©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2023; 29(17): 2551-2570
Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2551
Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2551
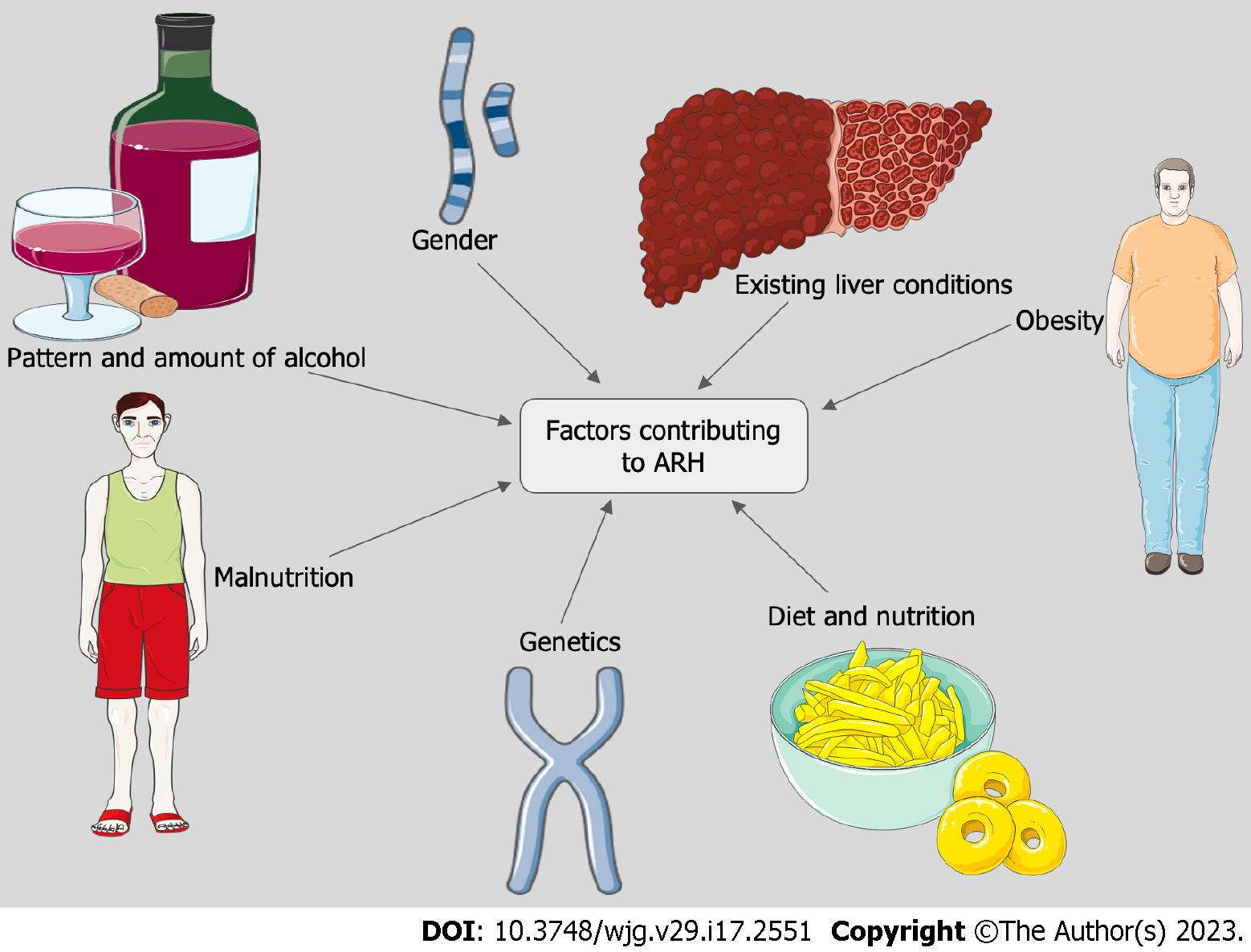
Figure 1 Risk factors of alcohol-related hepatitis.
ARH: Alcohol-related hepatitis.
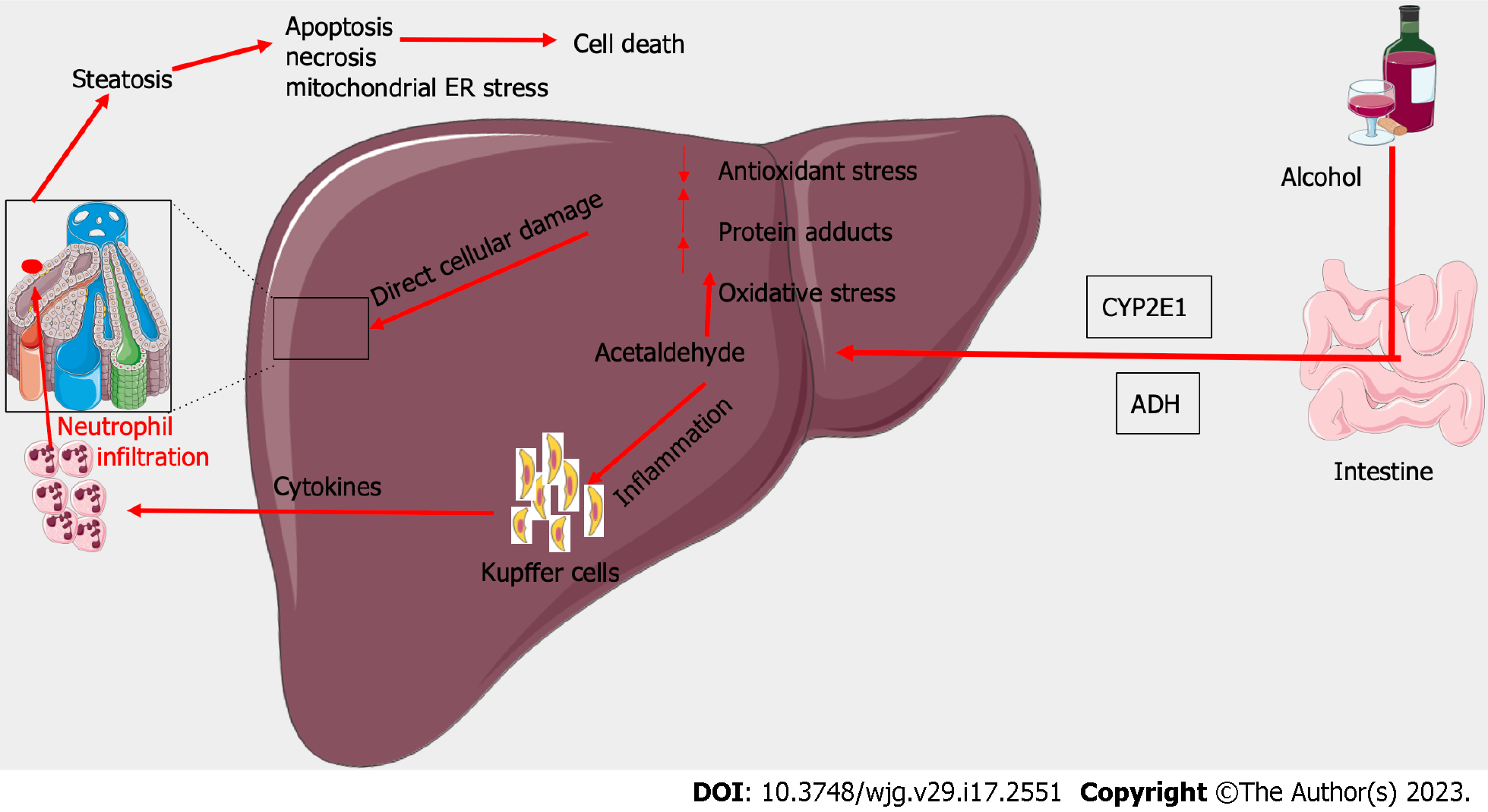
Figure 2 Pathogenesis of alcohol-related hepatitis.
ADH: Alcohol dehydrogenase.
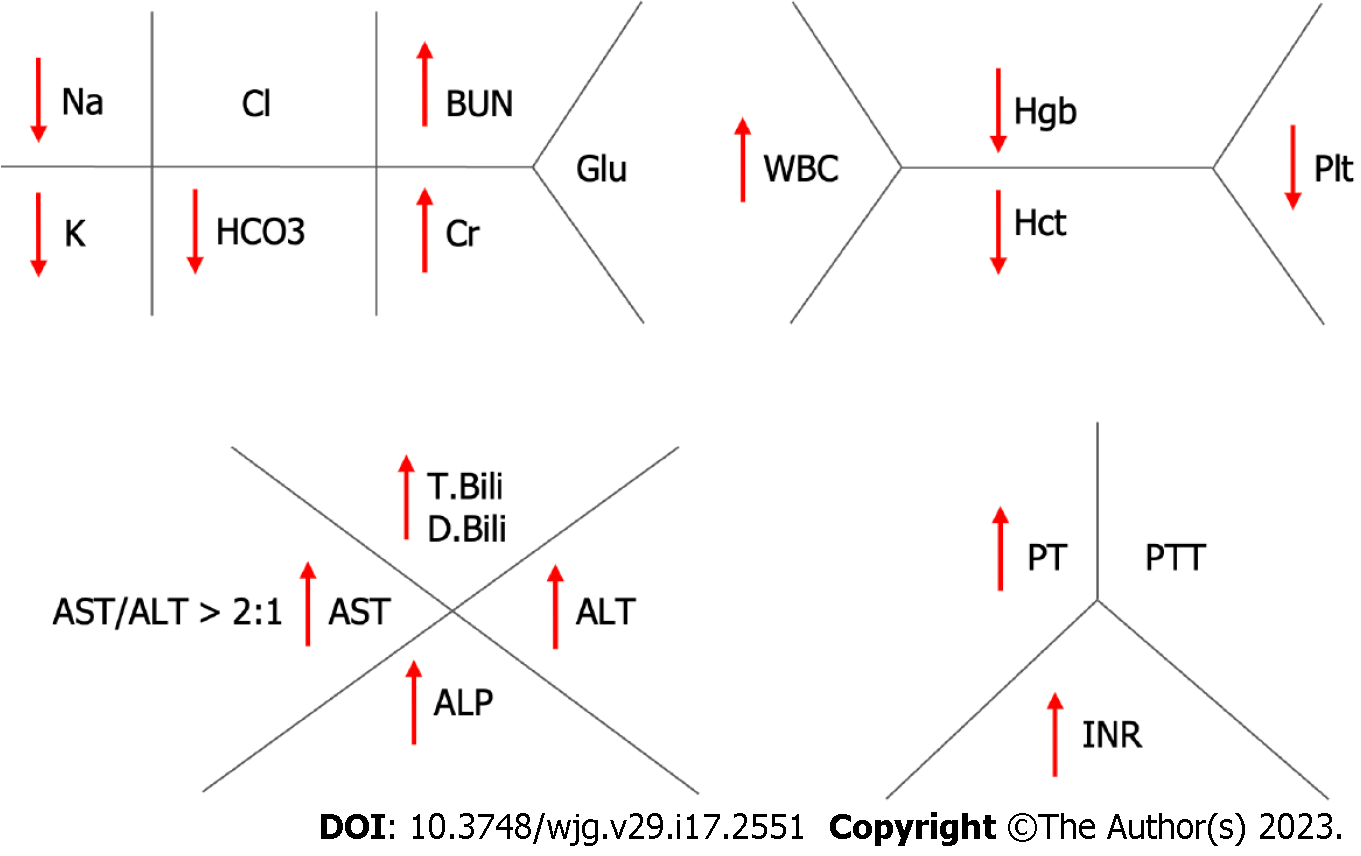
Figure 3 Fishnet diagram showing laboratory abnormalities, commonly seen in patients with alcohol-related hepatitis.
BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; WBC: White blood cell; Glu: Glucose; Hgb: Hemoglobin; Hct: Hematocrit; Plt: Platelet; T.Bili: Total bilirubin; D.Bili: Direct bilirubin; AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALT: Alanine transaminase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; PT: Prothrombin time; PTT: Partial thromboplastin time; INR: International normalized ratio.
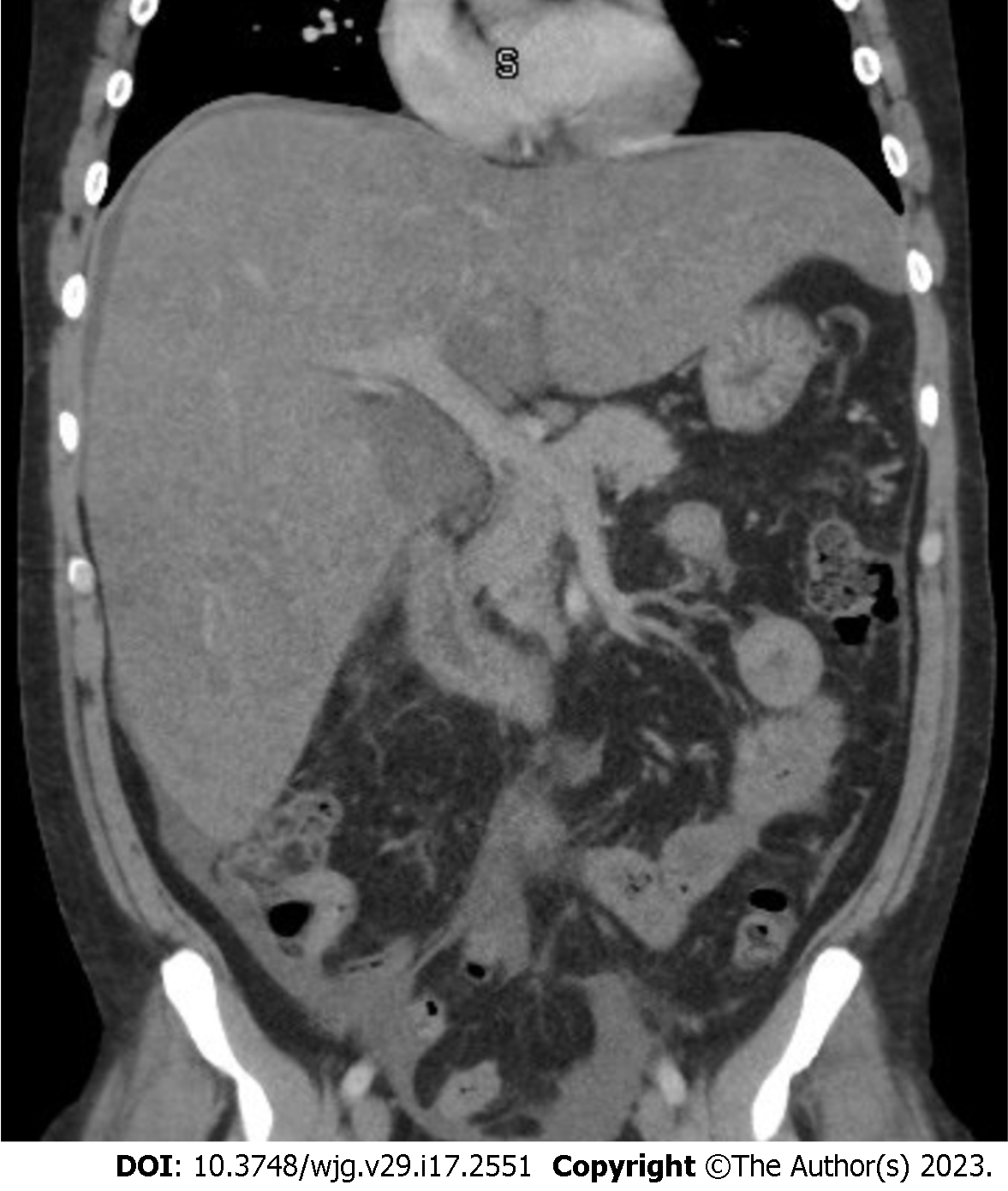
Figure 4 Computerized tomography showing enlarged liver with smooth contour.
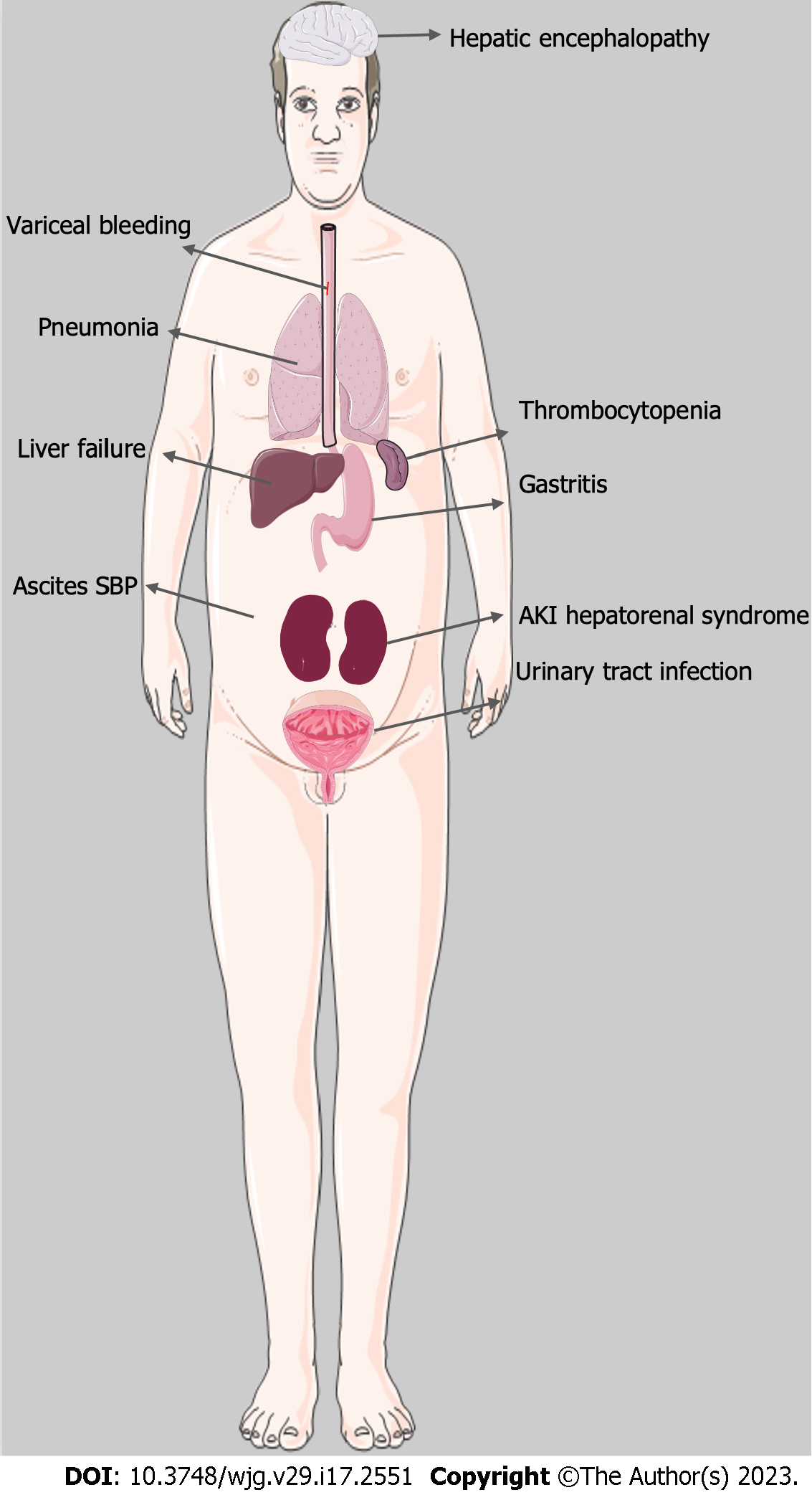
Figure 5 Complications and clinical features in patients with alcohol-related hepatitis.
SBP: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; AKI: Acute kidney injury.
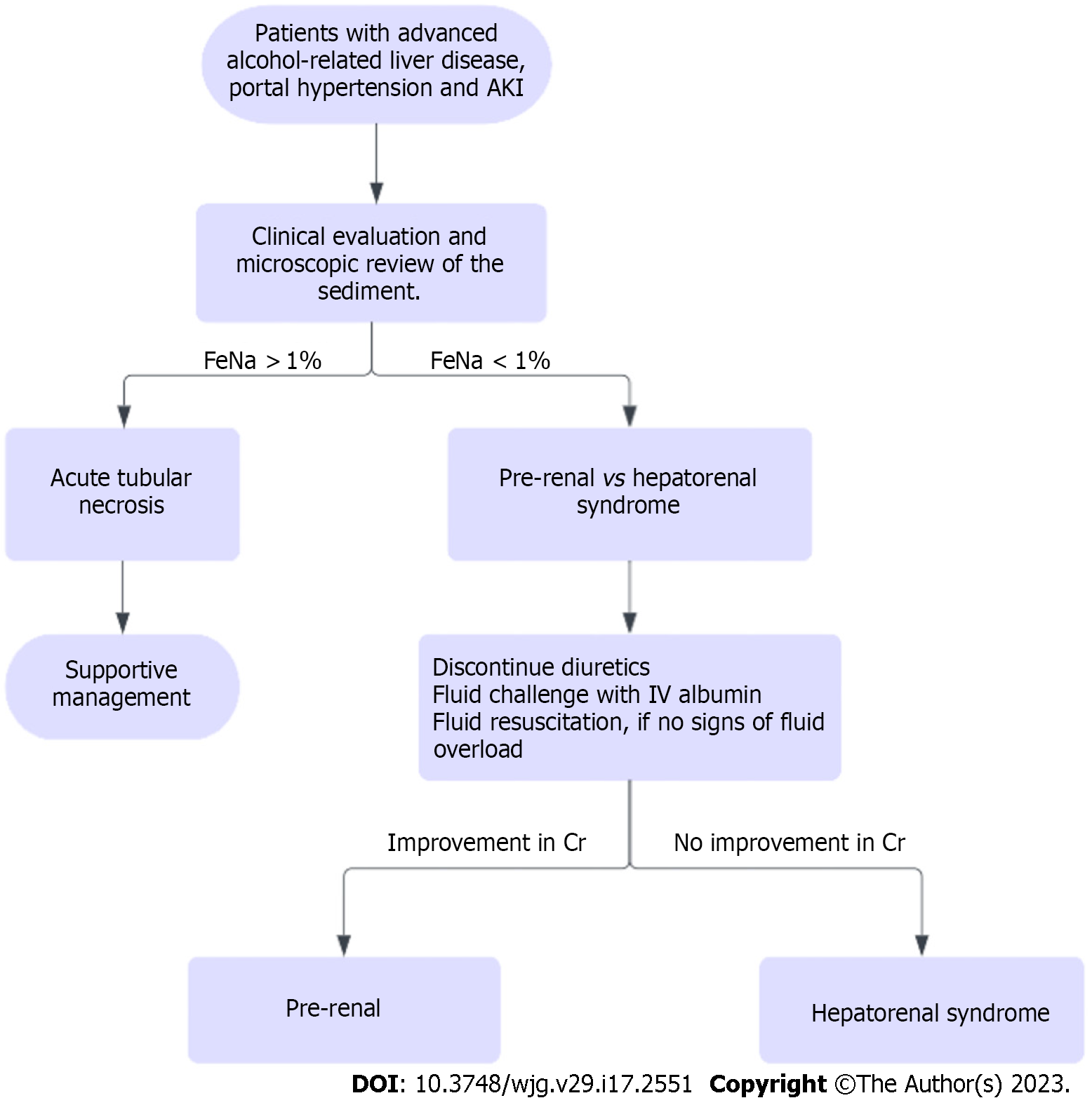
Figure 6 Diagnostic workup for acute kidney injury in patients with alcohol-related hepatitis.
MDF: Maddrey’s discriminant function.
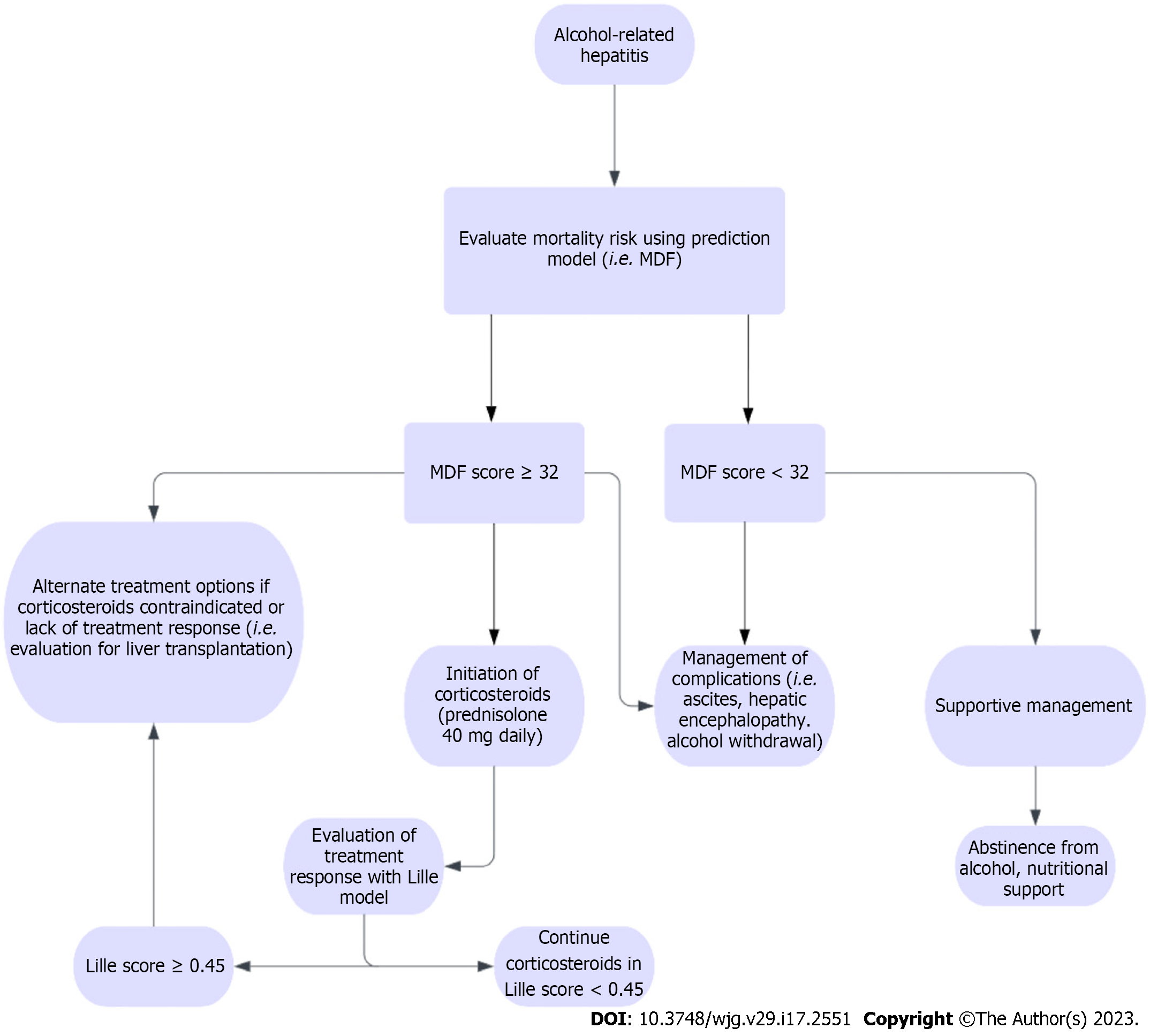
Figure 7 Treatment algorithm for alcohol-related hepatitis.
AKI: Acute kidney injury.
- Citation: Chaudhry H, Sohal A, Iqbal H, Roytman M. Alcohol-related hepatitis: A review article. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(17): 2551-2570
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i17/2551.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2551