©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2025; 31(23): 107100
Published online Jun 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.107100
Published online Jun 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.107100
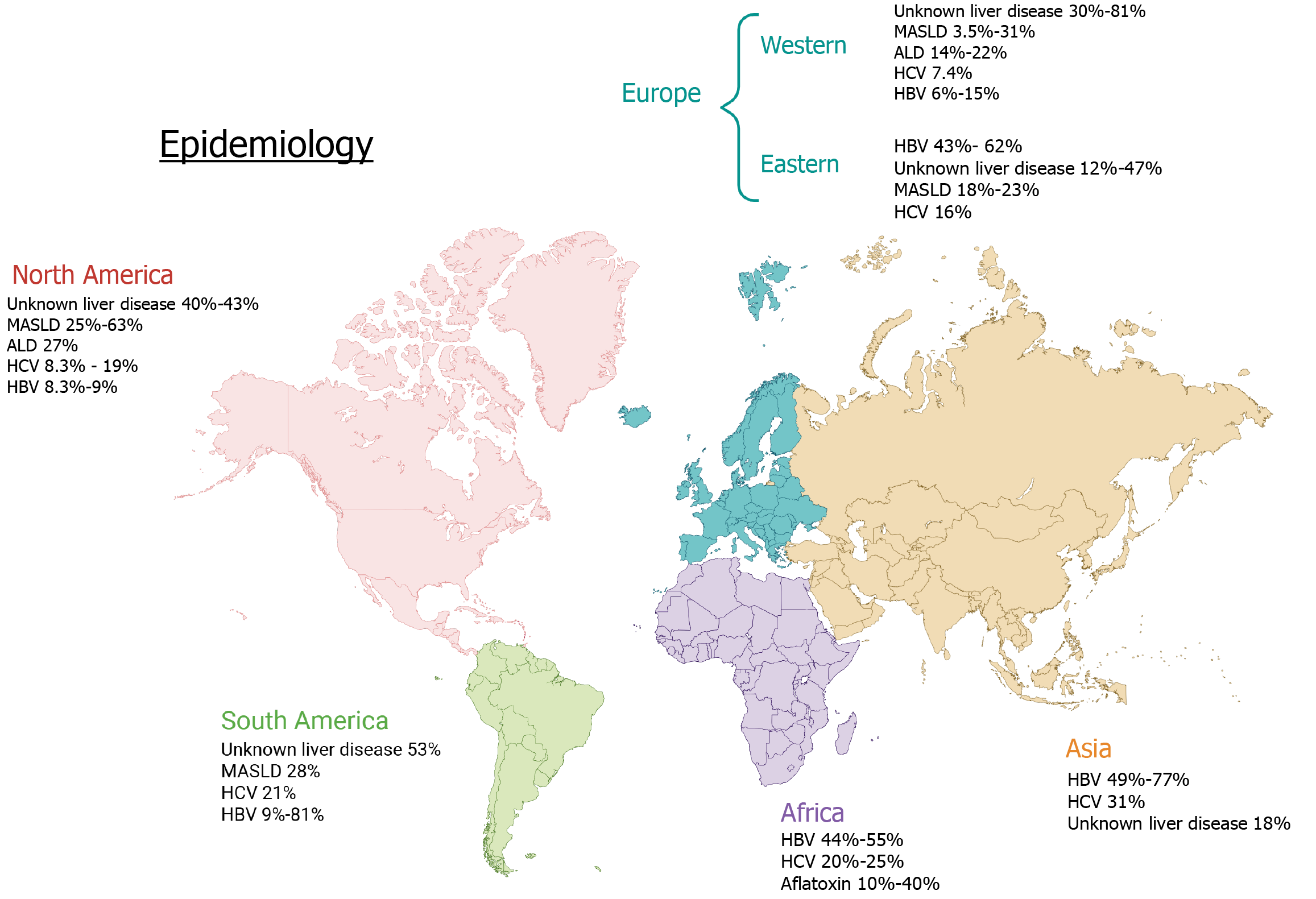
Figure 1 Geographic distribution of hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic liver based on different etiologies.
ALD: Alcohol-associated liver disease; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Created in BioRender (Supplementary material).
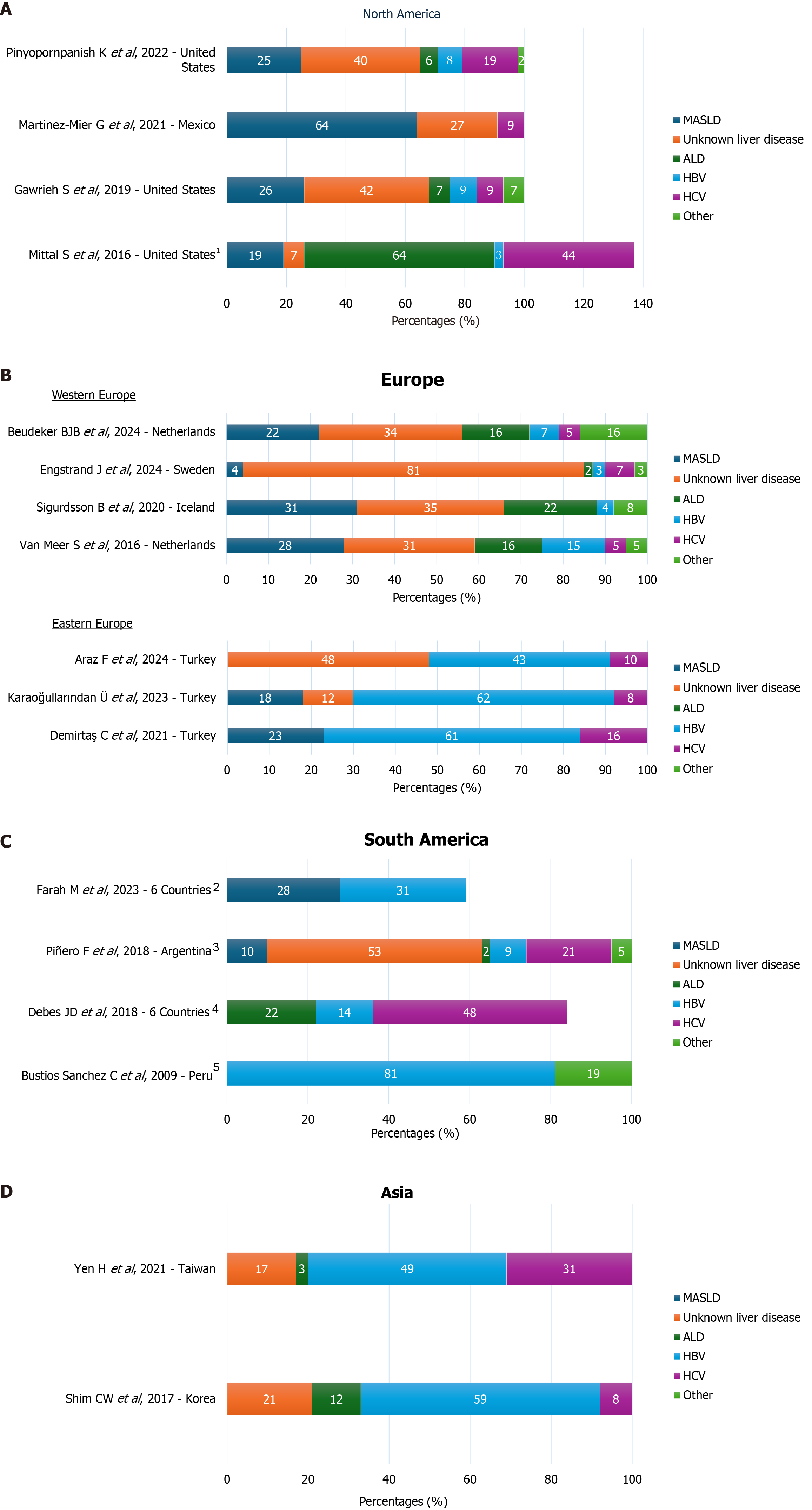
Figure 2 Summary of percentage by etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in individuals without cirrhosis from studies conducted.
A: North America; B: Europe; C: Summary of percentage by etiology of individuals with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from studies conducted in South America; D: Asia. 1Risk factor distribution was not mutually exclusive as many patients had more than one risk factor, and the percentage sum was more than 100%; 2Percentage of non-cirrhotic HCC by country: Peru 31%, Ecuador 28%, Chile 26%, Brazil 12%, Argentina 7%, Colombia 4%. Limitation of the study: The reported etiology was combined with that of individuals with cirrhosis; 3The data were inferred from the individuals with cirrhosis available status, but no confirmation of non-cirrhosis was reported in the study; 4Countries included in the analysis: Peru, Ecuador, Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Uruguay. No data on the number of individuals without cirrhosis were available. The study’s limitation was that the reported etiology was combined with that of individuals with cirrhosis; 5Only data available on hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in non-cirrhosis available. ALD: Alcohol-associated liver disease; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
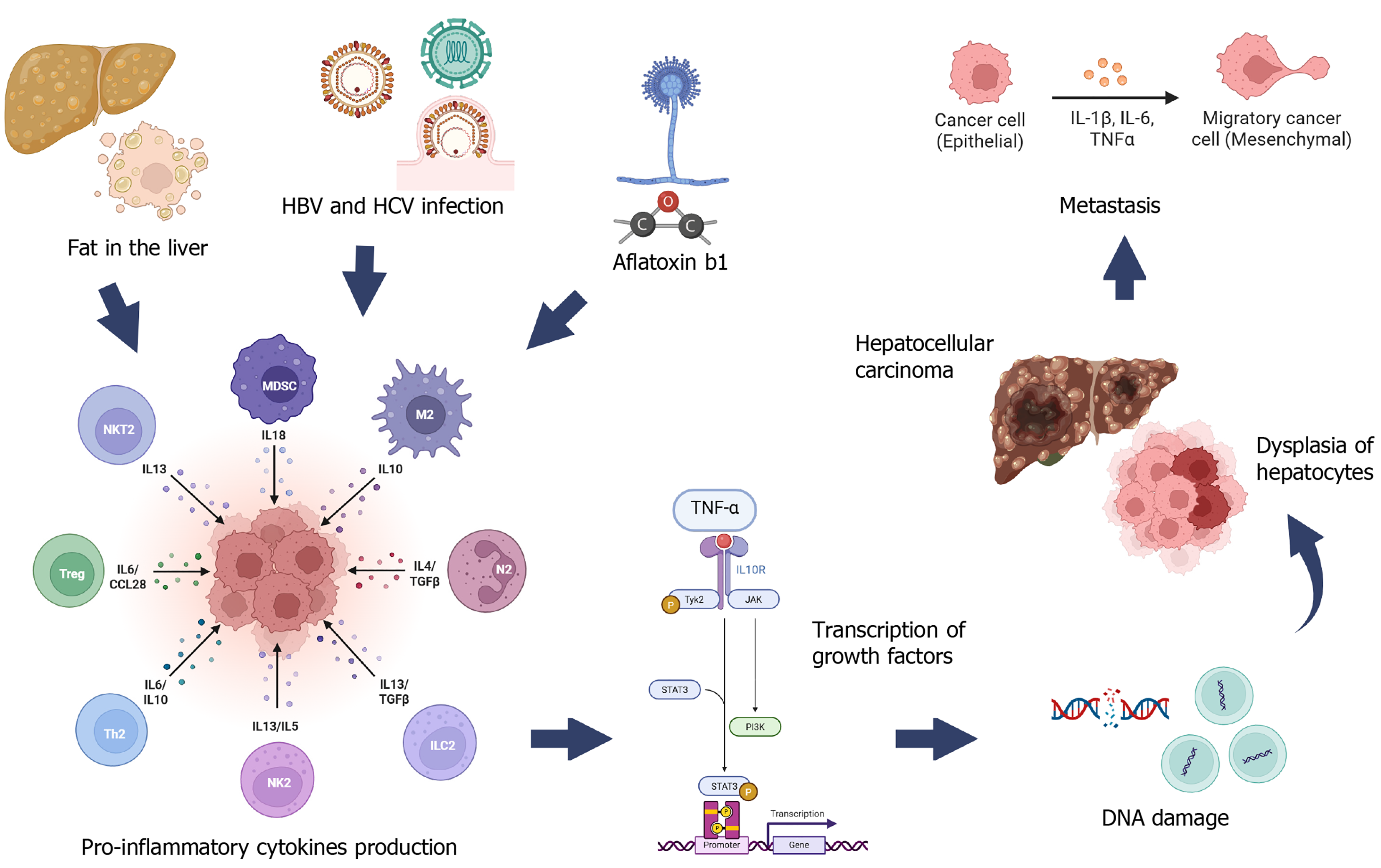
Figure 3 Inflammatory mechanism in hepatic carcinogenesis and metastasis.
IL: Interleukin; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha. Created in BioRender (Supplementary material).
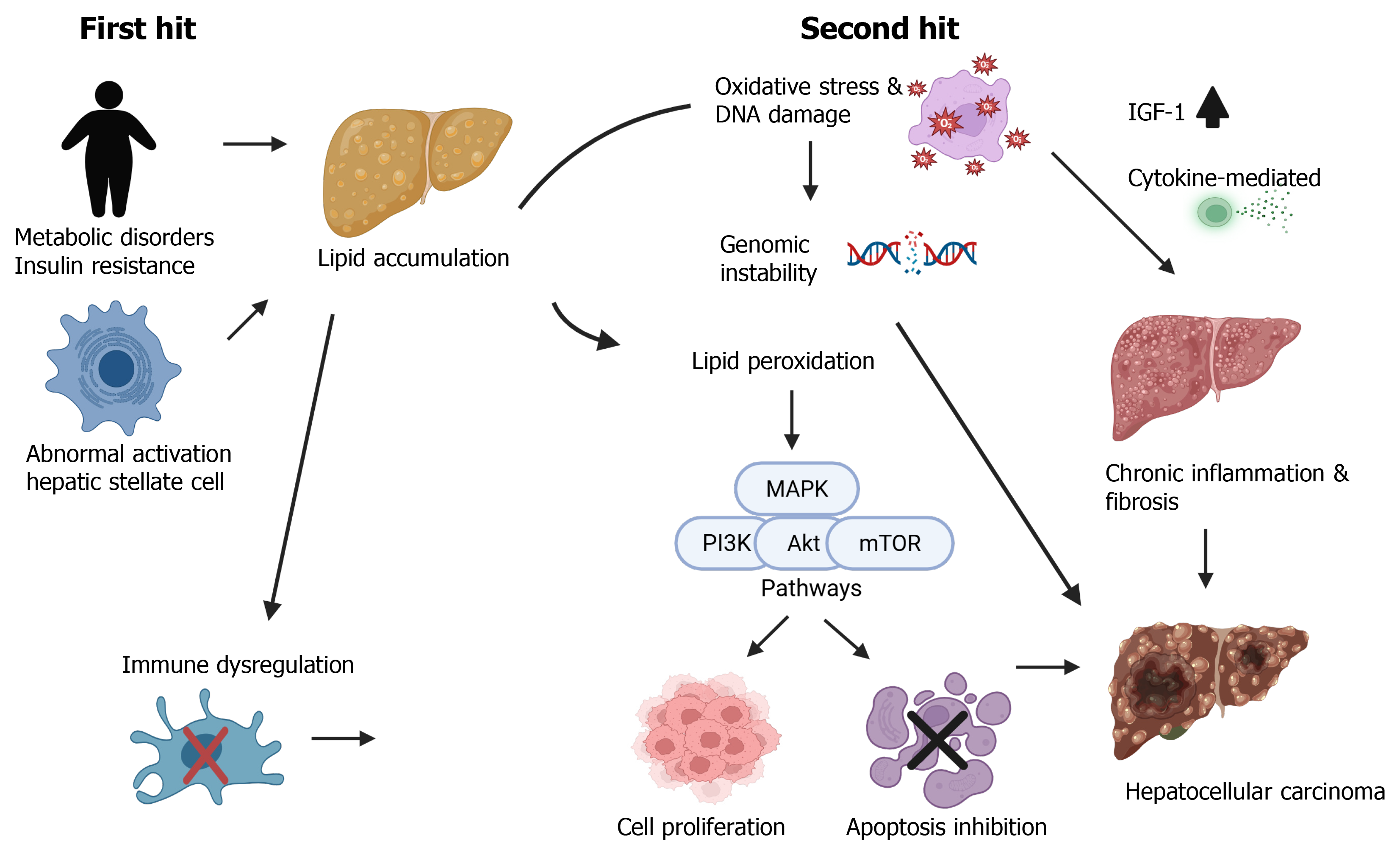
Figure 4 Hypothesis of the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in individuals with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
Akt: Protein kinase B; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Created in BioRender (Supplementary material).
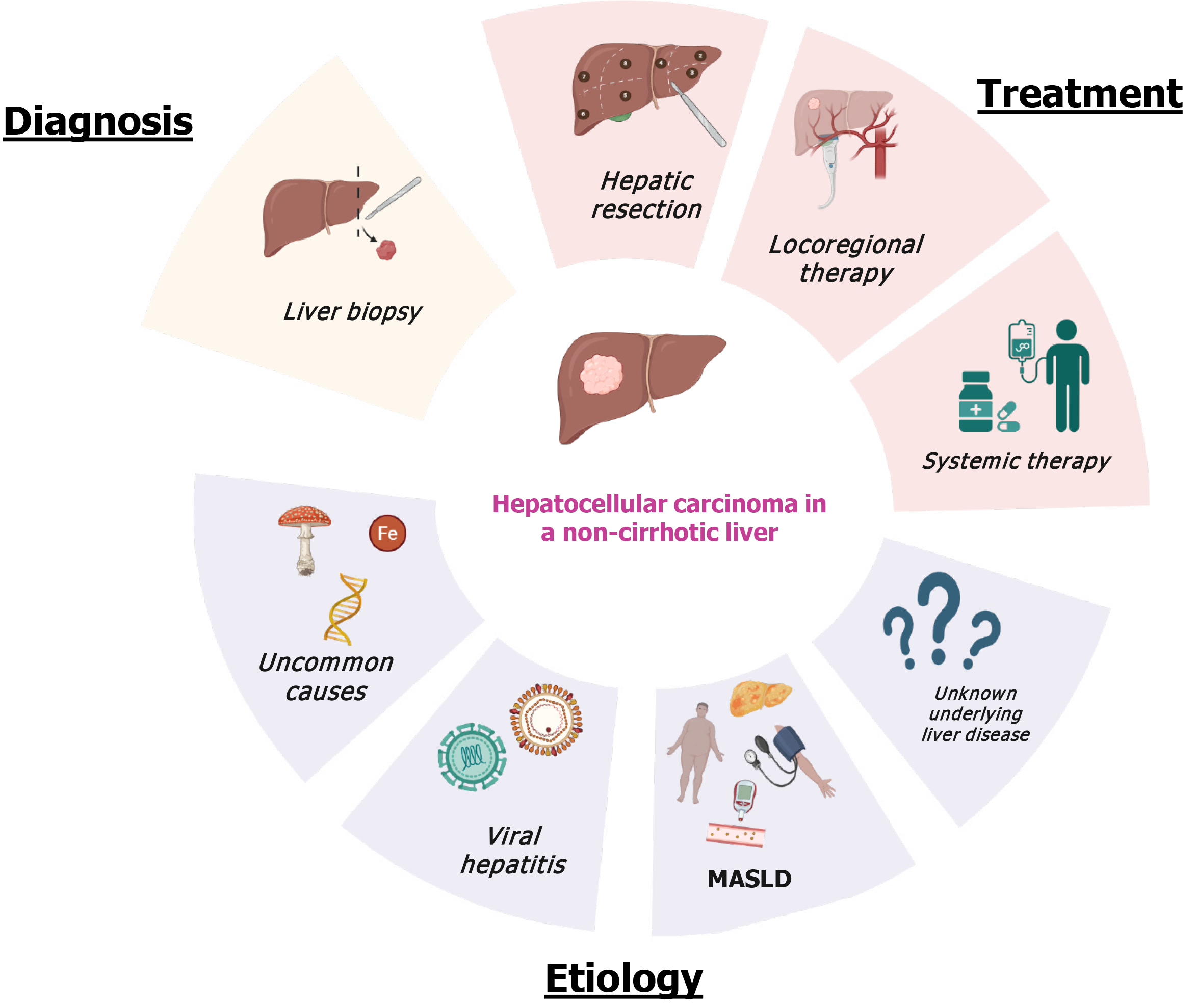
Figure 5 Graphical abstract summarizing the etiology, treatments, and diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in individuals without cirrhosis.
MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Created in BioRender (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Sato-Espinoza K, Valdivia-Herrera M, Chotiprasidhi P, Diaz-Ferrer J. Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients without cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(23): 107100
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i23/107100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.107100