©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2021; 27(24): 3595-3608
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3595
Published online Jun 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3595
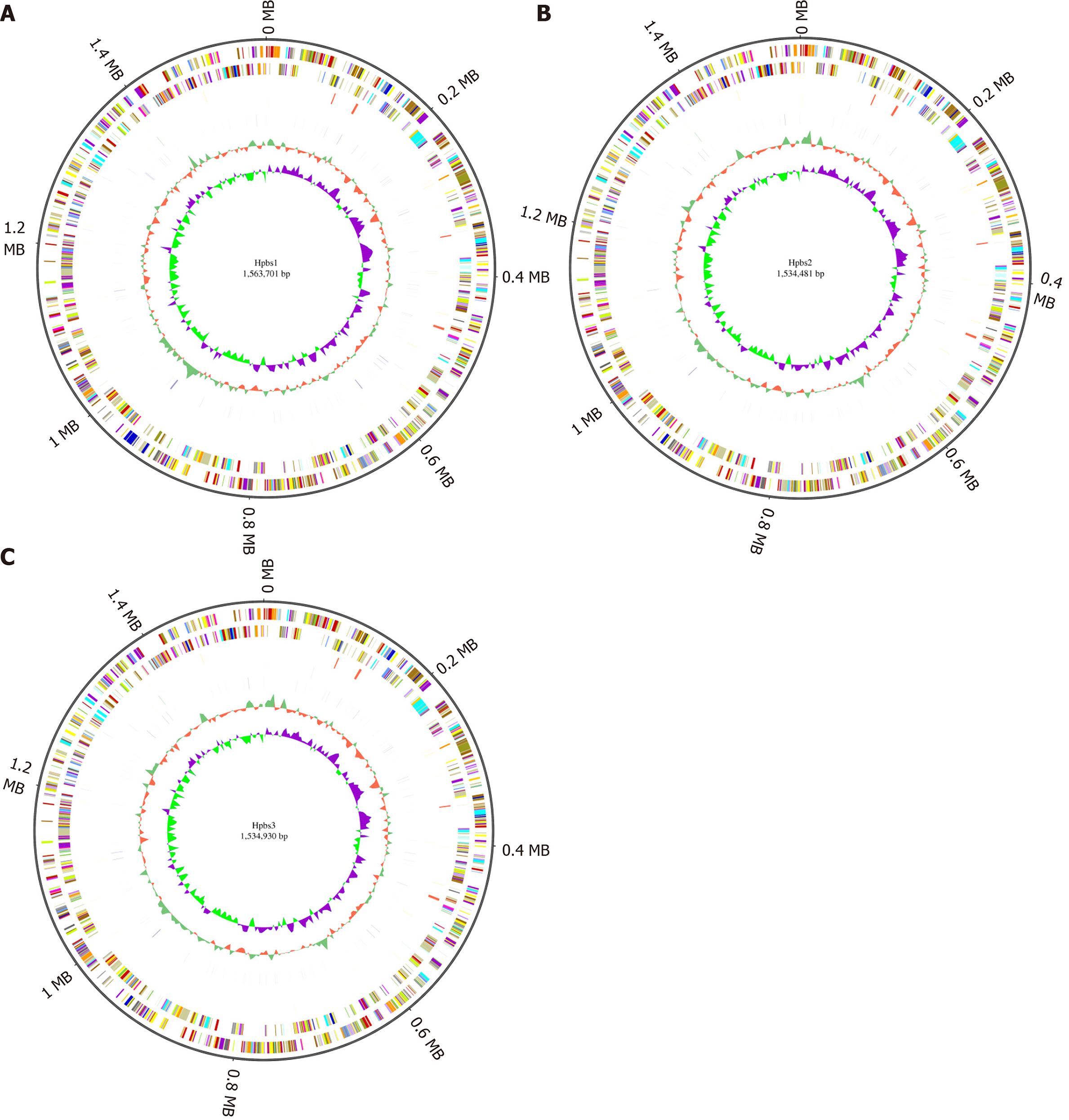
Figure 1 Circular genome analysis of three drug-resistant strains.
A: Hpbs1; B: Hpbs2; C: Hpbs3.
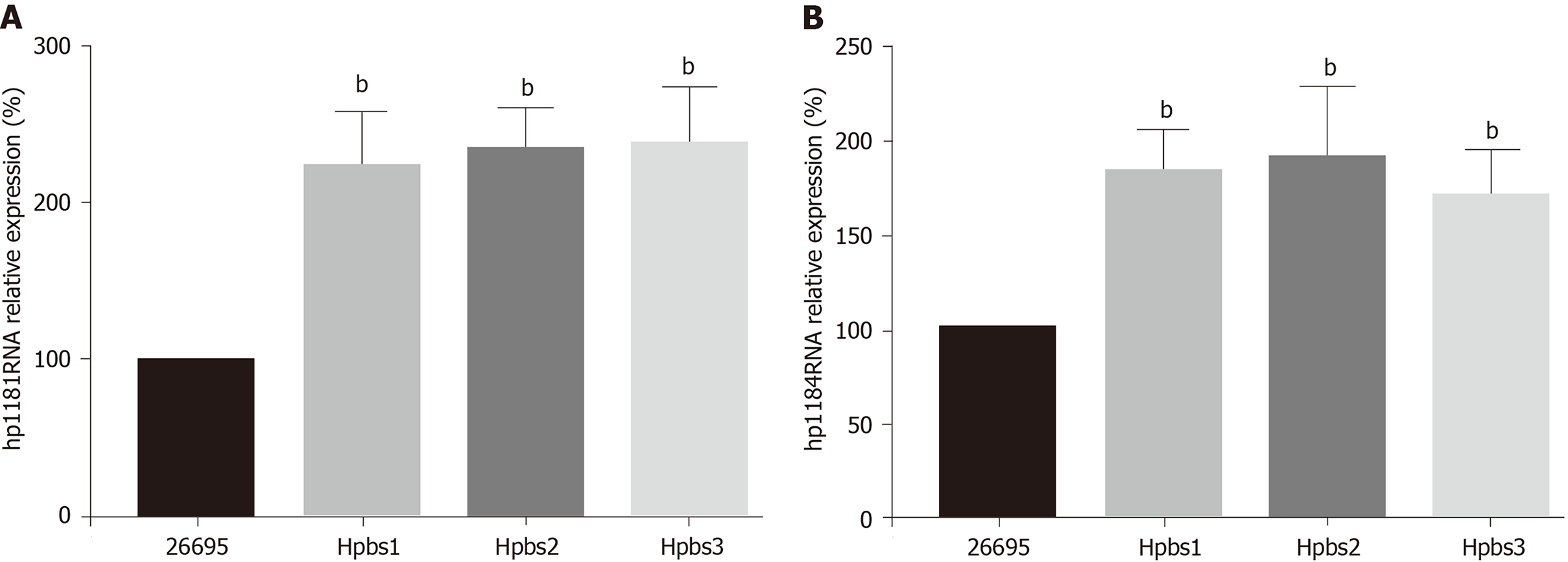
Figure 2 Hp1181 and hp1184 gene expression in drug-resistant strains.
A: Hp1181; B: Hp1184. bP < 0.01.
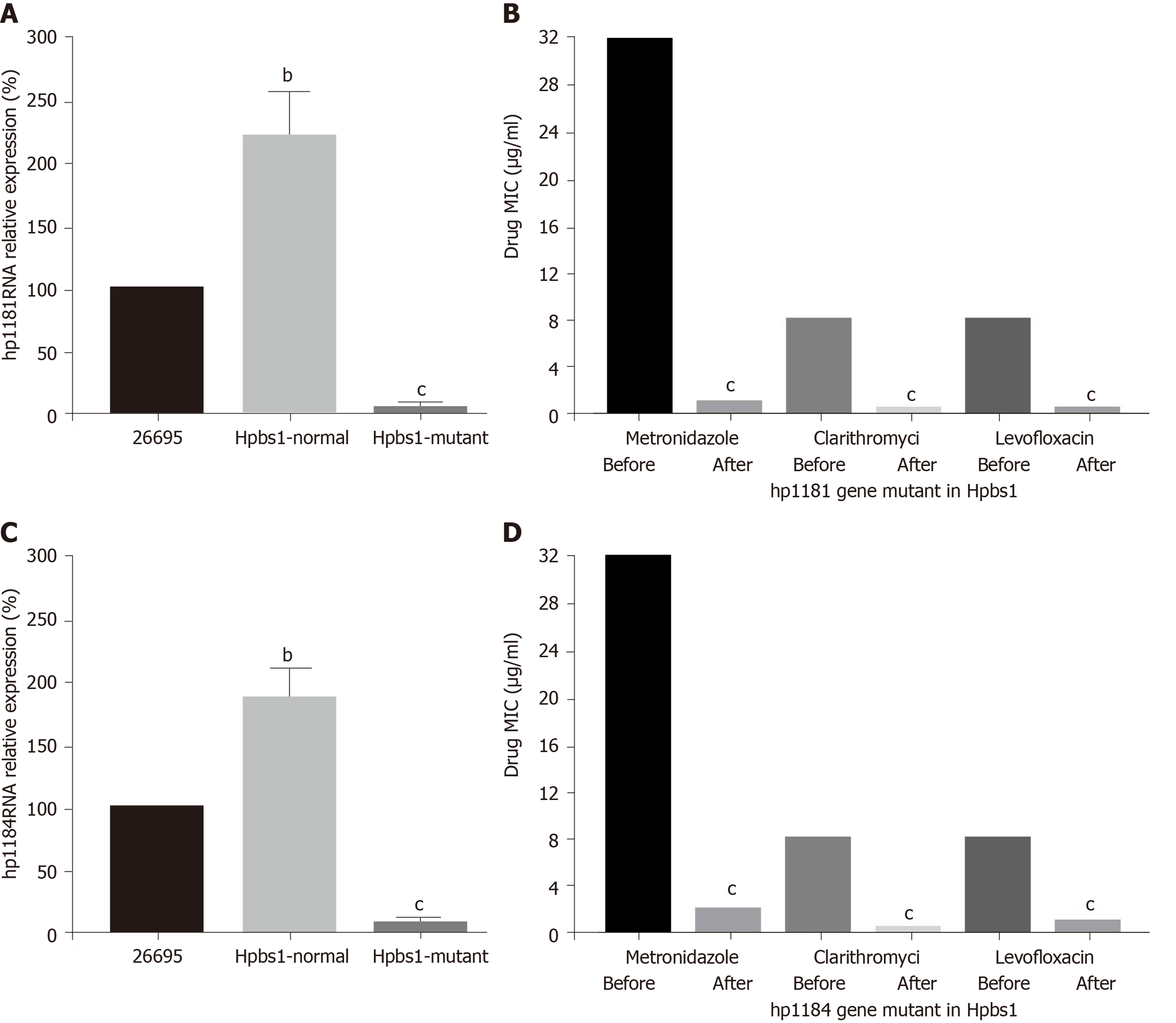
Figure 3 Drug sensitivity is improved after knockout of the drug-resistant genes.
A: Hp1181 knockout; B: Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) after hp1181 knockout; C: Hp1184 knockout; D: MIC after hp1184 knockout. MIC: Minimal inhibitory concentration. bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001.
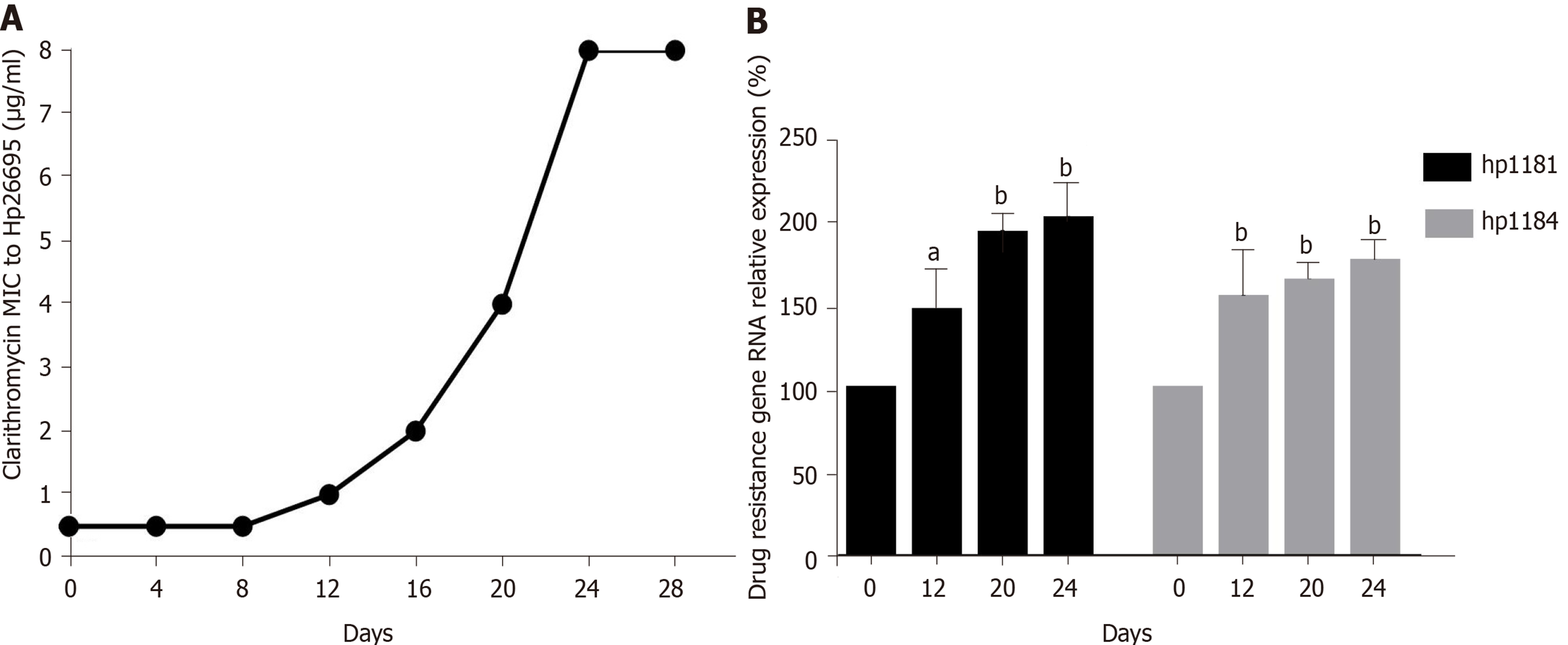
Figure 4 Induction of resistance to clarithromycin and expression of drug-resistant genes in Helicobacter pylori.
A: Induction of clarithromycin resistance; B: Expression of drug-resistant genes. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Li XH, Huang YY, Lu LM, Zhao LJ, Luo XK, Li RJ, Dai YY, Qin C, Huang YQ, Chen H. Early genetic diagnosis of clarithromycin resistance in Helicobacter pylori. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(24): 3595-3608
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i24/3595.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3595