©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2025; 31(27): 107740
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.107740
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.107740
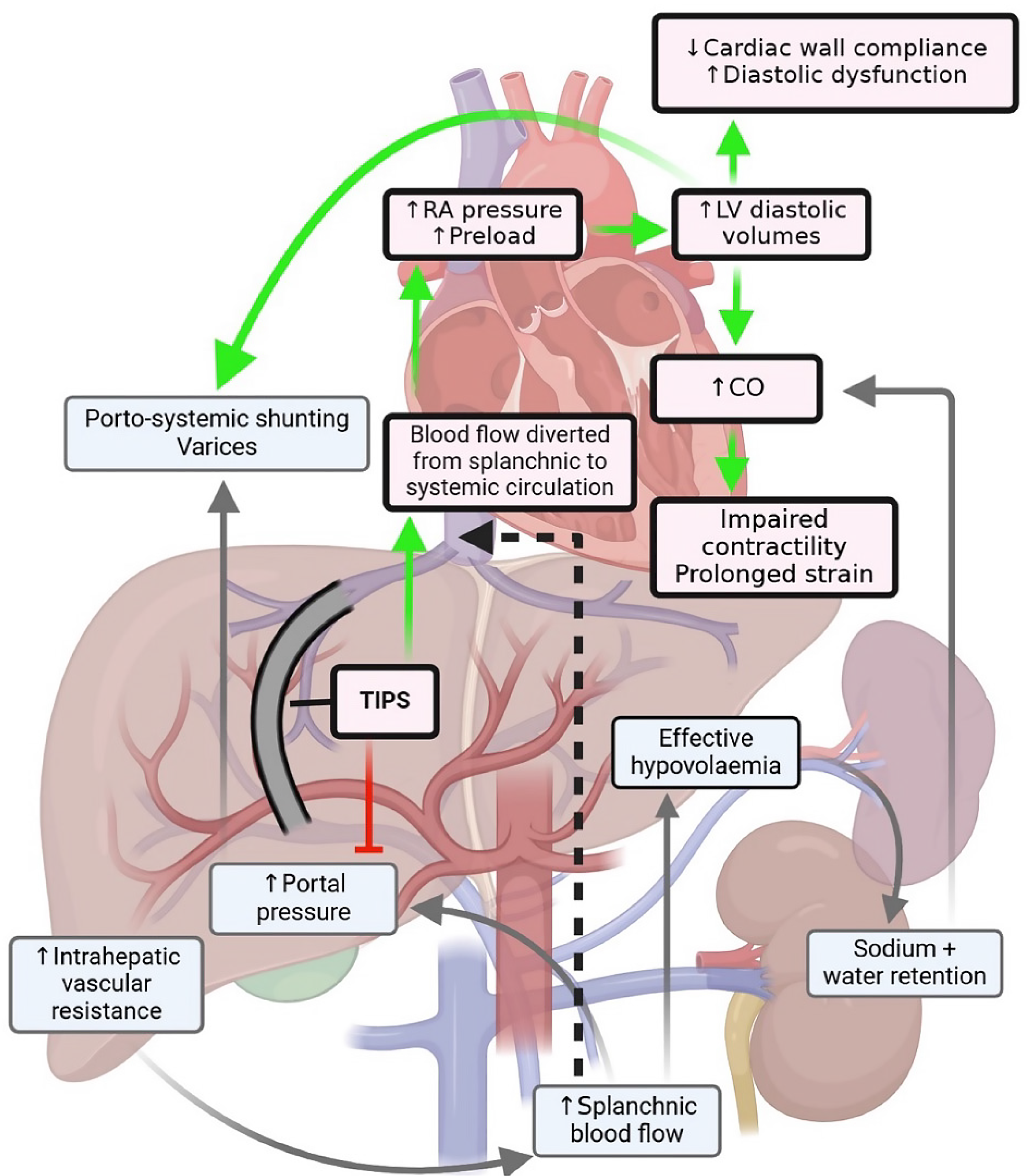
Figure 1 Hyperdynamic alterations in advanced chronic liver disease and post-transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt[30].
Depicted: Hyperdynamic changes seen in advancing chronic liver disease (grey arrows), with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt changes (green) demonstrating haemodynamic changes with resultant effects. TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; RA: Right atrium; LV: Left ventricle; CO: Cardiac output.
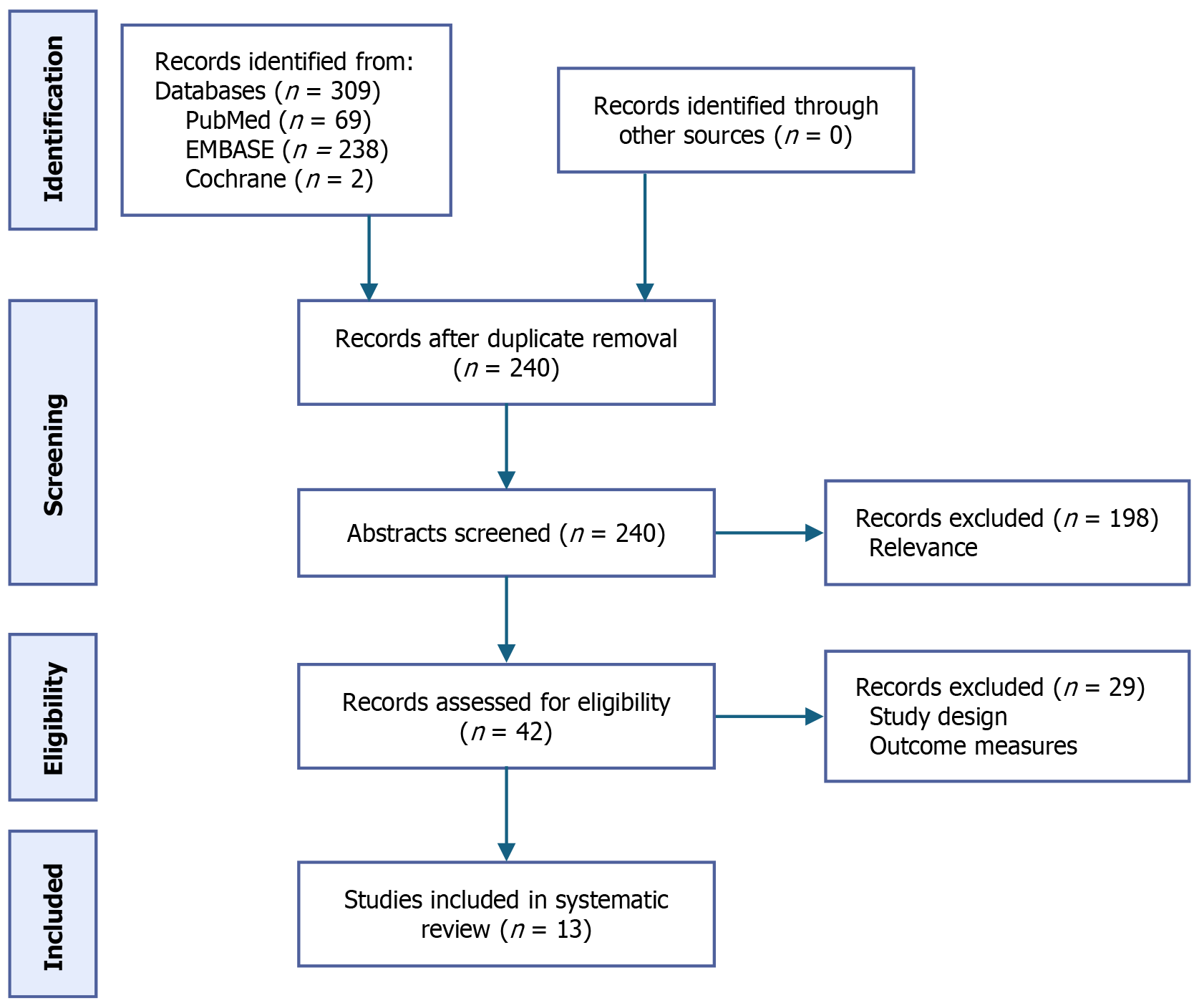
Figure 2
Screening process: From identification to inclusion.
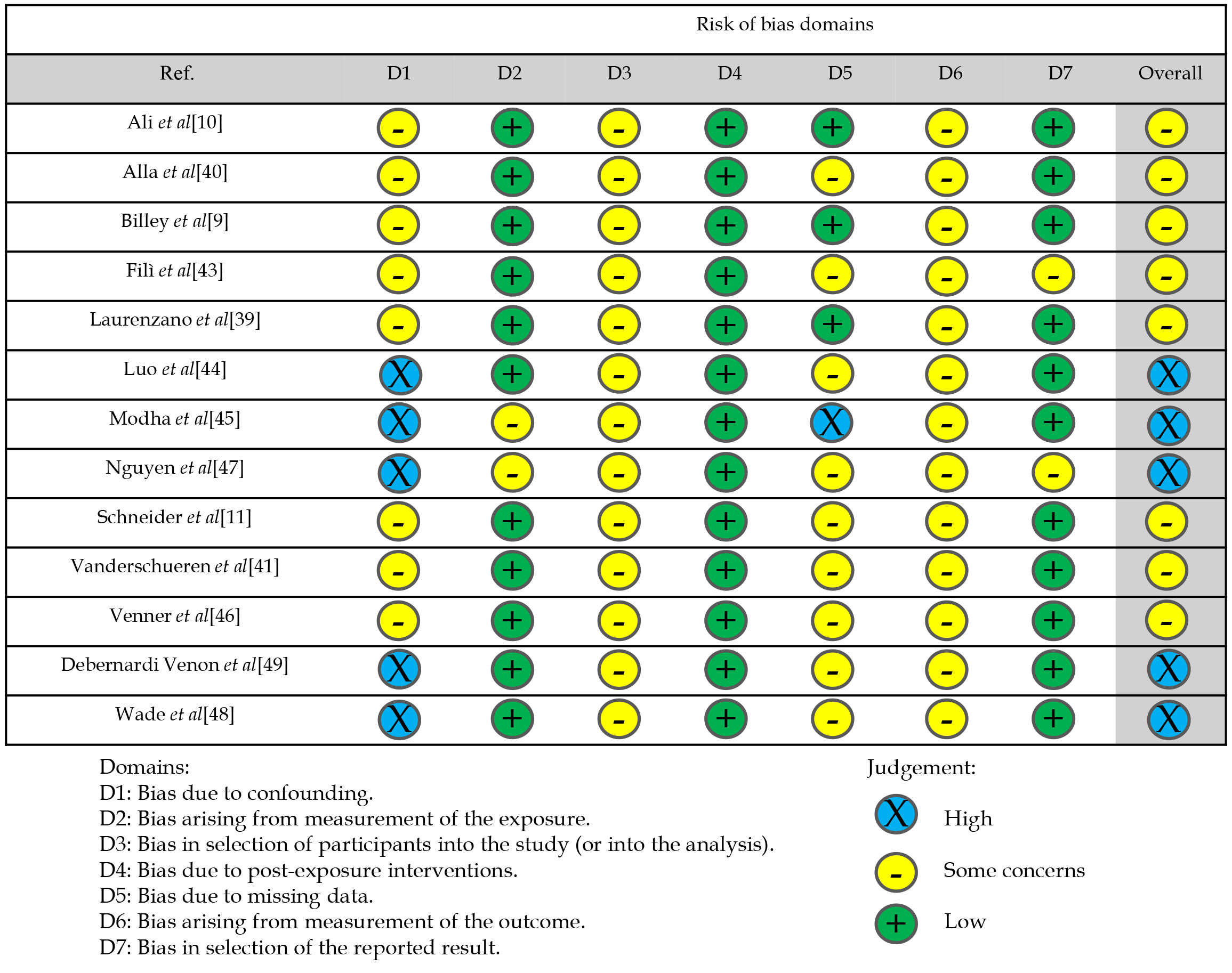
Figure 3
ROBINS-E, risk of bias tool on selected cohort studies[110].
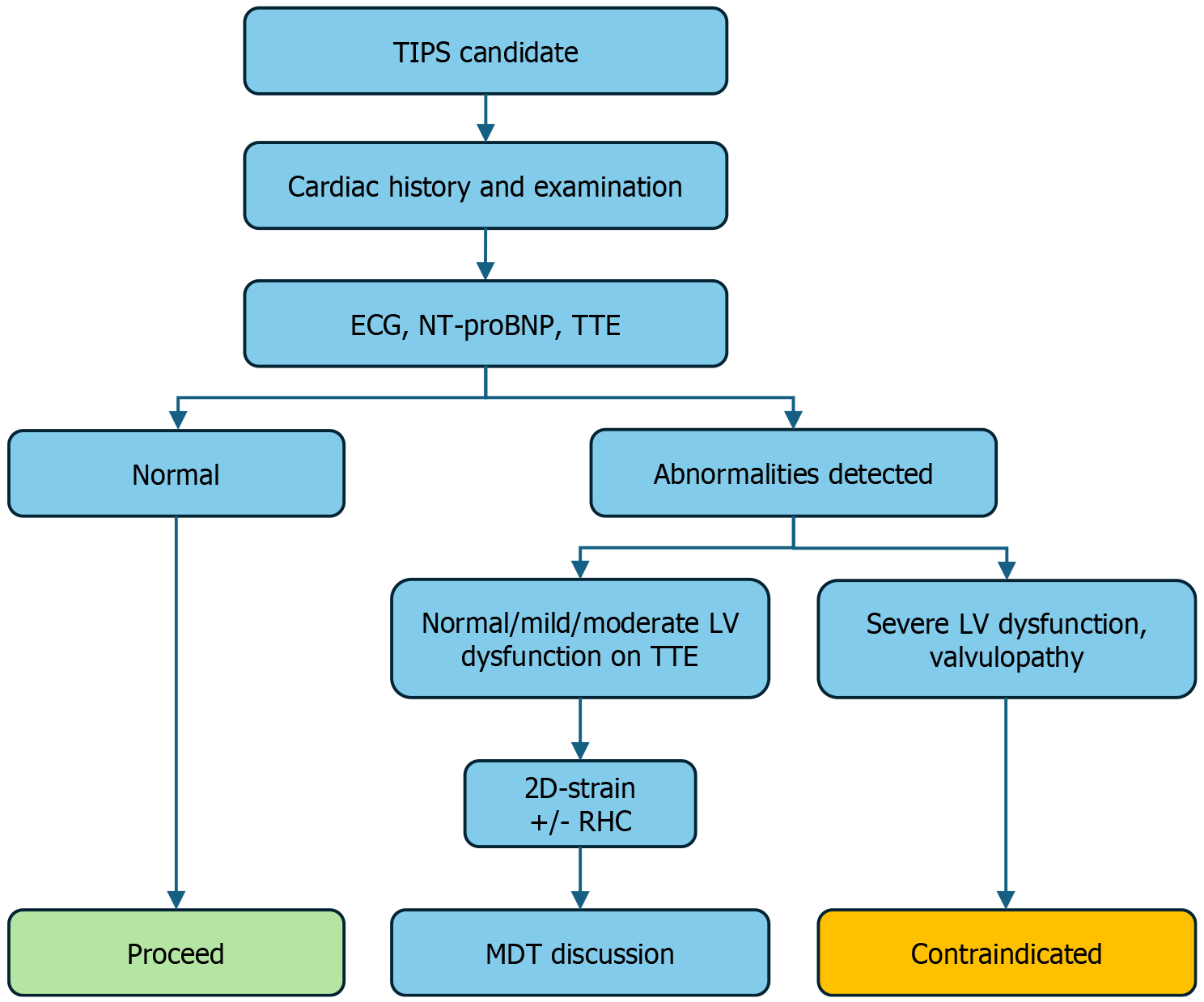
Figure 4 Proposed algorithm for cardiovascular workup prior to transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedure.
TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; Cardiac history: History of peripheral oedema, congestive cardiac failure, pulmonary hypertension, valvular disease; ECG: Electrocardiogram; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; TTE: Transthoracic echocardiography; LV: Left ventricular; 2D-strain: Two-dimensional speckle-tracing echocardiography assessing for left atrial strain; RHC: Right heart catheterisation; MDT: Multi-disciplinary team gastroenterology, anaesthesiology, interventional radiology, cardiology inputs.
- Citation: Tomassoni DR, Schildkraut T, Ramachandran V, Cooke JC, Sawhney R. Cardiovascular risk assessment and predictors of cardiac decompensation after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(27): 107740
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i27/107740.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.107740