©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2025; 31(39): 111380
Published online Oct 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i39.111380
Published online Oct 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i39.111380
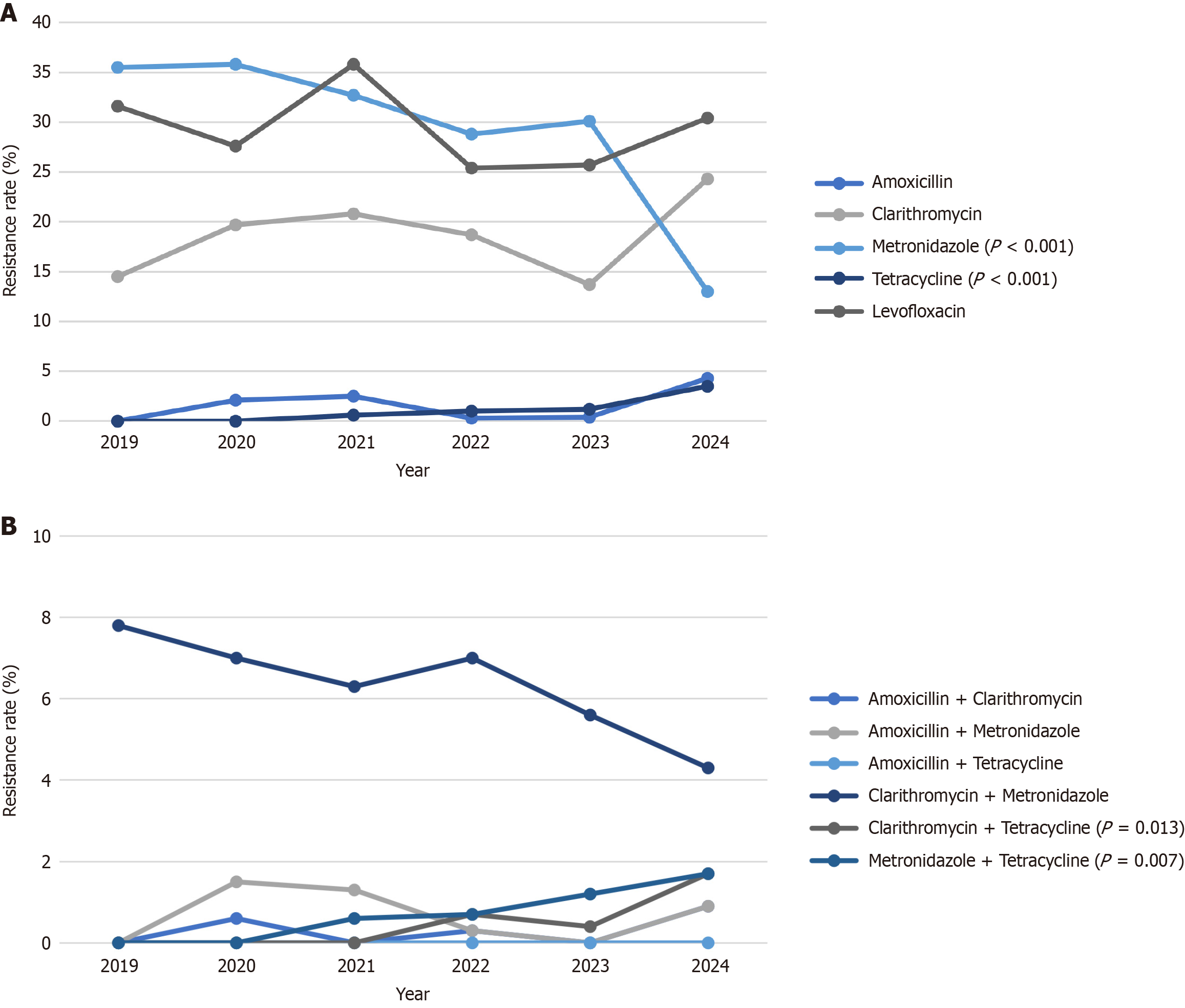
Figure 1 Sequential changes of antibiotic resistances and dual resistances of Helicobacter pylori in Taiwan from 2019 to 2024 among treatment naive patients.
A: Illustrated sequential changes of antibiotic resistances to amoxicillin, clarithromycin, metronidazole, tetracyclin, and levofloxacin. There was a statistically significant decreasing trend in metronidazole resistance; and a significant increasing trend in tetracycline resistance (P < 0.05 means significant change in linear trend); B: Illustrated sequential changes of antibiotic dual resistances. The dual resistance to clarithromycin plus tetracycline and metronidazole plus tetracycline both increased significantly from 0% to 1.7% during the study period (P < 0.05 means significant change in linear trend).
- Citation: Wu PJ, Tsay FW, Wu DC, Yang JC, Chuah SK, Chen KY, Chen CL, Lee CL, Shih CA, Liu YH, Shiu SI, Tai WC, Kuo CH, Lei WY, Kao SS, Tsai TJ, Feng IC, Koseki M, Hsu PI, Sheu MJ. Sequential changes of antibiotic resistances of Helicobacter pylori in Taiwan from 2019 to 2024. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(39): 111380
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i39/111380.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i39.111380