©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2018; 24(17): 1919-1924
Published online May 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1919
Published online May 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1919
Figure 1 Full sequencing analysis of the hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase gene from the patient (Korean sample).
The sequence analysis shows that mutations occurred at 9 sites compared to the wild-type genotype C (the patient was infected with genotype C). The rt106 and rt118 sites are expressed as “?” because the sites contained a substitution by 2 different nucleotides.
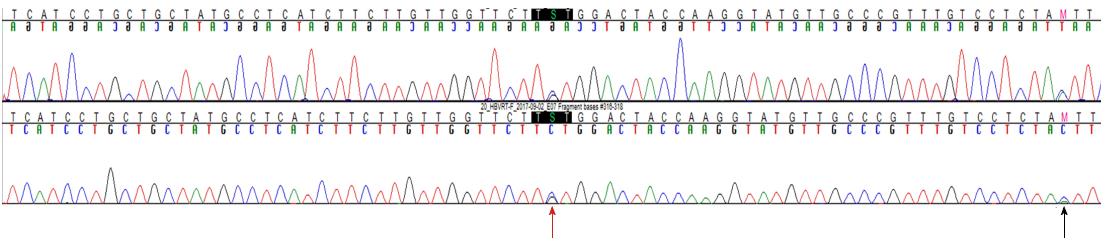
Figure 2 Chromatogram of the hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase gene from the patient.
The rt101 (red arrow) and rt118 (arrow) sites are shown as a double line because the site contained a substitution by 2 different nucleotides (cytosine and guanine).
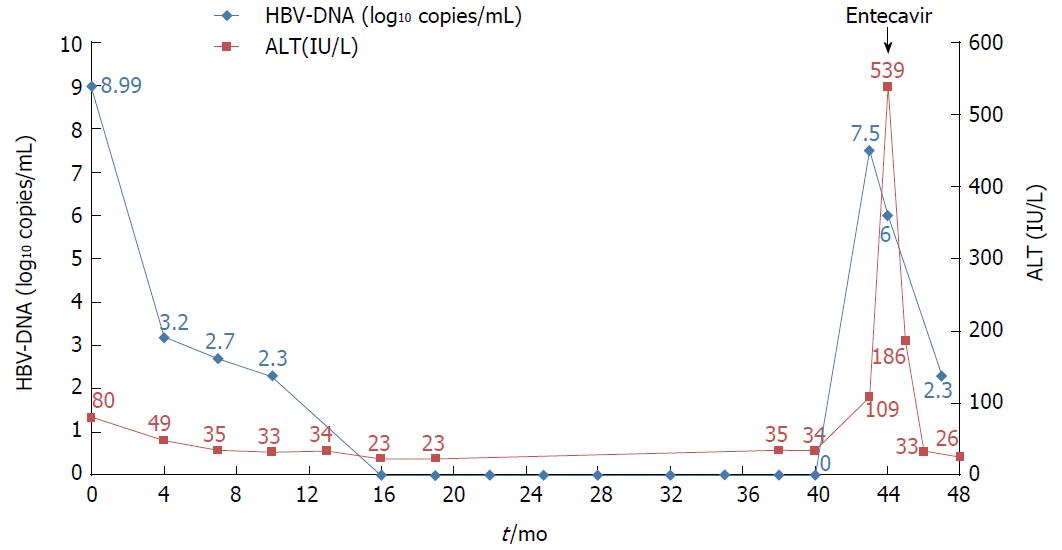
Figure 3 Clinical course of the patient.
Hepatitis B virus DNA became undetectable after 16 mo of antiviral treatment with TDF. Virologic and biochemical breakthroughs occurred at 43 mo after treatment initiation.
- Citation: Cho WH, Lee HJ, Bang KB, Kim SB, Song IH. Development of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate resistance after complete viral suppression in a patient with treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B: A case report and review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(17): 1919-1924
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i17/1919.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1919