Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2025; 31(38): 110999
Published online Oct 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i38.110999
Published online Oct 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i38.110999
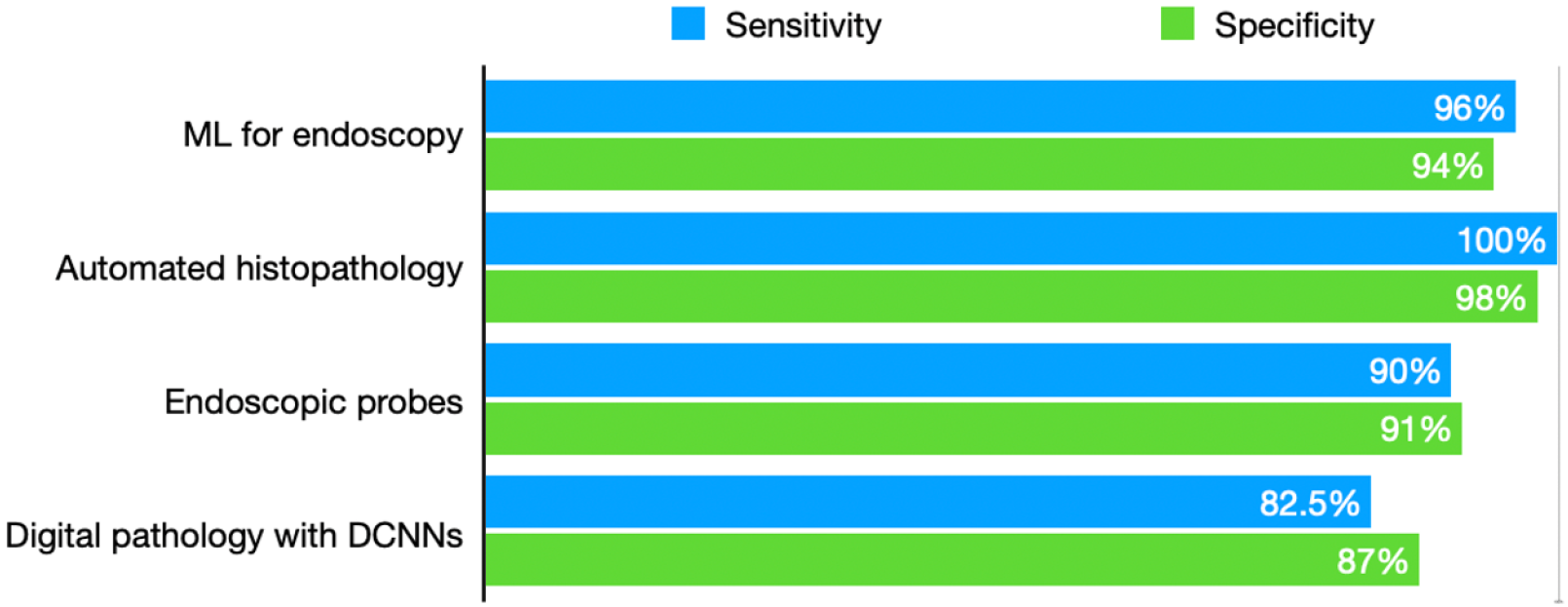
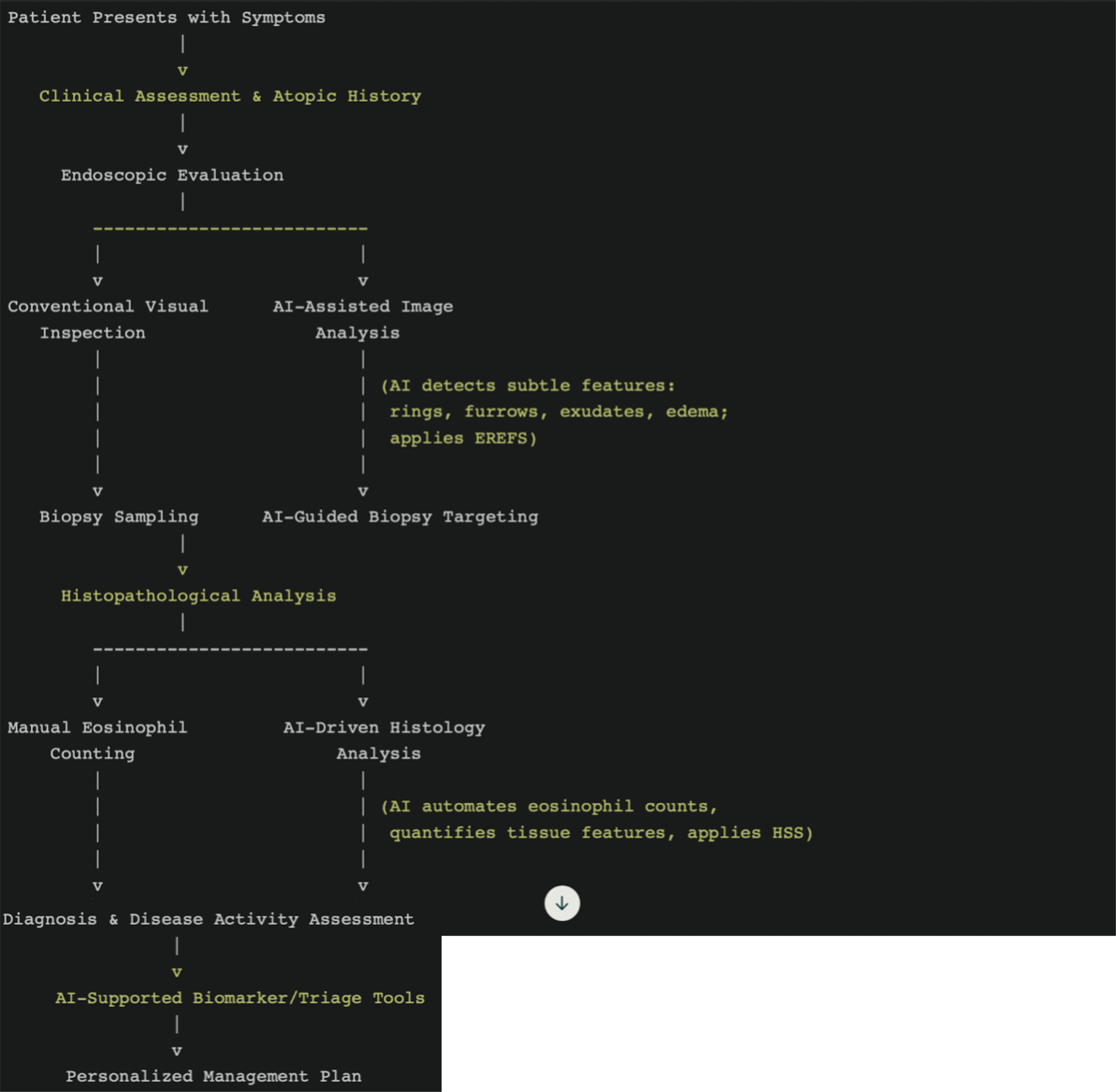
Figure 2 Schematic representation of the integration points for artificial intelligence algorithms in the diagnostic pathway for eosinophilic esophagitis.
Artificial intelligence (AI) augments the traditional workflow at multiple stages: (1) During endoscopic evaluation, AI models assist in real-time image analysis, enhancing detection of subtle mucosal features and standardizing scoring (e.g., eosinophilic esophagitis endoscopic reference score), and can guide targeted biopsy sampling; (2) In histopathology, AI automates eosinophil counts and evaluates global tissue features, reducing inter-observer variability and expediting diagnosis; and (3) AI-driven biomarker analysis and triage tools (using blood, urine, or non-invasive devices) further support risk stratification and may reduce the need for invasive procedures. These integrations aim to increase diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and consistency, ultimately supporting more timely and individualized patient management. AI: Artificial intelligence; EREFS: Eosinophilic esophagitis endoscopic reference score; HSS: Histologic scoring system.
- Citation: Issa IA, Youssef O, Issa T. Can artificial intelligence improve the diagnosis and management of patients with eosinophilic esophagitis? World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(38): 110999
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i38/110999.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i38.110999