©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2023; 29(14): 2101-2113
Published online Apr 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2101
Published online Apr 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2101
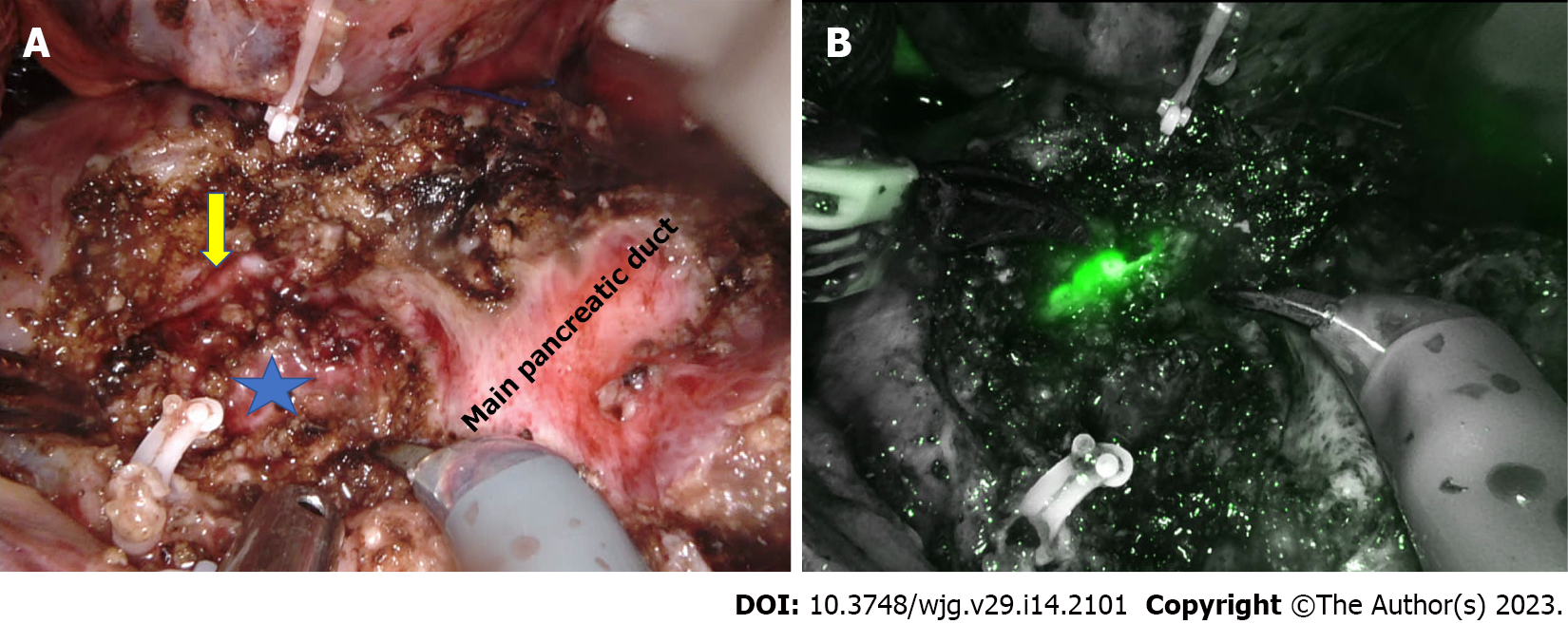
Figure 1 Robotic modified Frey’s procedure.
A: Pancreatic head coring is done till the level of the posterior wall of the pancreatic duct (marked with star). The bile duct can be seen on the medial wall of the cored-out tissue (arrow); B: Indocyanine green fluorescence demonstrates the bile duct on the medial wall of the cored-out tissue.
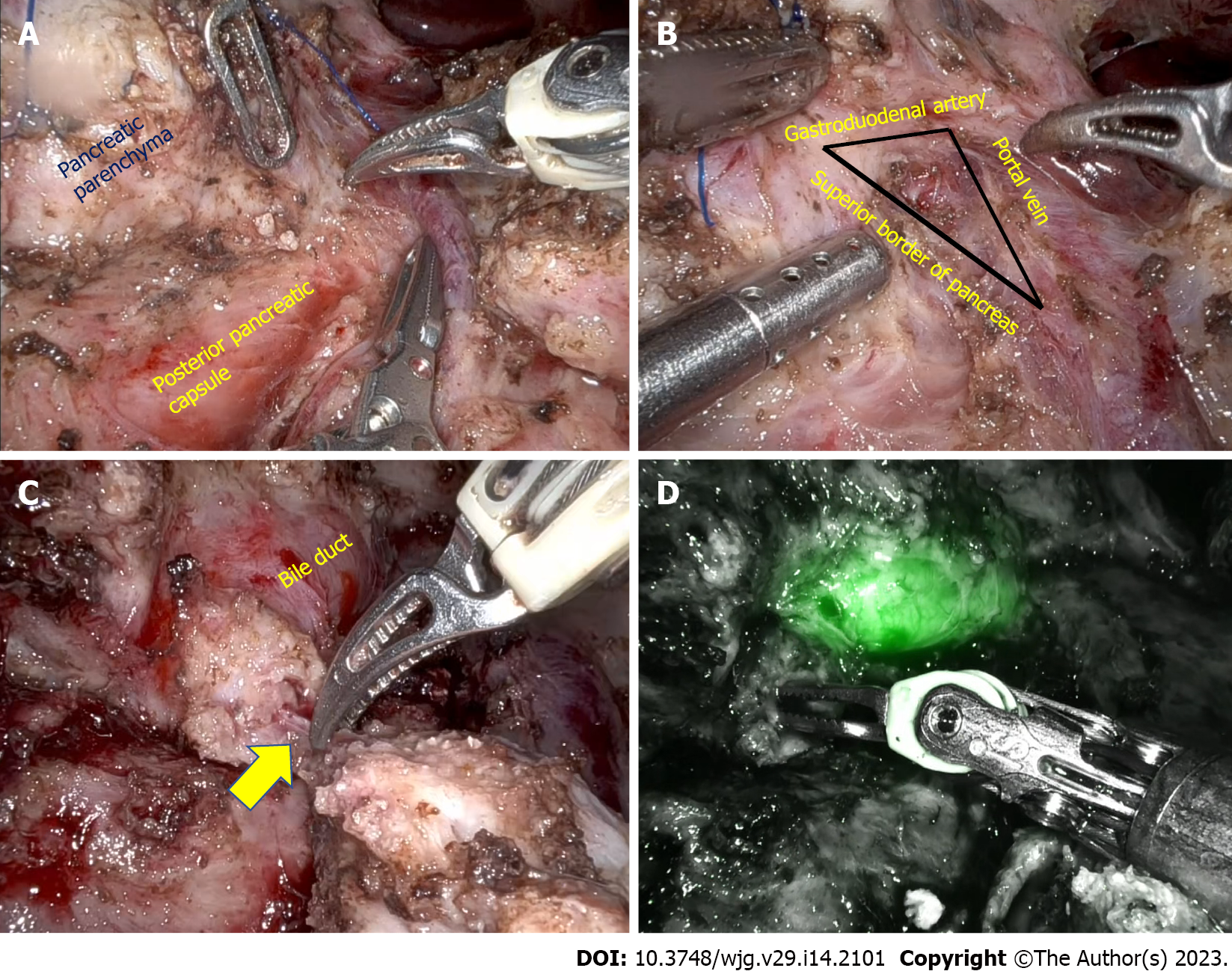
Figure 2 Robotic duodenum preserving pancreatic head resection.
A: Dissection of the pancreatic parenchyma from the posterior pancreatic capsule; B: Identification of the common bile duct in the triangle formed by the gastroduodenal artery, superior border of the pancreas, and portal vein; C: Pancreatic duct (arrow) divided at its junction with the bile duct; D: Post pancreatic head resection, indocyanine green fluorescence demonstrates bile duct.
- Citation: Kalayarasan R, Shukla A. Changing trends in the minimally invasive surgery for chronic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(14): 2101-2113
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i14/2101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2101