©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2025; 31(37): 111327
Published online Oct 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i37.111327
Published online Oct 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i37.111327
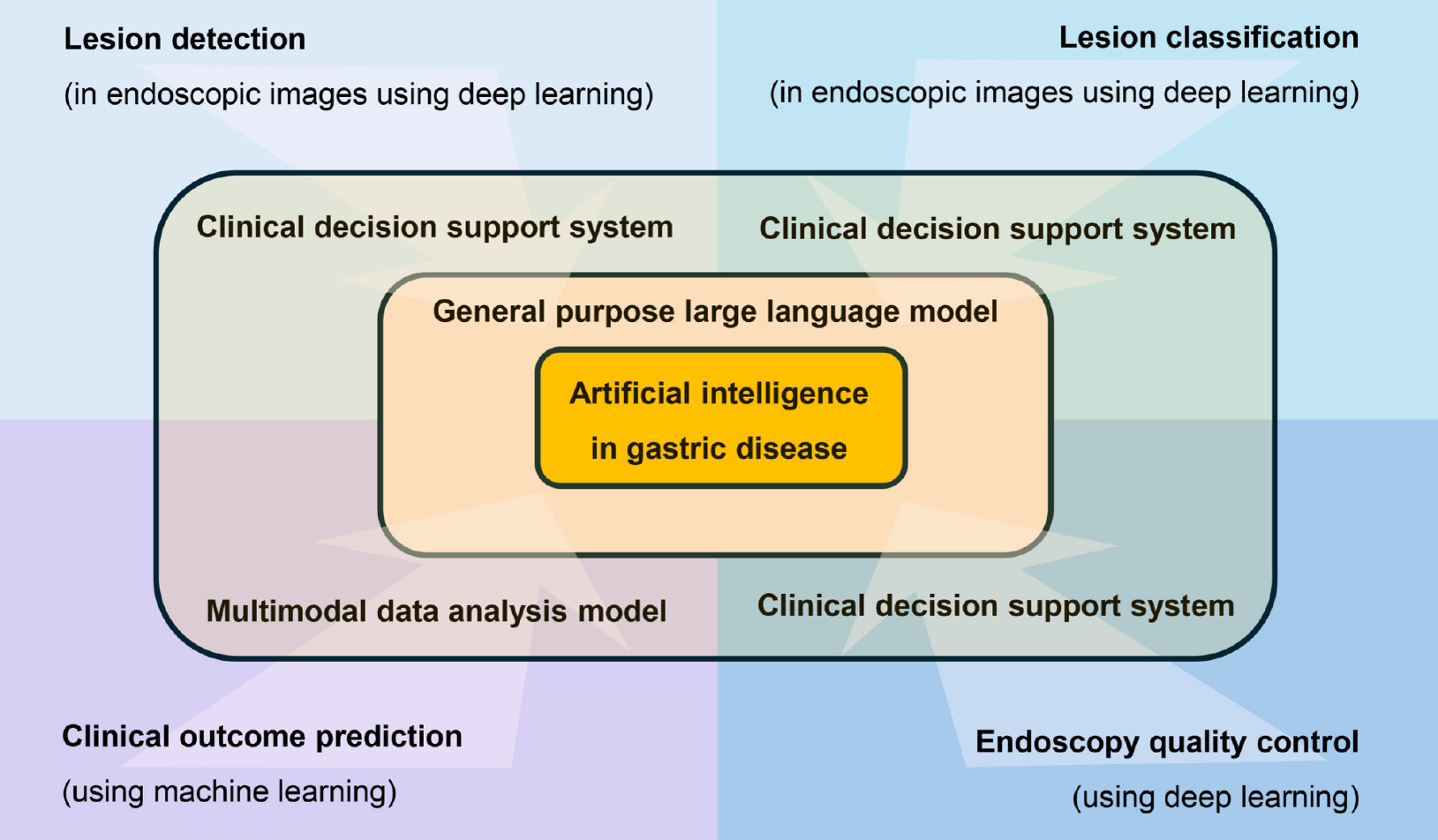
Figure 1
Schematic overview of the current application of artificial intelligence in gastric diseases.
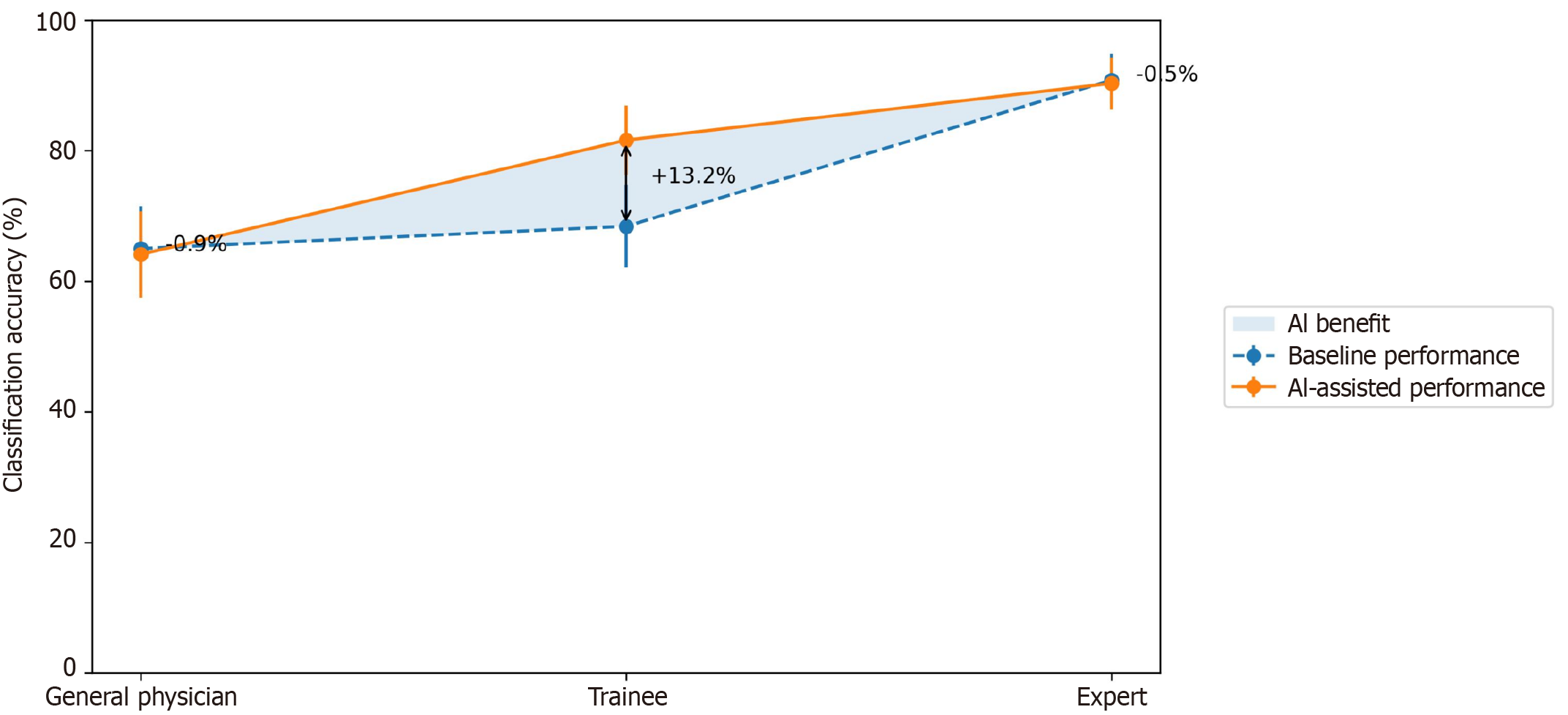
Figure 2 Inverse relationship between endoscopist experience and artificial intelligence assistance benefits in gastric endoscopy.
The curve demonstrates the differential benefit of artificial intelligence assistance across expertise levels based on our analysis of endoscopic images in the prediction of submucosal invasion[7]. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals (CI) for each performance measurement. Maximum benefit occurs at moderate expertise levels (trainees: +13.2%, 95%CI: 10.1%-16.3%), while general physicians show decreased performance (-2.9%, 95%CI: -5.2% to -0.6%) and experts show minimal change (-0.5%, 95%CI: -2.1% to 1.1%). Data derived from Bang et al[7].
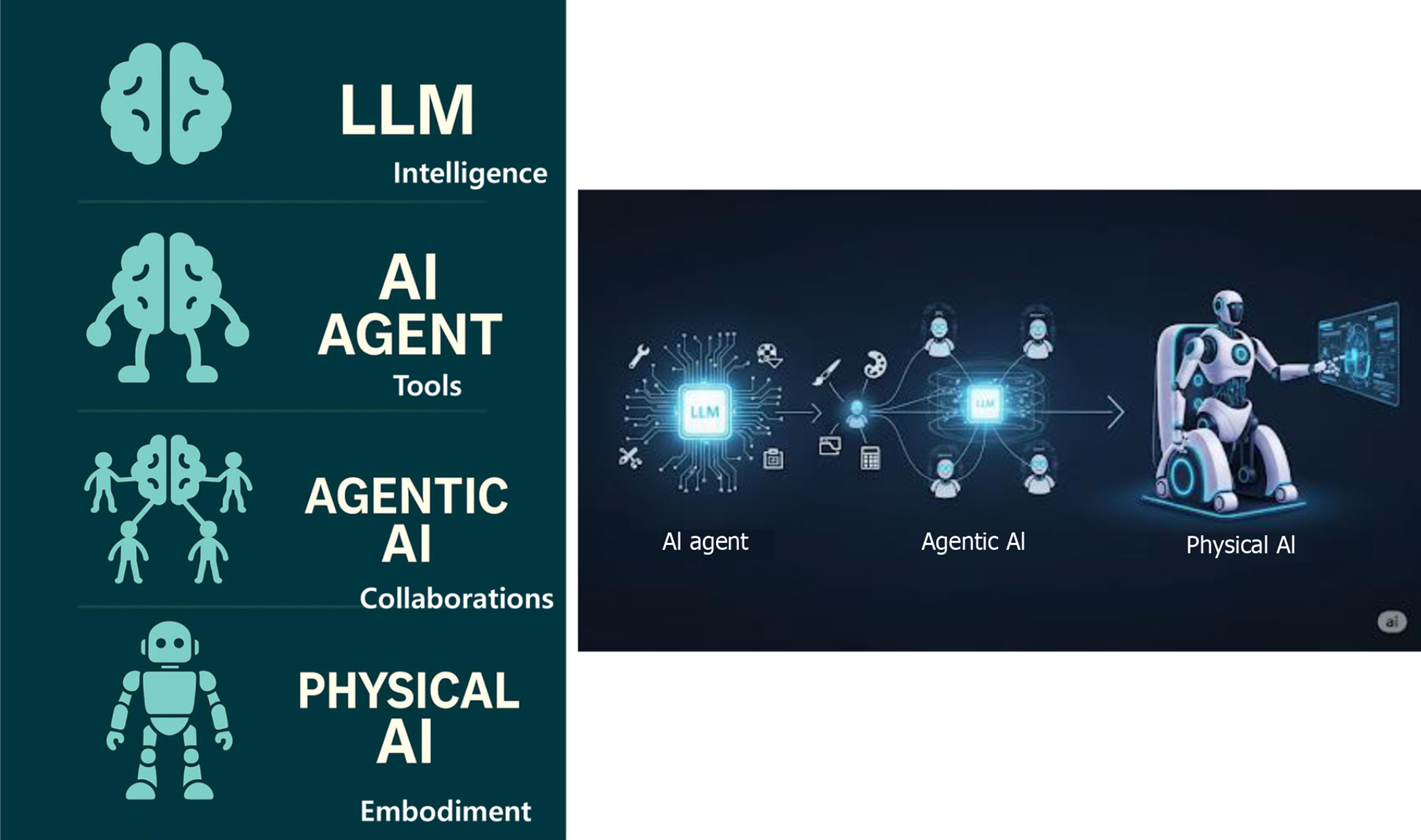
Figure 3 Evolution of large language models.
AI: Artificial intelligence; LLM: Large language model.
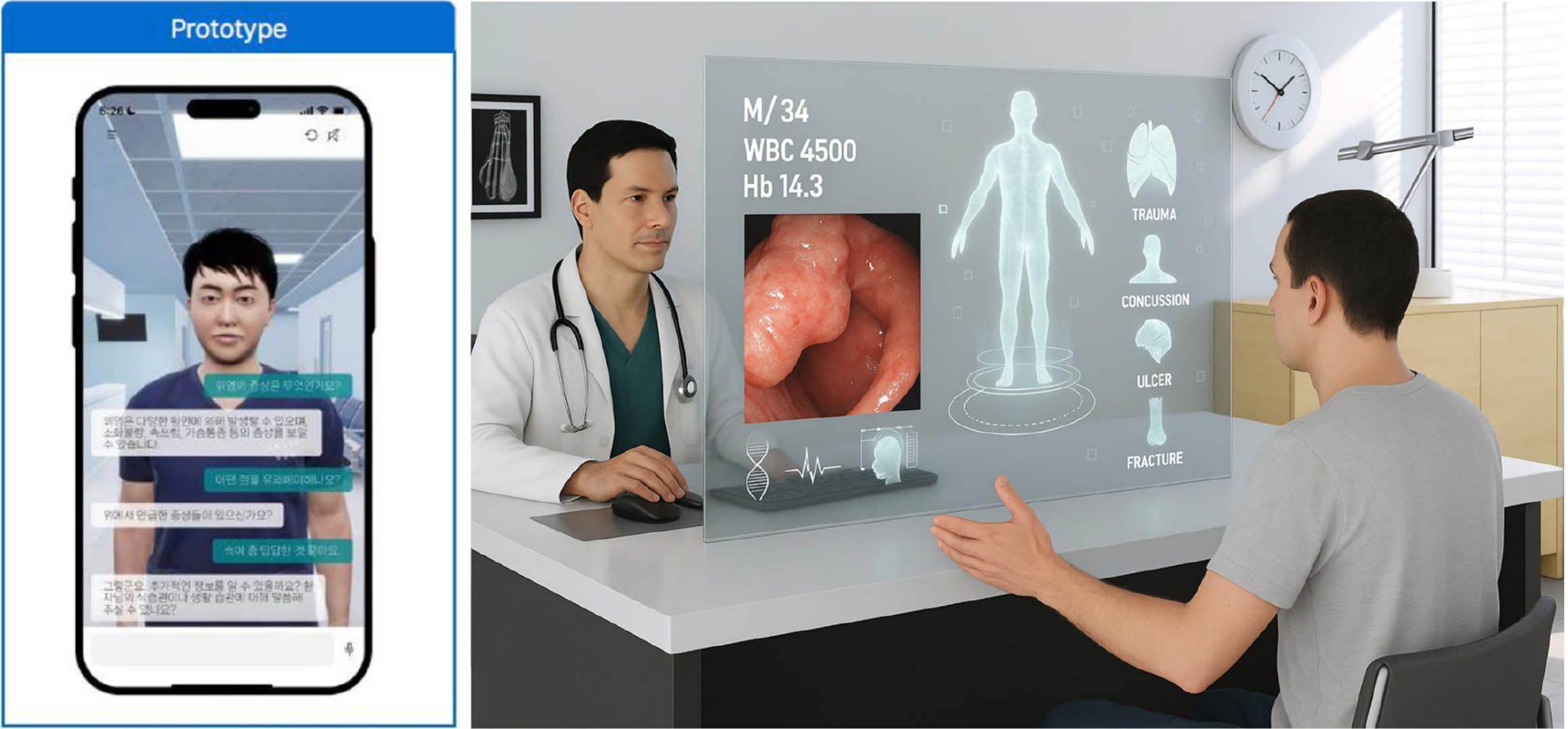
Figure 4
Personal artificial intelligence model: Large language model fine-tuned on clinical recordings learning individual patterns, reasoning, and recommendations mirroring the clinician’s approach.
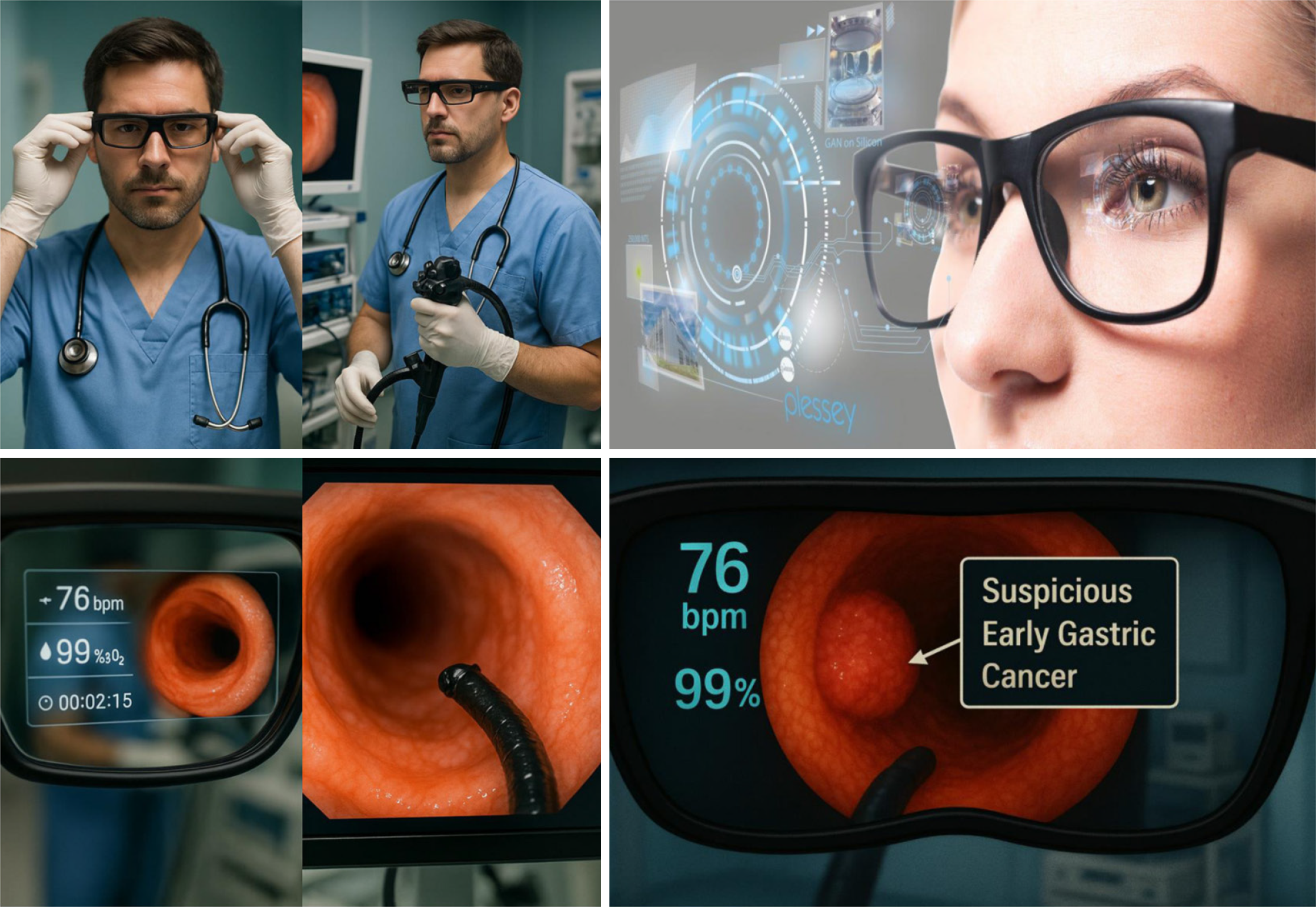
Figure 5
Smart glasses with embedded vision models for the lesion detection and characterization during upper gastrointestinal procedures.
- Citation: Gong EJ, Woo J, Lee JJ, Bang CS. Role of artificial intelligence in gastric diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(37): 111327
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i37/111327.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i37.111327