©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2020; 26(22): 3098-3109
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3098
Published online Jun 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3098
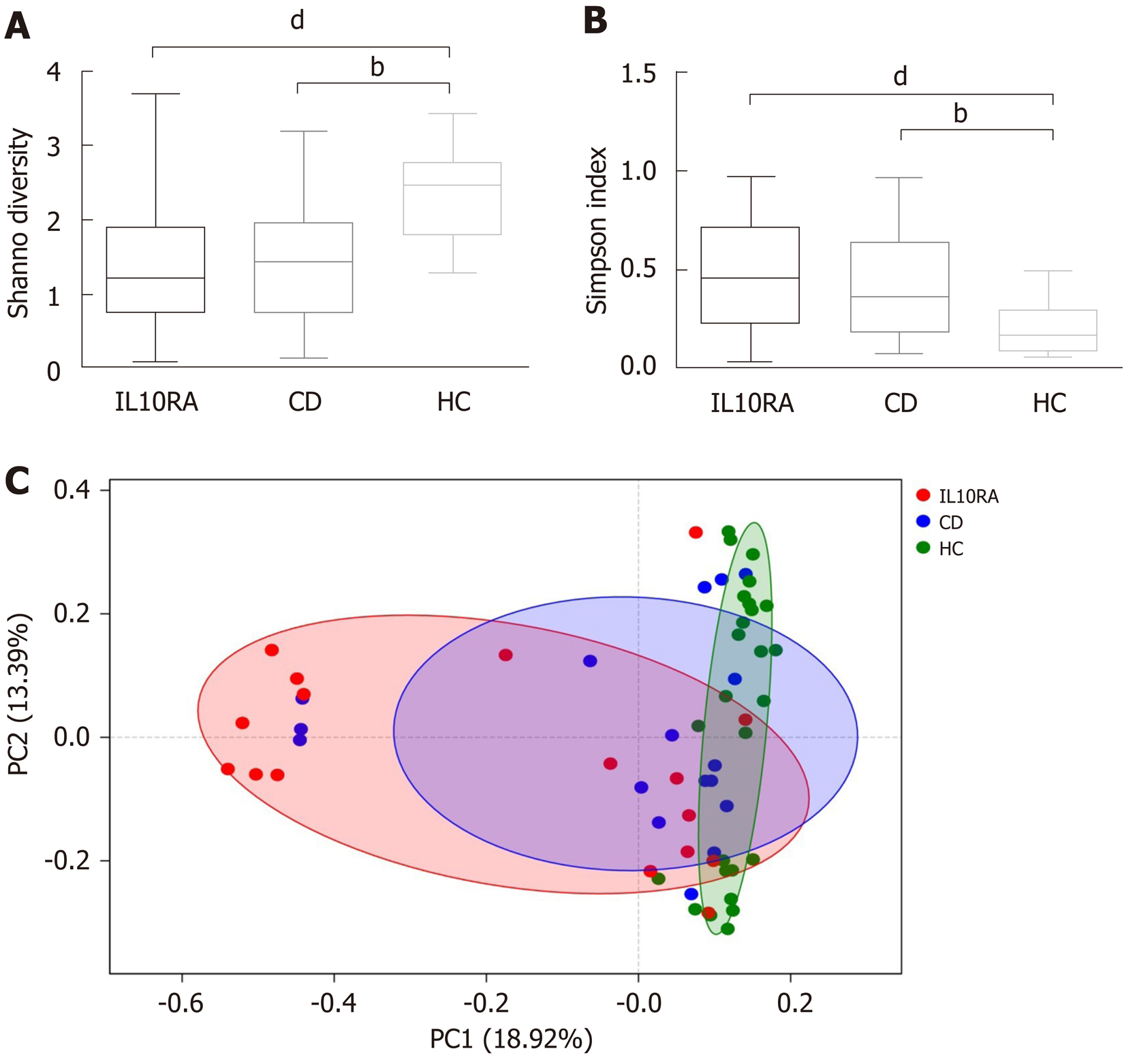
Figure 1 Diversity of the gut microbiome at the operational taxonomic unit level.
A: Box plot of Shannon and Simpson index. For Shannon index, IL10RA vs healthy control (HC) group, P = 0.0007; Crohn's disease (CD) group vs HC, P = 0.0020. For Simpson index, IL10RA vs HC, P = 0.0008; CD vs HC, P = 0.0040. bP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001; B: PCoA using unweighted unifrac distance of operational taxonomic unit community structure. R = 0.2750, P = 0.0011. IL10RA: IL10RA group; CD: Crohn's disease group; HC: Healthy control group.
Figure 2 Community barplot and Kruskal-Wallis H test bar plot of the relative abundance of microbiome at phylum level (A, B) and LEfSe bar of the different taxa between groups using the linear discriminant analysis (C).
Taxa with higher linear discriminant analysis scores had a greater effect on the dysbiosis in each group. IL10RA: IL10RA group; CD: Crohn's disease group; HC: Healthy control group; LDA: Linear discriminant analysis.
- Citation: Xue AJ, Miao SJ, Sun H, Qiu XX, Wang SN, Wang L, Ye ZQ, Zheng CF, Huang ZH, Wang YH, Huang Y. Intestinal dysbiosis in pediatric Crohn's disease patients with IL10RA mutations. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(22): 3098-3109
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i22/3098.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3098