©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2020; 26(28): 4076-4093
Published online Jul 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4076
Published online Jul 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4076
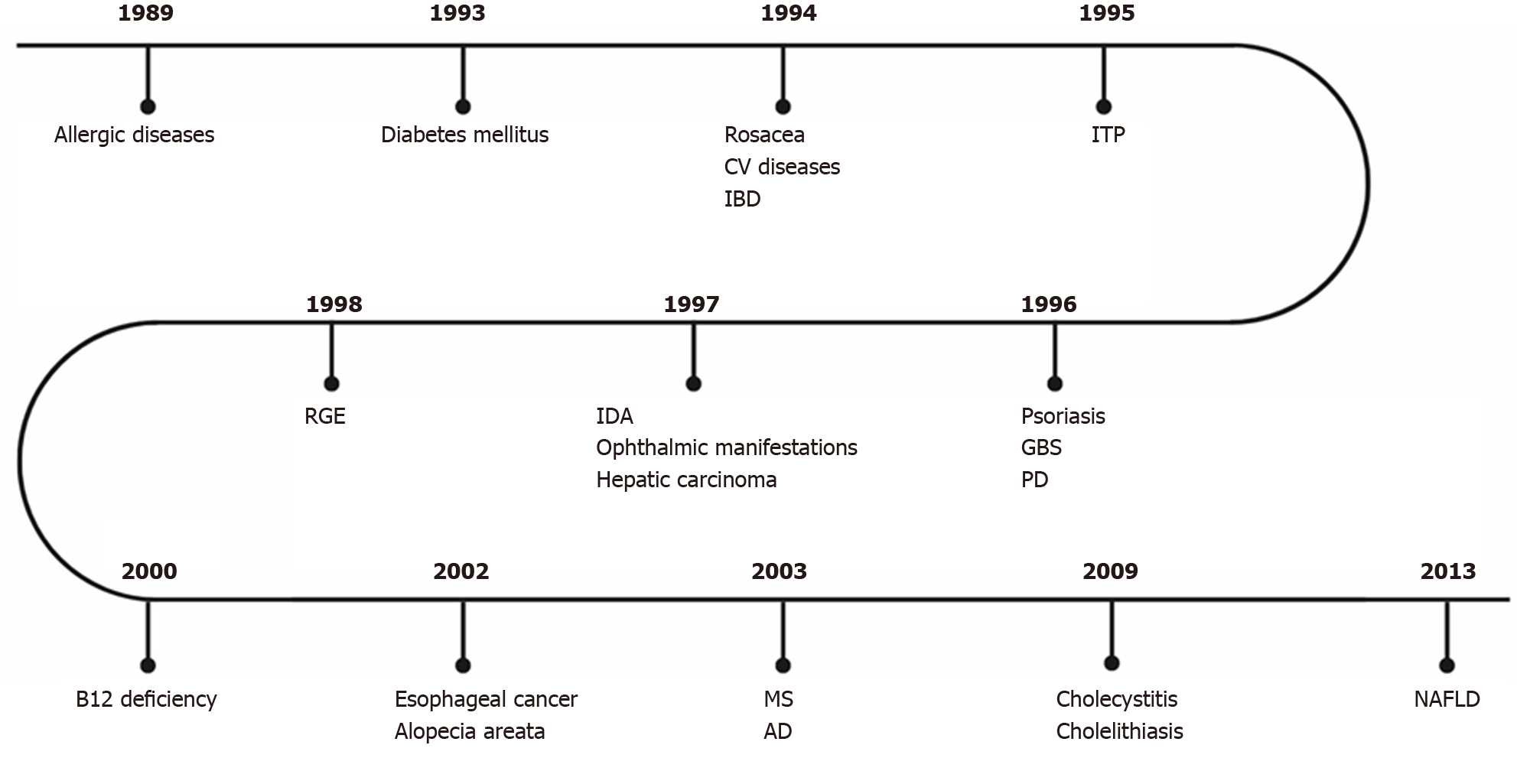
Figure 1 First studies on the association between Helicobacter pylori infection and extragastric manifestations over time.
CV: Cardiovascular; IBD: Intestinal bowel disease; ITP: Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura; GBS: Guillain-Barré Syndrome; IDA: Iron deficiency anemia; RGE: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; PD: Parkinson’s disease; MS: Multiple sclerosis; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
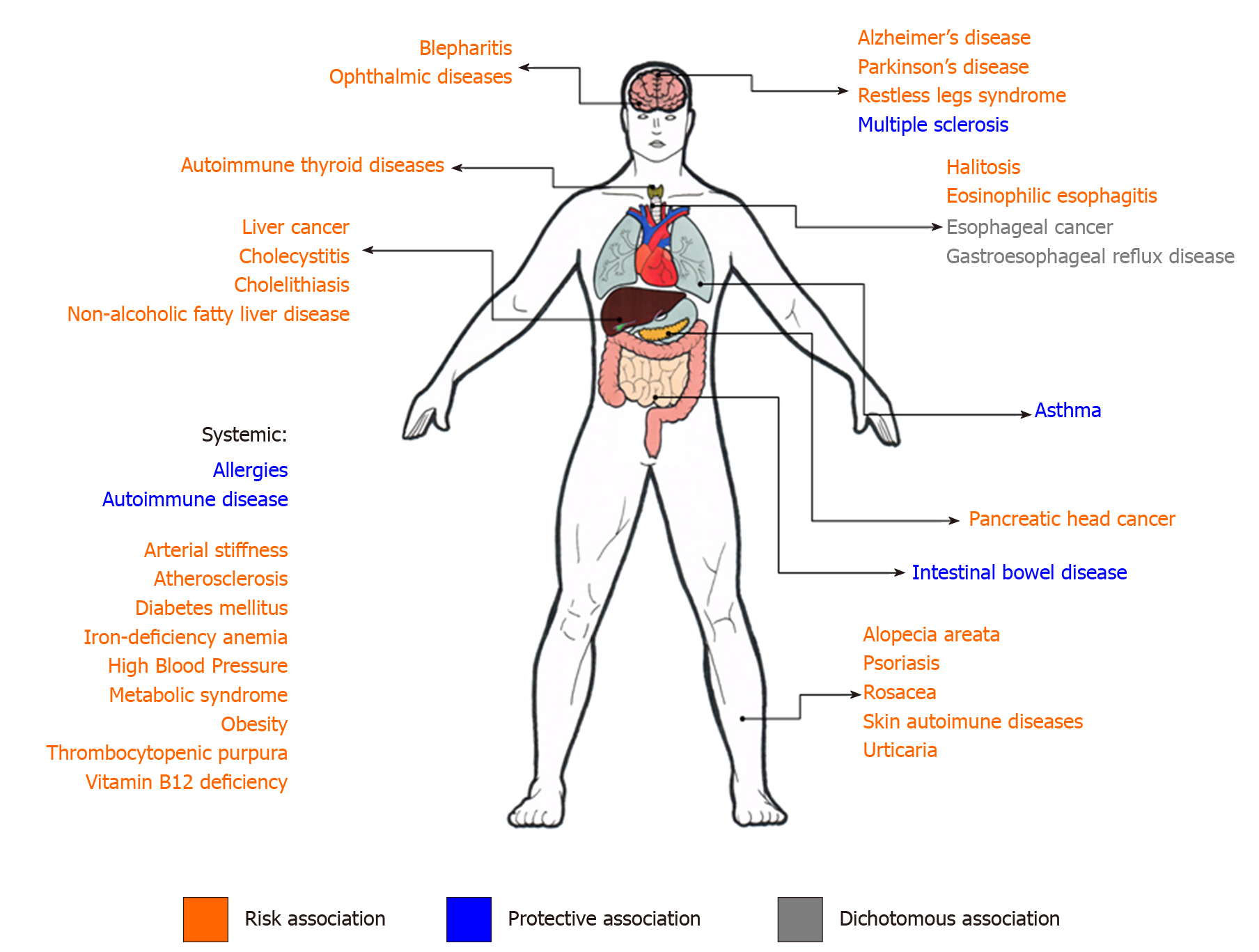
Figure 2 Summary scheme of non-gastric manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection.
In orange, the manifestations for which Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection represents a risk association. In green, the manifestations for which H. pylori infection represents a protective association. In gray, the manifestations for which studies show a dichotomous association.
- Citation: Santos MLC, de Brito BB, da Silva FAF, Sampaio MM, Marques HS, Oliveira e Silva N, de Magalhães Queiroz DM, de Melo FF. Helicobacter pylori infection: Beyond gastric manifestations. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(28): 4076-4093
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i28/4076.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4076