©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2021; 27(25): 3863-3876
Published online Jul 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i25.3863
Published online Jul 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i25.3863
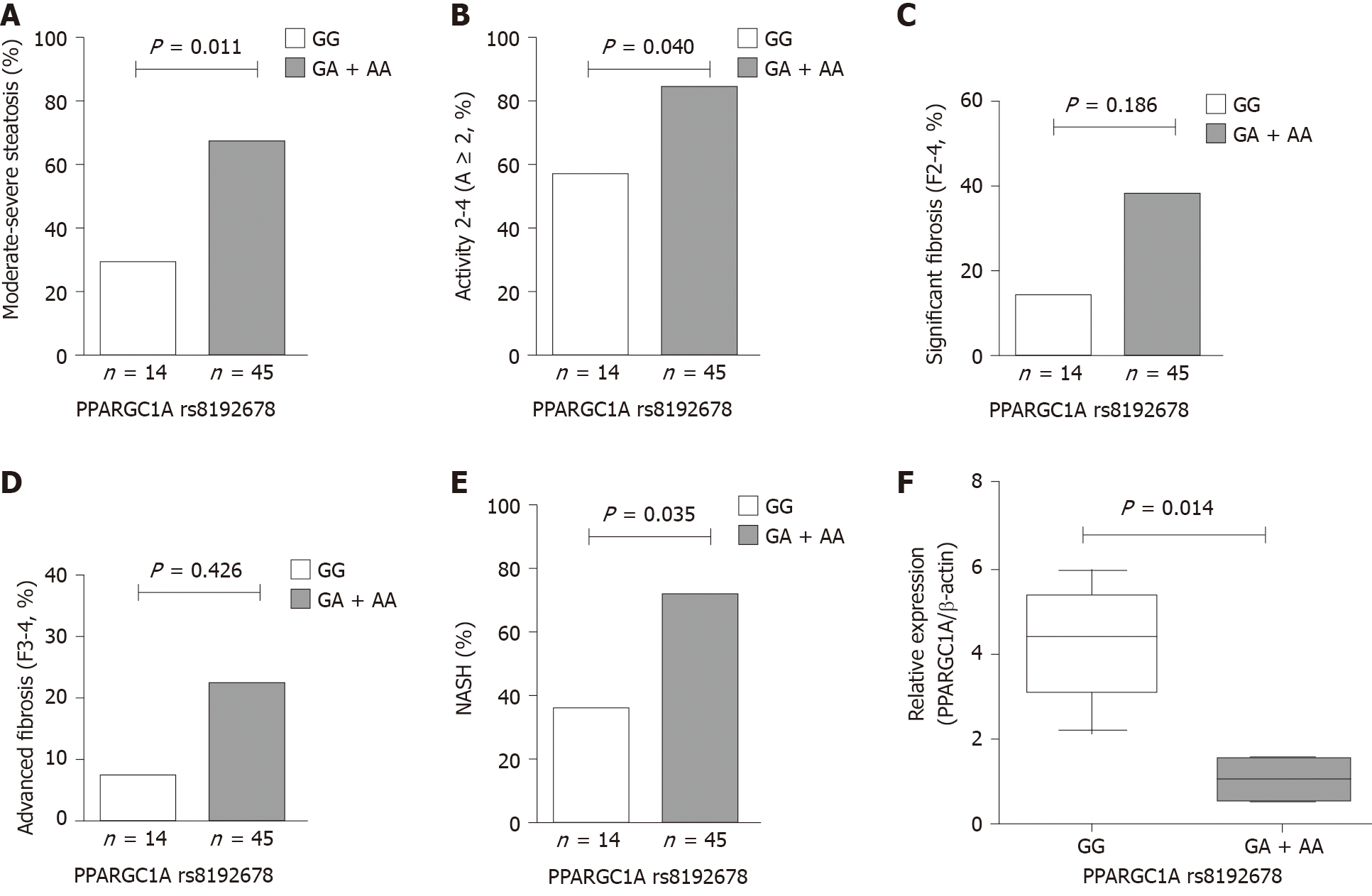
Figure 1 Comparison of various quantitative phenotypes (hepatic histological features and mRNA expression) in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease at the PPARGC1A rs8192678 polymorphism.
A-E: Prevalence of moderate-severe steatosis (S2-3), activity 2-4 (A ≥ 2), significant fibrosis (F2-4), advanced fibrosis (F3-4), and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis according to the PPARGC1A rs8192678 polymorphism in 59 patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The reference genotype for the PPARGC1A rs8192678 polymorphism was GG, and a mode of dominant inheritance was used; F: The intrahepatic mRNA expression of PPARGC1A between the GG group (n = 5) and the GA or AA group (n = 5) at PPARGC1A rs8192678. NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Zhang RN, Shen F, Pan Q, Cao HX, Chen GY, Fan JG. PPARGC1A rs8192678 G>A polymorphism affects the severity of hepatic histological features and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease . World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(25): 3863-3876
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i25/3863.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i25.3863