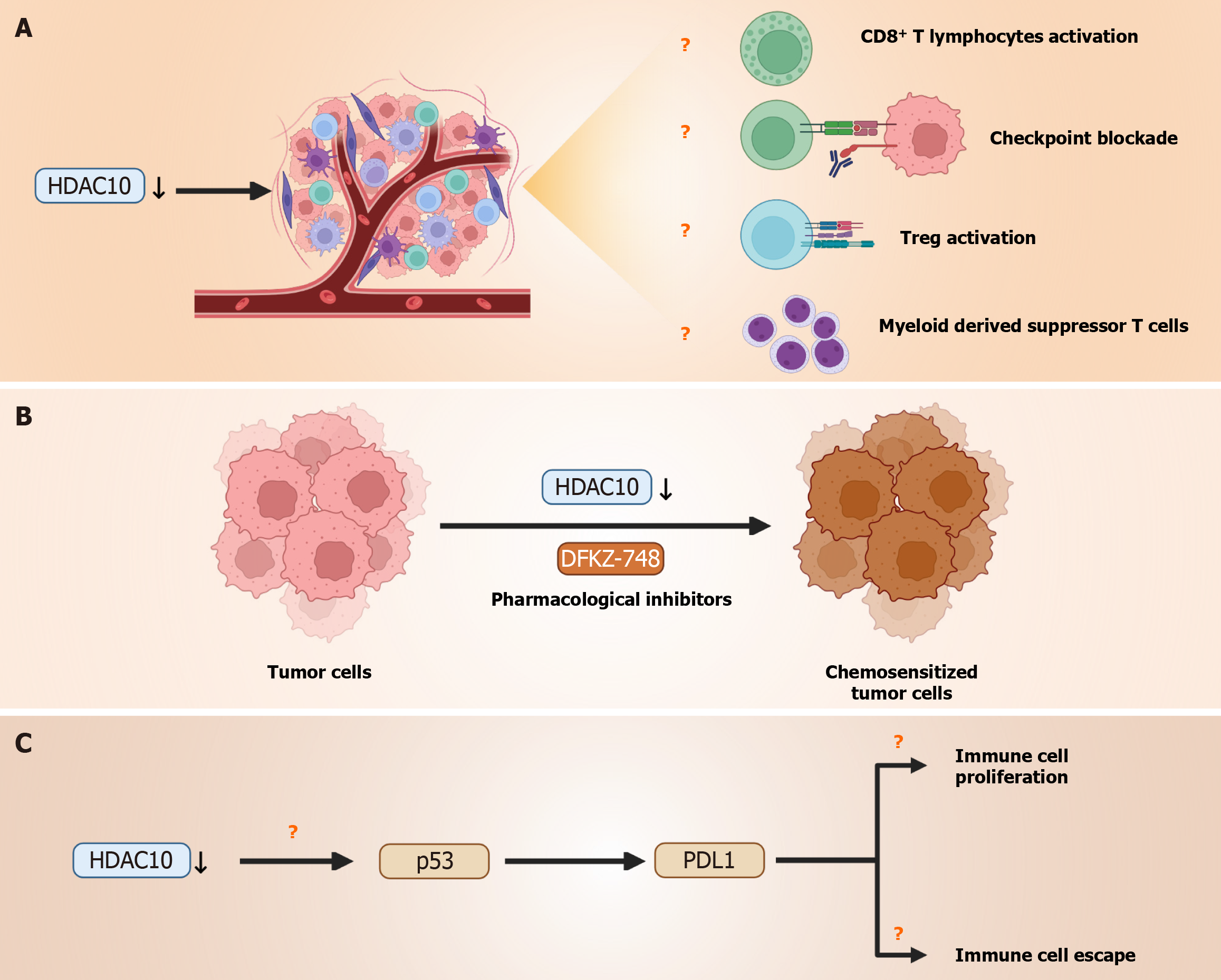
Figure 1 Schematic overview of histone deacetylase 10’s multifaceted role in colorectal cancer progression and therapy response.
A: Downregulation of histone deacetylase 10 (HDAC10) is proposed to reshape the tumor microenvironment, but its precise effects on CD8+ T cell activation, regulatory T cells, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells remain to be elucidated; B: Pharmacological inhibition of HDAC10 (e.g., DKFZ-748) leads to chemosensitization of colorectal cancer cells, yet the clinical benefit of this approach vs pan-HDAC inhibition is undetermined; C: HDAC10 suppression is associated with increased p53 and reduced programmed death ligand 1 expression; however, the mechanistic pathway remains unclear, especially in the context of immune cell proliferation and immune evasion. Orange question marks indicate hypothetical mechanisms that remain to experimentally validate. HDAC10: Histone deacetylase 10; PDL1: Programmed death ligand 1.
- Citation: Afzal A, Muanprasat C, Khawar MB. Prognostic role of histone deacetylase 10 in colorectal cancer: Strengths and gaps. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(40): 111951
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i40/111951.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i40.111951