©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2022; 28(32): 4635-4648
Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4635
Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4635
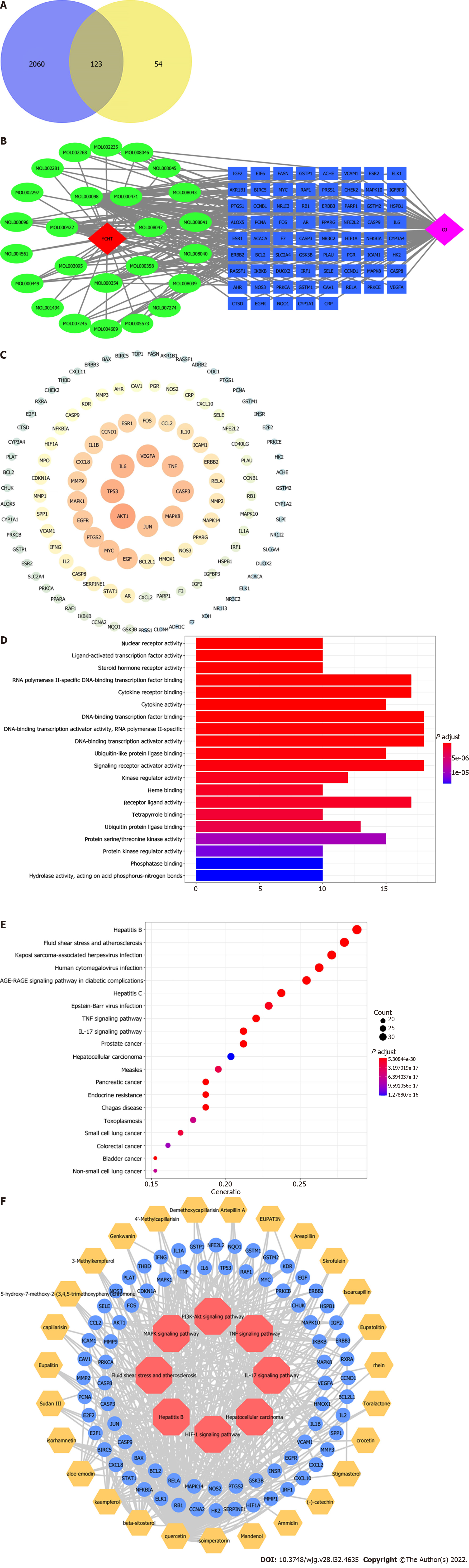
Figure 1 Network construction.
A: Venn diagram of the candidate targets in Yinchenhao decoction (YCHD) and obstructive jaundice (OJ); B: The Component-Target network. The blue circles refer to 123 putative targets of YCHD for the treatment of OJ. The red and purple diamonds represent YCHD and OJ, respectively. The green oval represents the chemical composition. The blue rectangle represents the target protein. The degree indicates the number of routes connected to this node in the network; C: The protein–protein interaction network. The size of the set node is proportional to the degree, and the larger the degree, the redder the color, indicating that the target interaction is higher. The key targets are protein kinase B, tumor protein 53, interleukin 6, vascular endothelial growth factor A, and caspase-3. They are the core targets of YCHD in treating OJ; D: The Gene Ontology enrichment analysis of involved biological processes; E: The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomics pathway enrichment analysis of putative targets; F: Component-target-signaling pathway network. The red hexagon represents the signaling pathway; the yellow hexagon represents the component; and the blue circle represents the target.
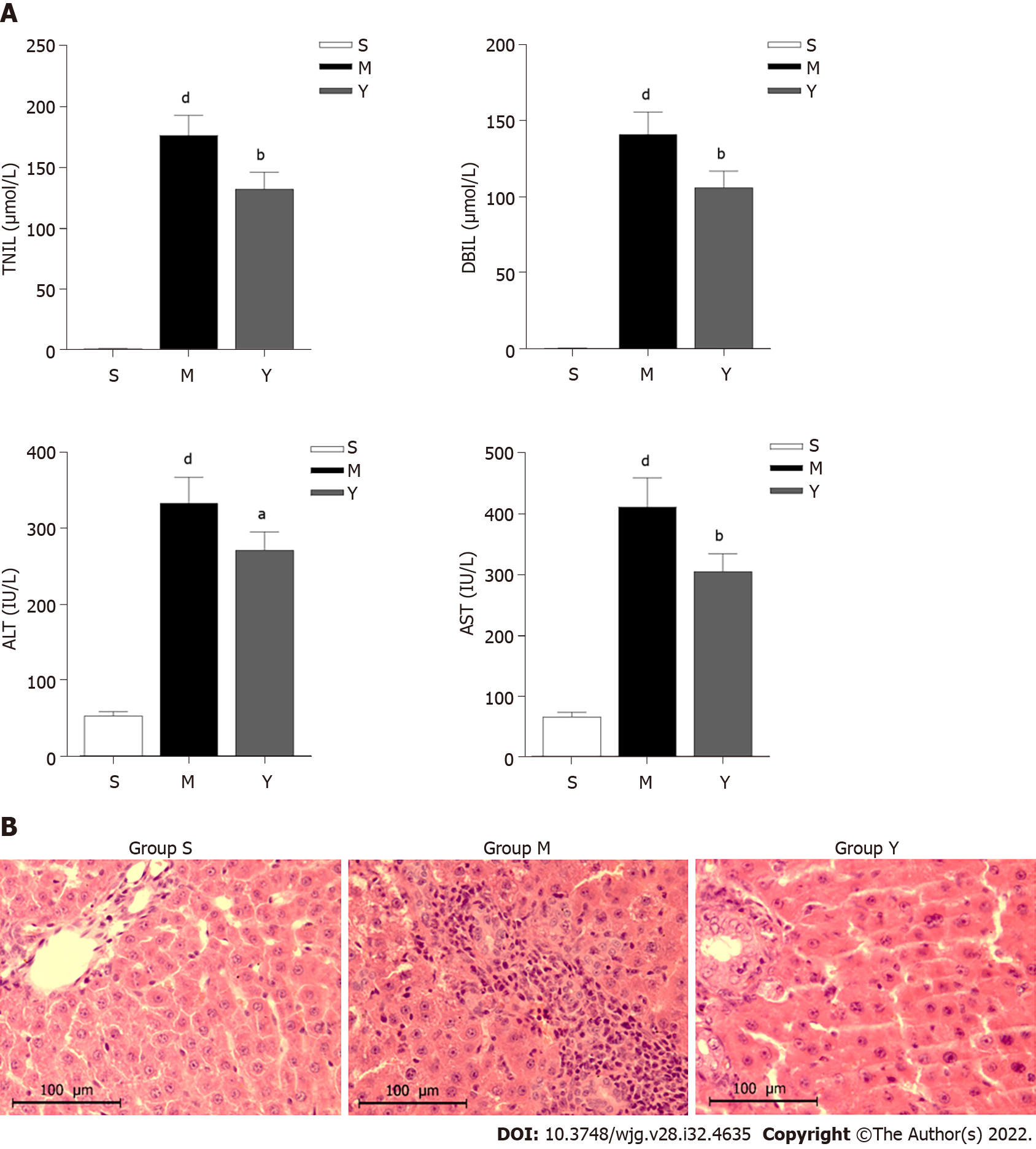
Figure 2 Yinchenhao decoction relieves the hepatic injury induced by obstructive jaundice.
A: Yinchenhao decoction (YCHD) treatment improved the liver function of obstructive jaundice (OJ) rats. The concentrations of total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, aspartate transaminase, and alanine aminotransferase in the serum of rats; B: Histological changes of liver tissue (hematoxylin and eosin staining ×400, scale bar 100 µm). Group S: Sham group; Group M: OJ model group; Group Y: YCHD-treated group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs Group M; and dP <0.001 vs Group S. TBIL: Total bilirubin; DBIL: Direct bilirubin; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate transaminase.
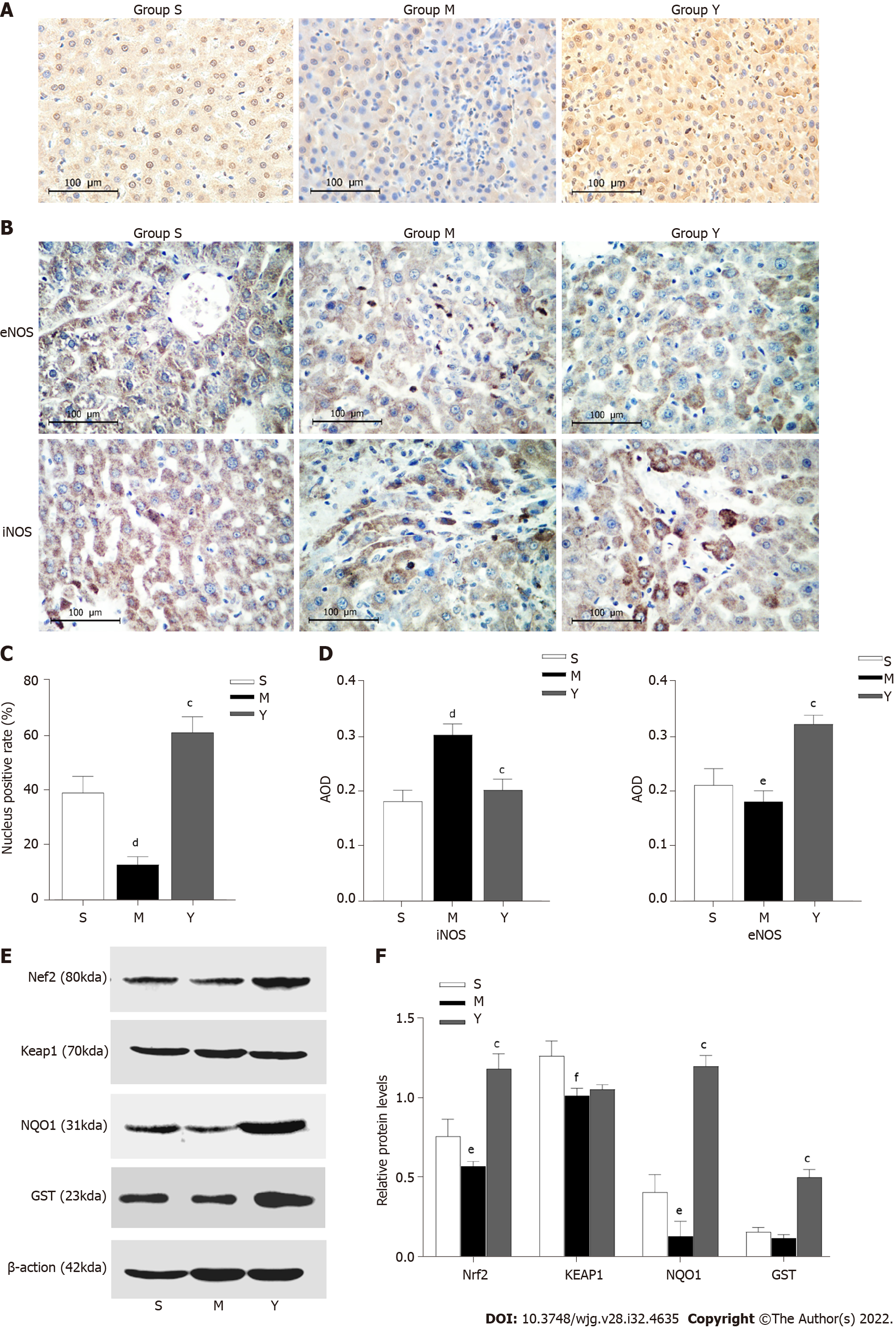
Figure 3 Effects of Yinchenhao decoction on the proteins related to the NF-E2 related factor 2 signaling pathway.
A: Effect of Yinchenhao decoction (YCHD) on NF-E2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) translocation. Nrf2 nucleus localization was measured by immunohistochemistry (DAB staining × 400, scale bar 100 µm). The nucleus is blue and the positive expression of DAB is brown; B: Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in each group (scale bar 100 µm); C: The nucleus positive rate of Nrf2; D: Relative expression levels of iNOS and eNOS; E: Validation of the potential targets using western blotting. Representative western blotting images of the protein kinase of Nrf2, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1), and glutathione-S-transferase (GST); F: The bar chart displays the relative levels of Nrf2, Keap1, NQO1 and GST. Group S: Sham group; Group M: Obstructive jaundice model group; Group Y: YCHD-treated group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs Group M; dP <0.001, eP < 0.05 , fP < 0.01 vs Group S.
- Citation: Liu JJ, Xu Y, Chen S, Hao CF, Liang J, Li ZL. The mechanism of Yinchenhao decoction in treating obstructive-jaundice-induced liver injury based on Nrf2 signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(32): 4635-4648
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i32/4635.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4635