©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2022; 28(48): 6909-6921
Published online Dec 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i48.6909
Published online Dec 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i48.6909
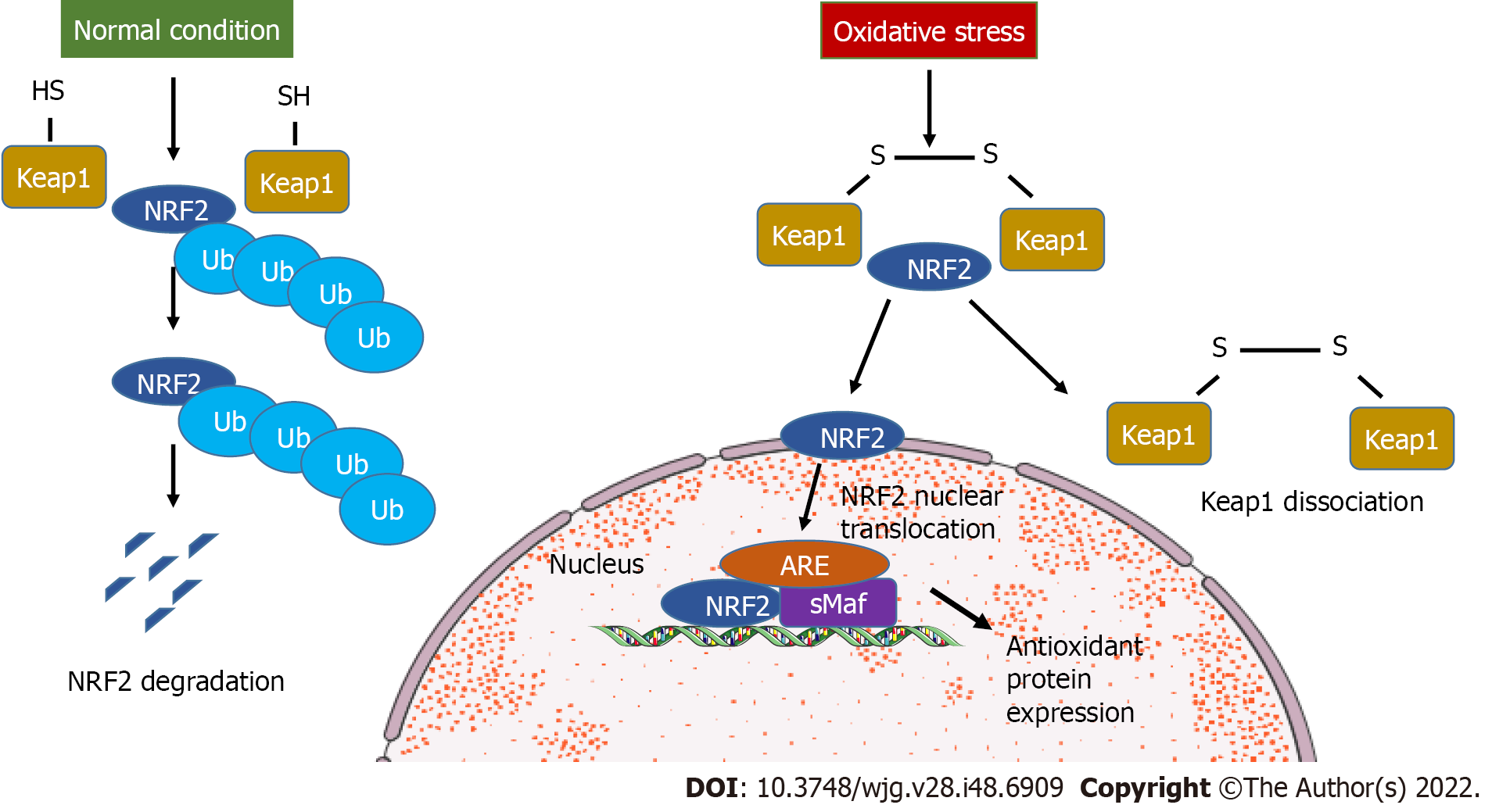
Figure 1 Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1-dependent nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling.
During oxidative stress, nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) detaches from kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) and translocates to the nucleus to bind the target genes. In normal conditions, NRF2 is ubiquitinylated and undergoes degradation. ARE: Antioxidant responsive element; SMaf: Small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homologue; Ub: Ubiquitin.
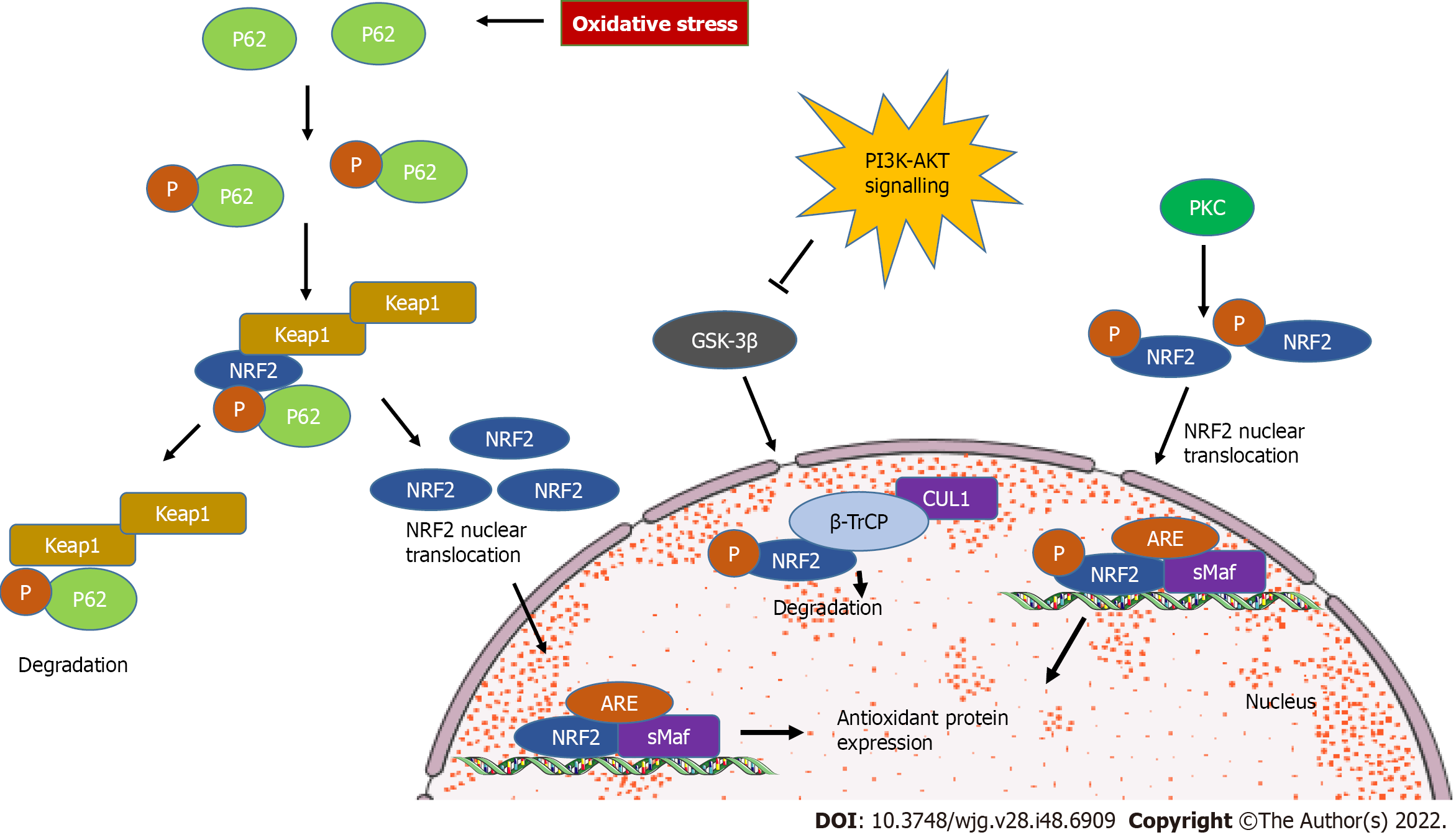
Figure 2 Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1-independent nuclear factor-erythroid 2 signaling.
During oxidative stress, selective autophagy substrate p62 competes with nuclear factor-erythroid 2 (NRF2) to bind with kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1). As a consequence, NRF2 dissociates from Keap1 and translocates to the nucleus to induce target genes. Glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) phosphorylates the NRF2 subunit Nrf-ECH homology (Neh) 6, leading to degradation by β-transducin repeats containing protein (β-TrCP). Phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase-protein kinase B (AKT) signaling could inhibit GSK-3β. Protein kinase C phosphorylates Ser40 in Neh2, inducing NRF2 translocation to the nucleus. ARE: Antioxidant responsive element; SMaf: Small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homologue.
- Citation: Bukke VN, Moola A, Serviddio G, Vendemiale G, Bellanti F. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2-mediated signaling and metabolic associated fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(48): 6909-6921
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i48/6909.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i48.6909