©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2025; 31(39): 111495
Published online Oct 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i39.111495
Published online Oct 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i39.111495
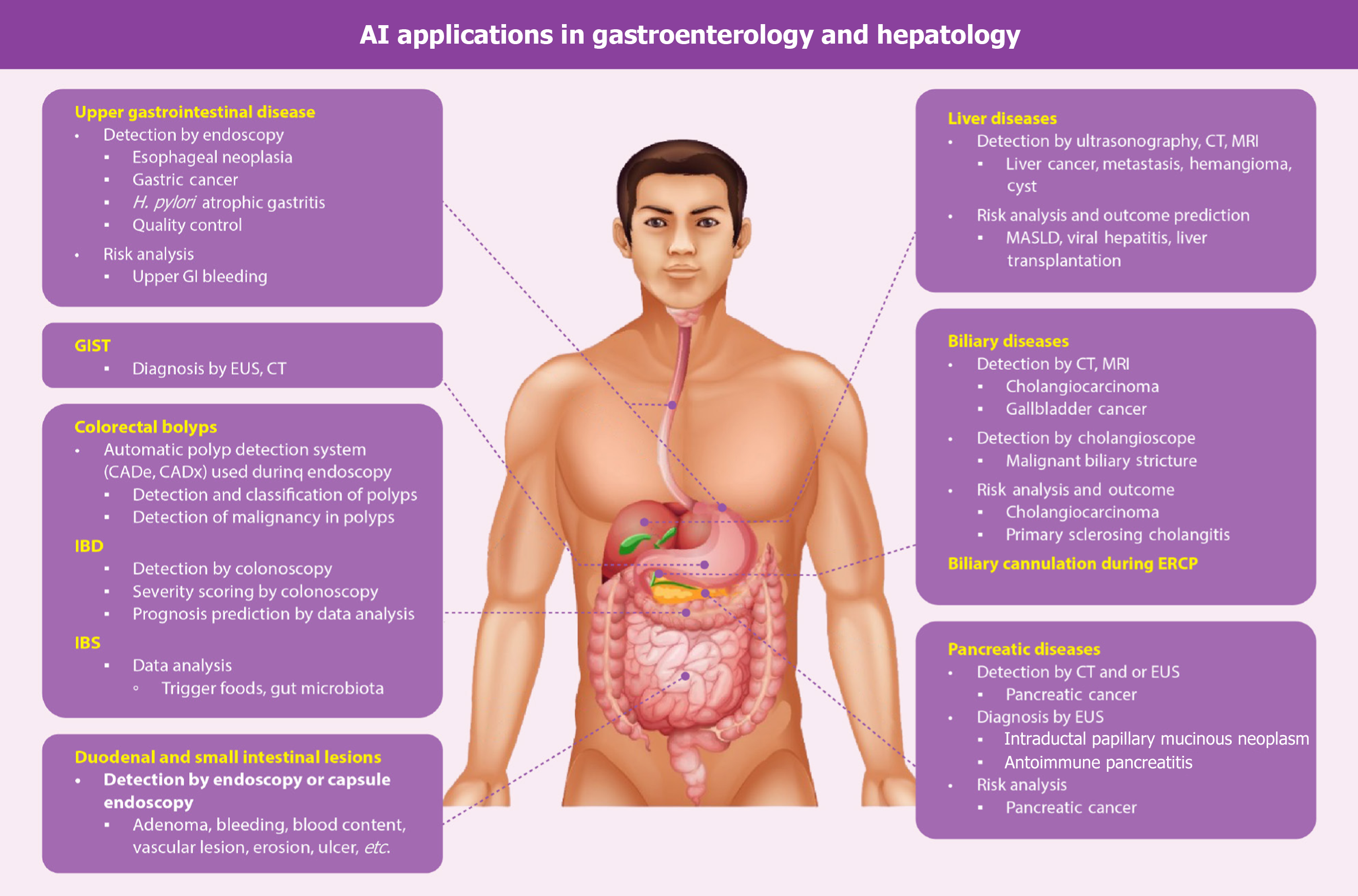
Figure 1 Artificial intelligence applications in gastroenterology and hepatology.
AI: Artificial intelligence; GIST: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor; EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound; CADe: Computer-aided detection; CADx: Computer-aided diagnosis; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; GI: Gastrointestinal; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
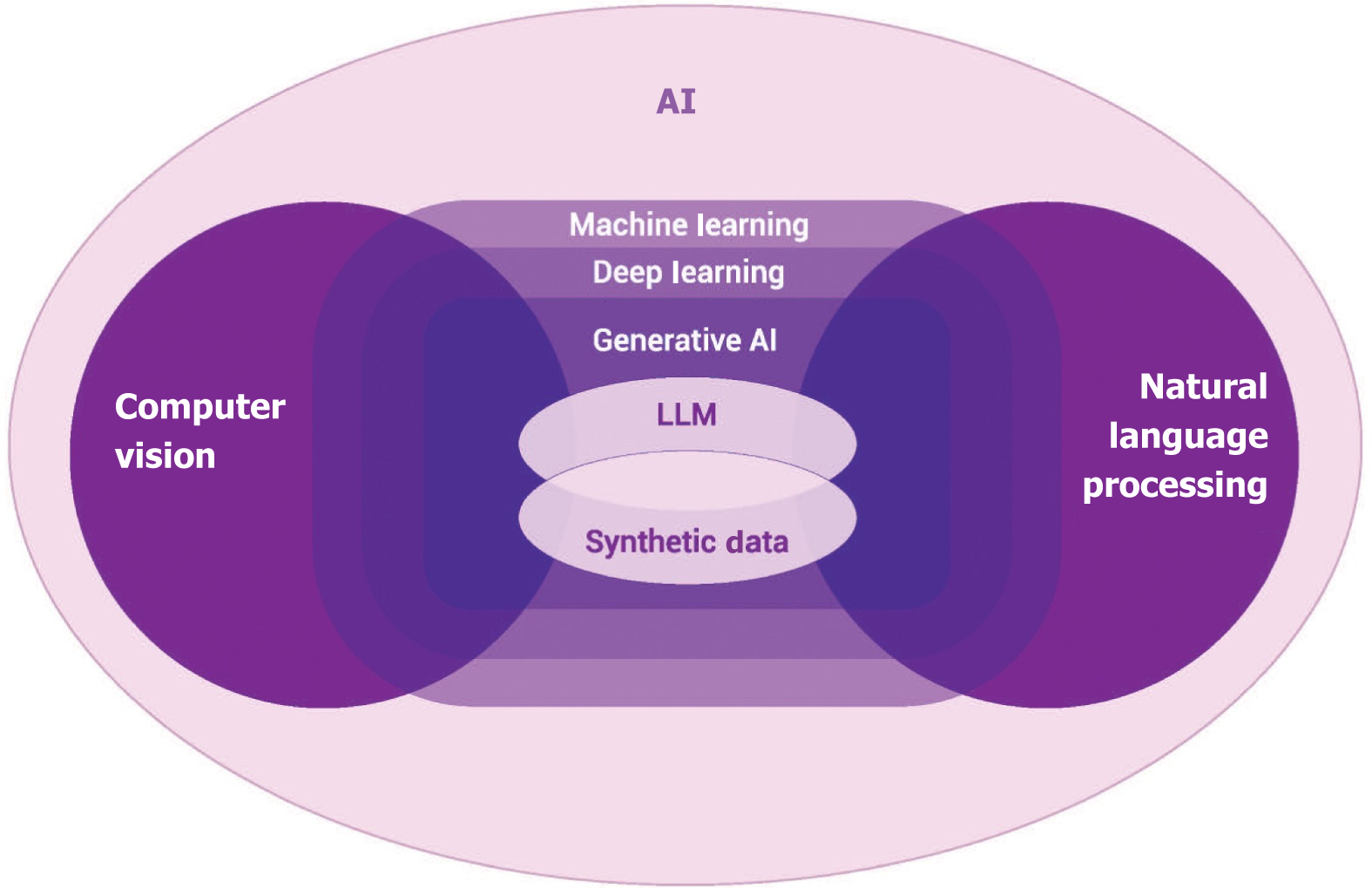
Figure 2 Artificial intelligence landscape.
Machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, computer vision, generative artificial intelligence, large language model and synthetic data are types of artificial intelligence. AI: Artificial intelligence; LLM: Large language model.
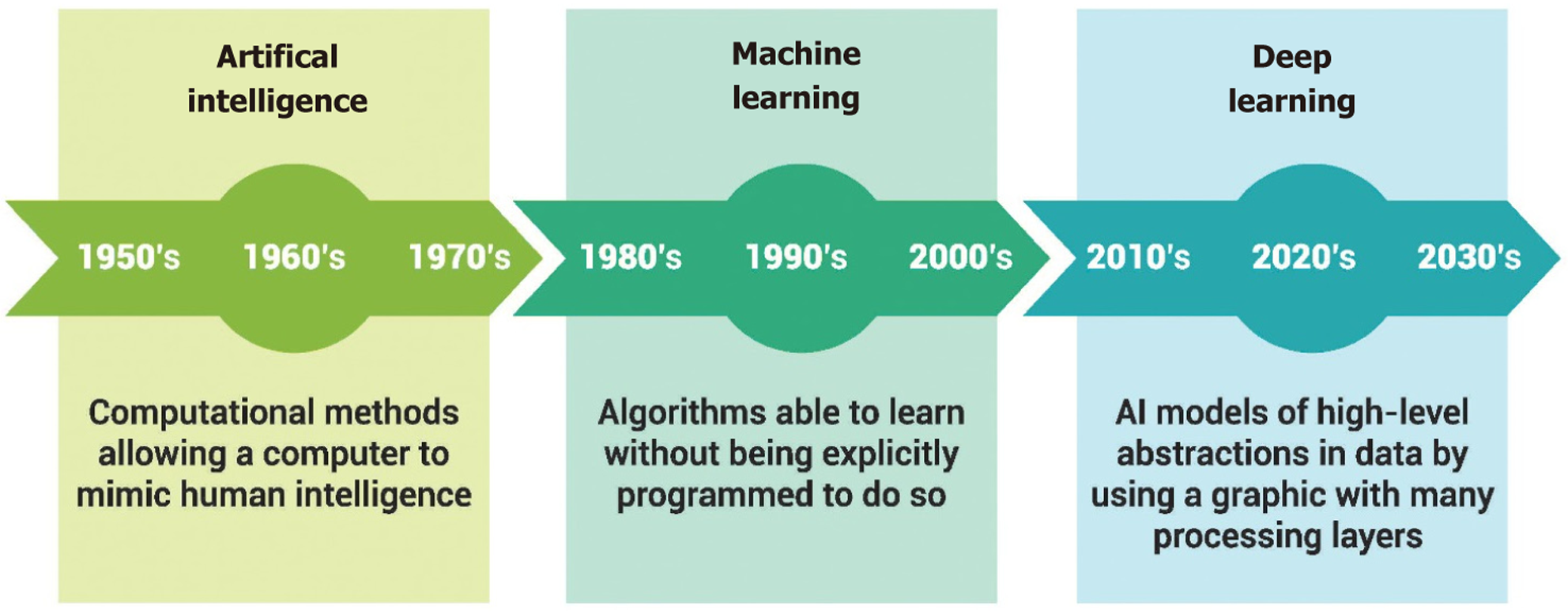
Figure 3 History of artificial intelligence.
AI: Artificial intelligence.
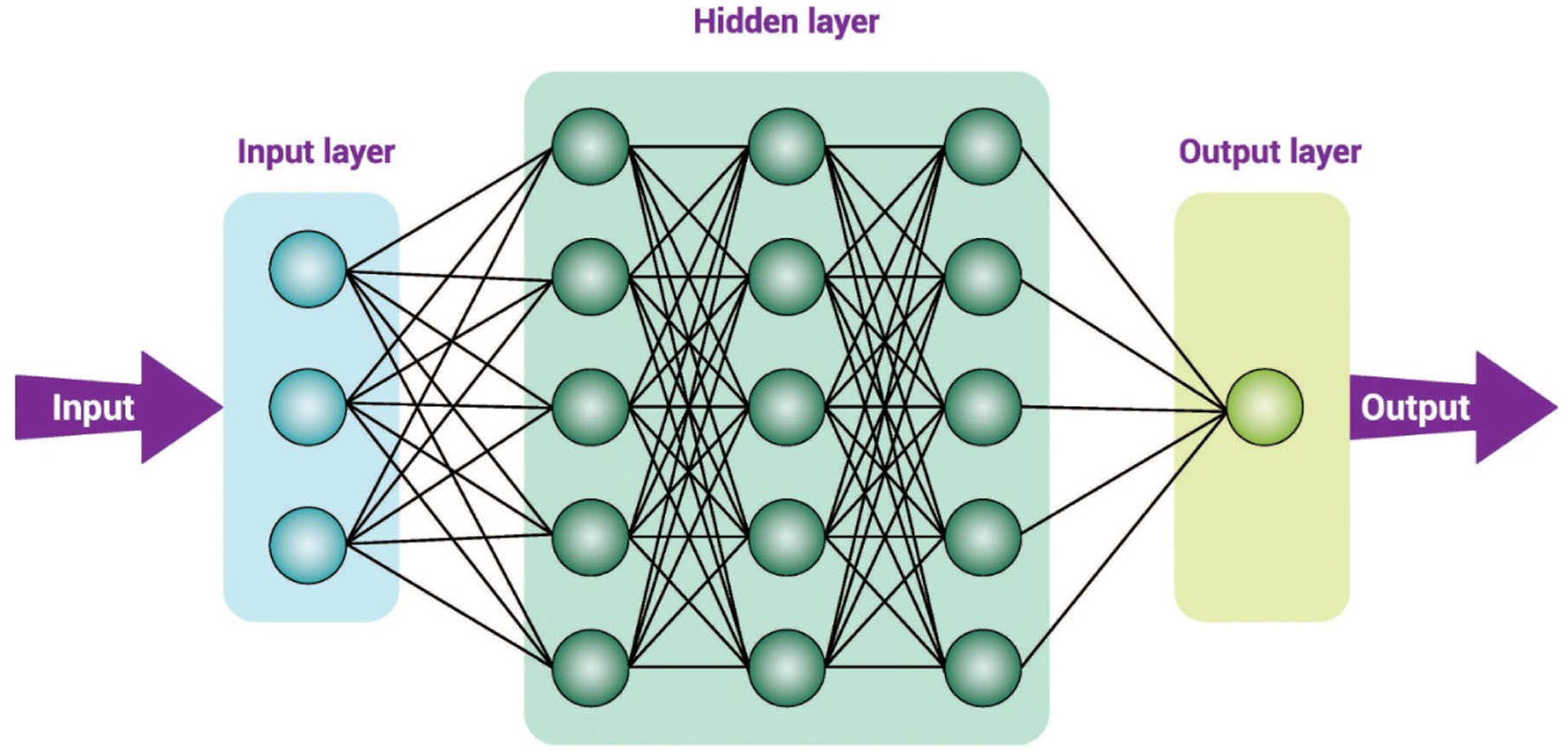
Figure 4 Layers of deep learning.
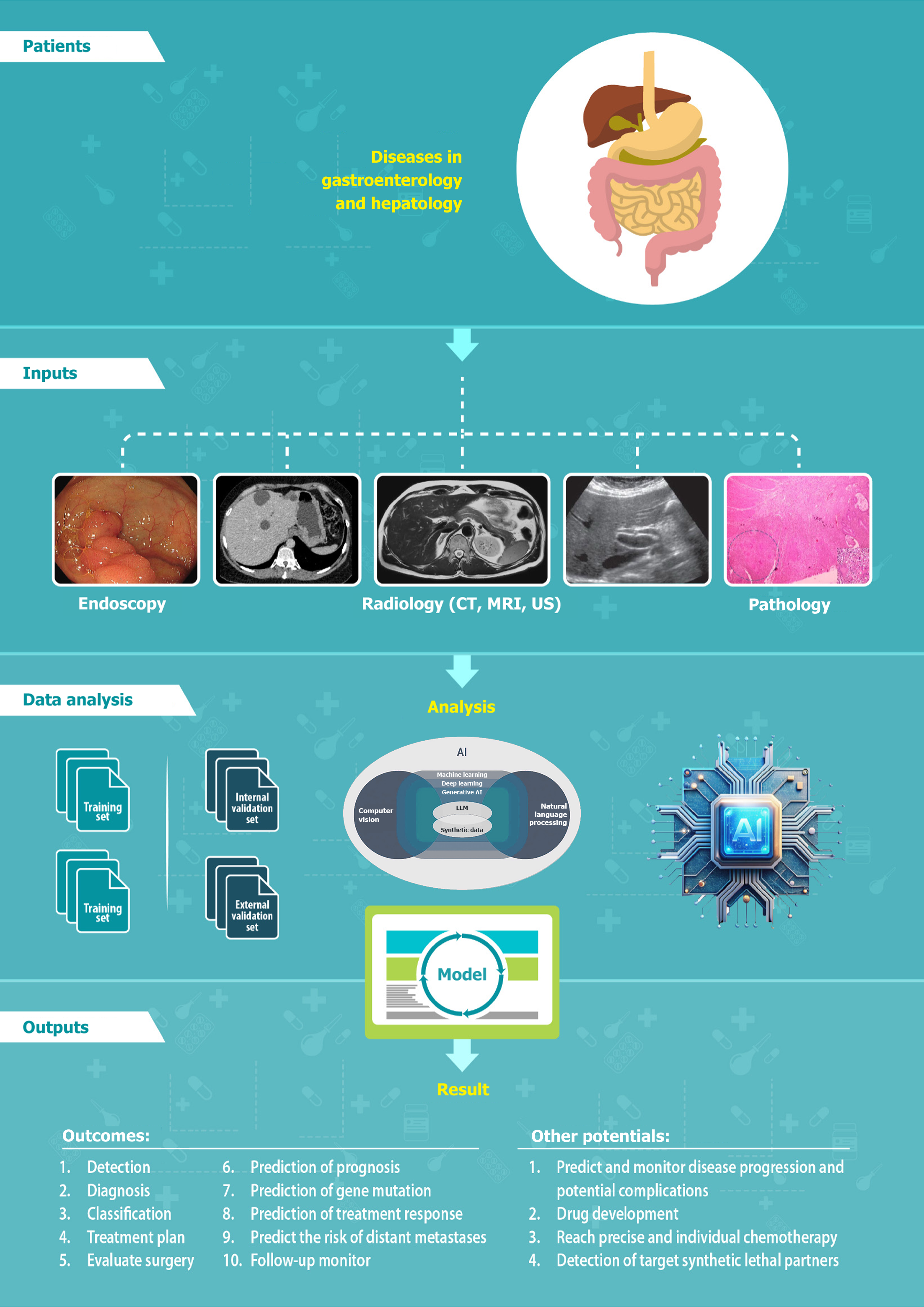
Figure 5 Flowchart of artificial intelligence after data collection.
Artificial intelligence-assisted endoscopy, radiology, and pathology applications for medical image analysis in the fields of gastroenterology and hepatology, including detecting and evaluating lesions, facilitating treatment, and predicting treatment response and prognosis using several AI models. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; US: Ultrasonography; AI: Artificial intelligence; LLM: Large language model.
- Citation: Shrestha UK. Emerging role of artificial intelligence in gastroenterology and hepatology. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(39): 111495
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i39/111495.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i39.111495