©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2025; 31(20): 106615
Published online May 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.106615
Published online May 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.106615
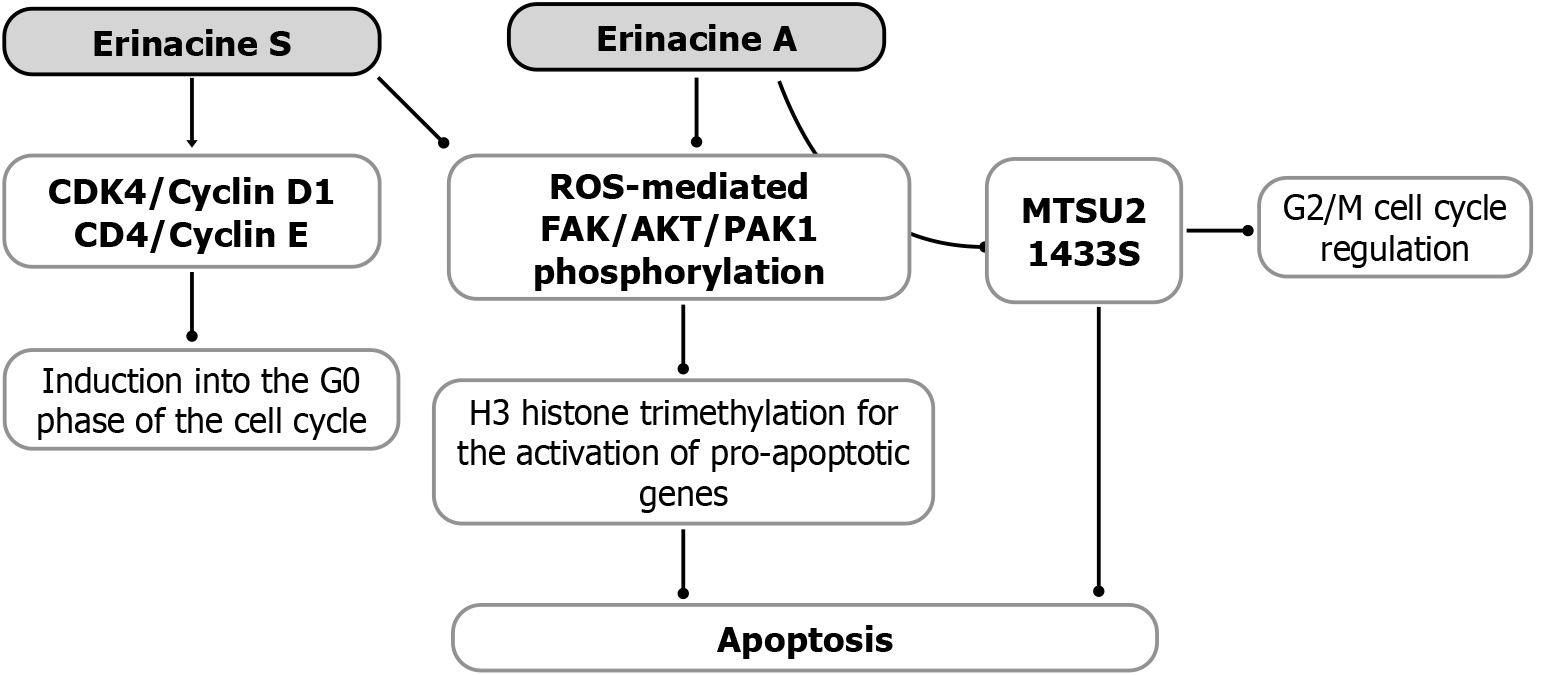
Figure 1 Antineoplastic mechanisms of Hericium erinaceus erinacines against gastric cancer.
Erinacine S has been shown in cellular models to induce a specific pathway through reactive oxygen species, leading to the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinases (FAK)/protein kinase B, also known as AKT, as well as p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1). This pathway promotes histone H3 trimethylation, facilitating the production of various molecules, including the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and Fas ligand receptors, which trigger the apoptotic cascade mediated by caspases 3, 8, and 9. Similarly, in gastric cancer cell models, erinacine A modulation of the FAK/AKT/PAK1 pathway can regulate two key proteins: Microtubule-associated scaffold protein 2 and the 14-3-3 sigma protein. This modulation negatively influences cell cycle regulation, particularly in the G2 and M phases. ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Pellegrino R, Gravina AG. Potential of traditional Chinese medicine in gastrointestinal disorders: Hericium erinaceus in chronic atrophic gastritis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(20): 106615
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i20/106615.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.106615