Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2021; 27(24): 3682-3692
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3682
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3682
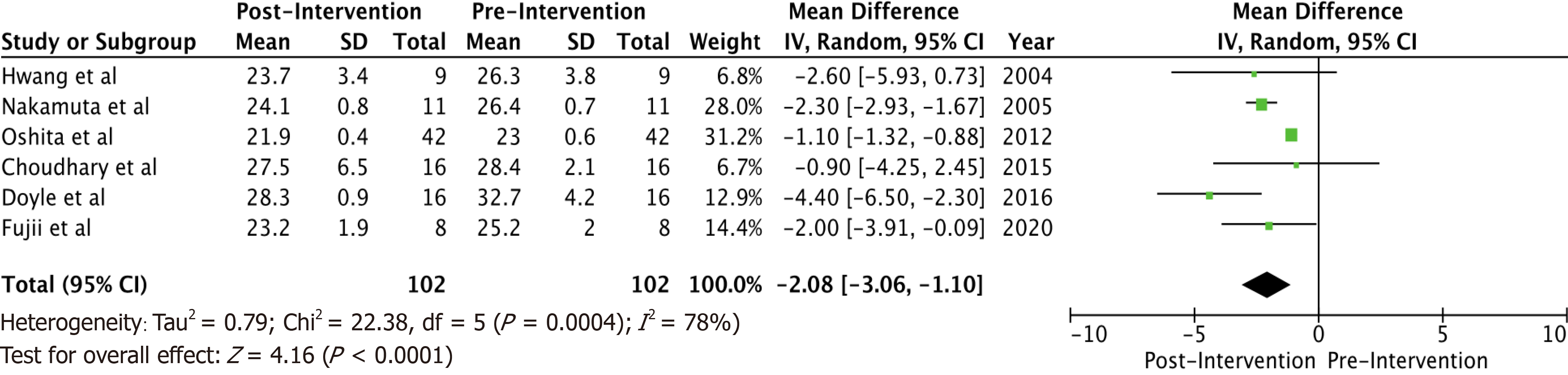
Figure 1 Forest plot showing mean difference in body mass index post-pre intervention in the intervention groups.
Mean difference = -2.08 (-3.06, 1.10, I2 = 78%), with a significantly lower post-intervention body mass index as compared to the pre-intervention body mass index. CI: Confidence interval; SD: Standard deviation.
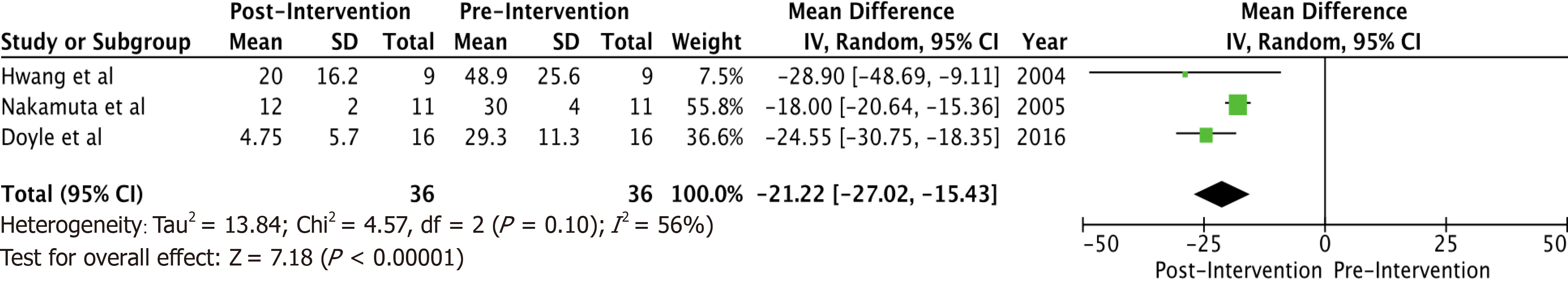
Figure 2 Forest plot showing mean difference in steatosis post-pre intervention.
Mean difference = -21.22 (-27.02, -15.43, I2 = 56%), with significantly lower post intervention steatosis as compared to pre intervention steatosis. CI: Confidence interval; SD: Standard deviation.
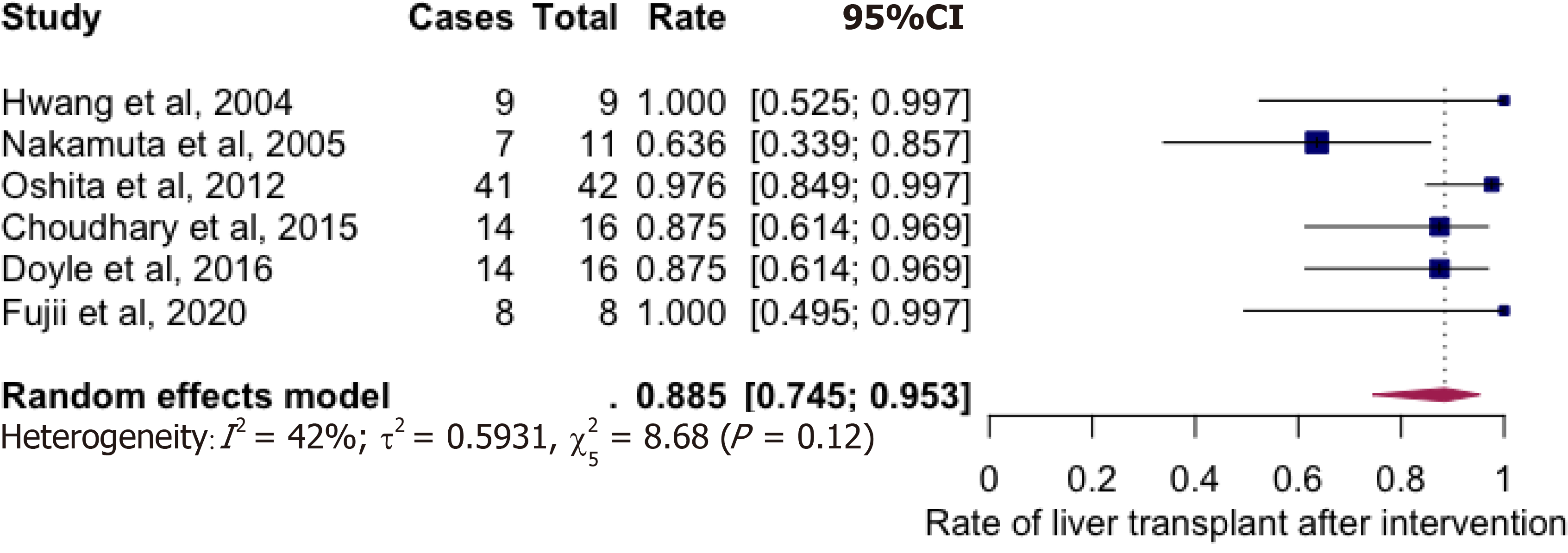
Figure 3 Living liver donation rates after weight loss interventions.
Rate = 88.5% (74.5%-95.3%, I2 = 42%). CI: Confidence interval.
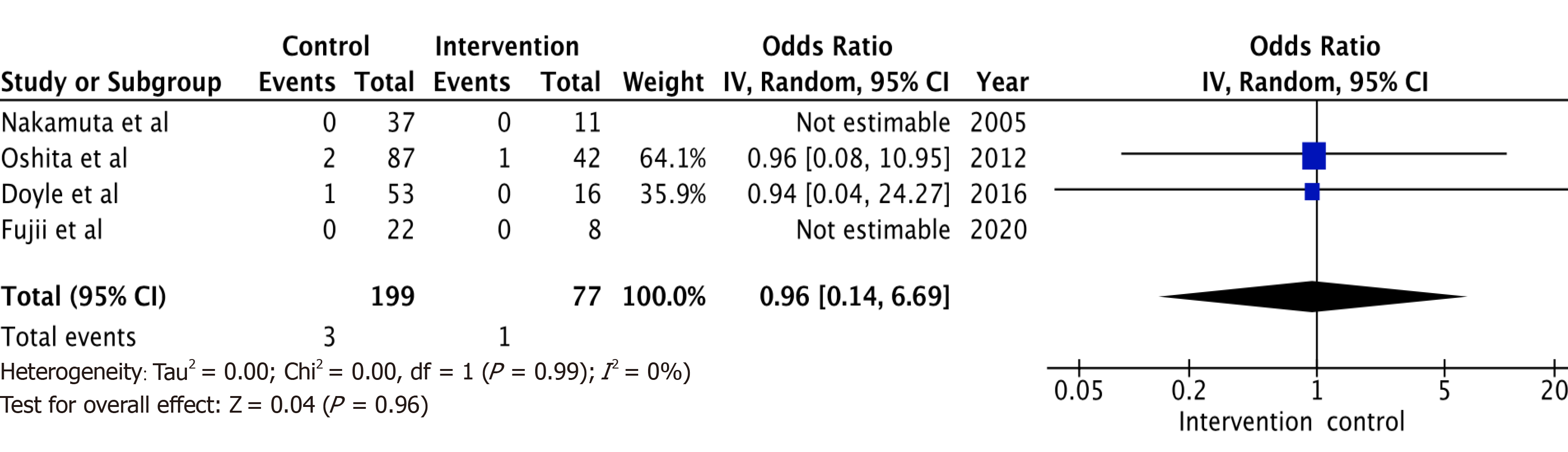
Figure 4 Odds ratio comparing rate of donor post-operative biliary complications in intervention group compared to control donors - odds ratio 0.
96 (0.14, 6.69), I2 = 0.
- Citation: Trakroo S, Bhardwaj N, Garg R, Modaresi Esfeh J. Weight loss interventions in living donor liver transplantation as a tool in expanding the donor pool: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(24): 3682-3692
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i24/3682.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3682