©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2017; 23(44): 7930-7938
Published online Nov 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i44.7930
Published online Nov 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i44.7930
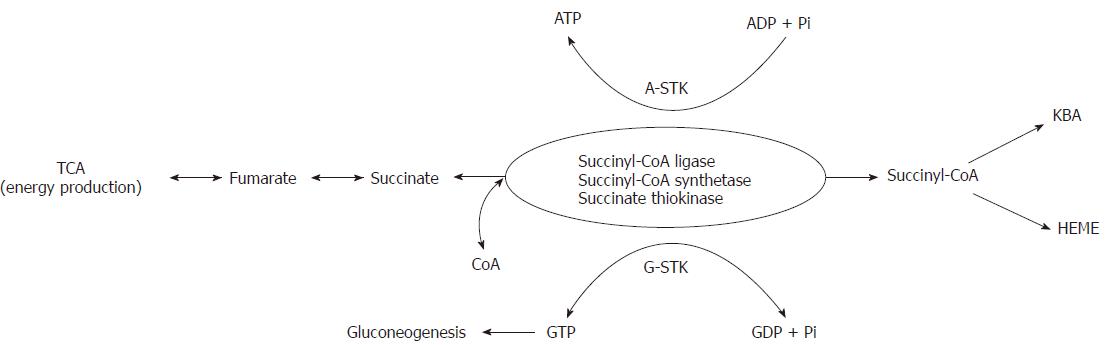
Figure 1 Metabolic catalytic activities of succinate thiokinase(s).
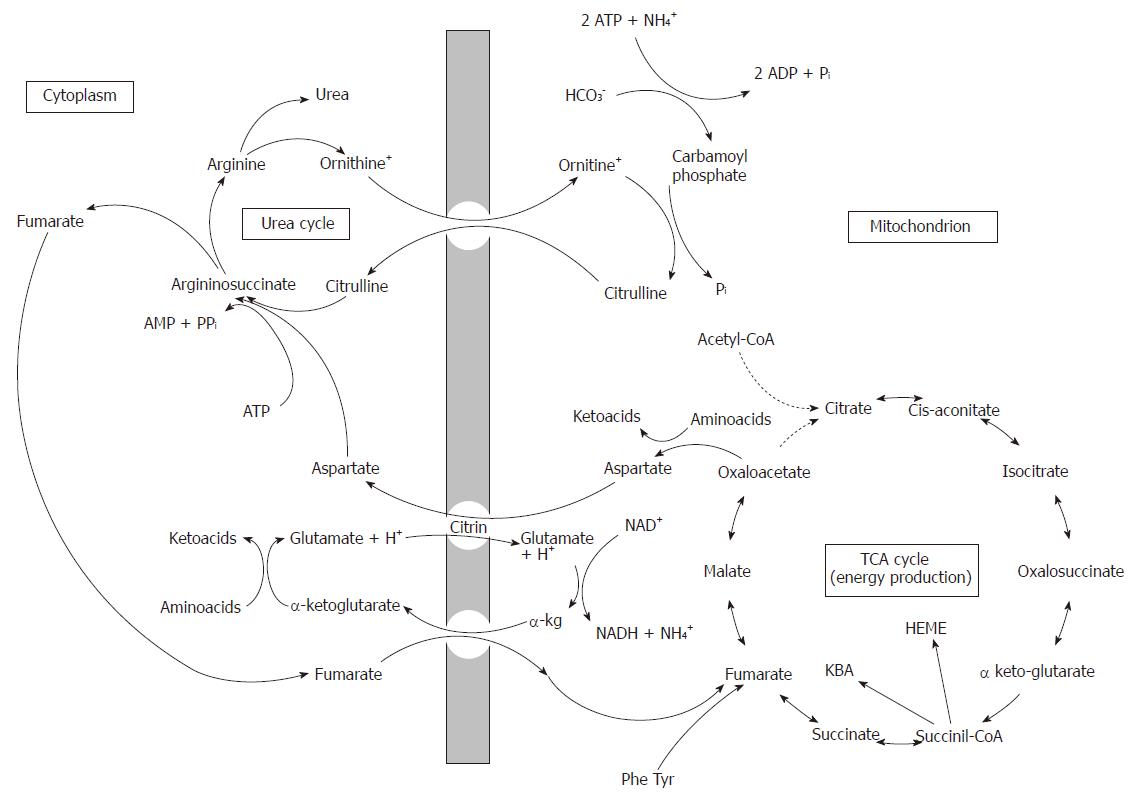
Figure 2 Metabolic interrelationships between urea cycle and TCA.
Depicted biochemical pathways show the interrelationship of the urea cycle and TCA cycle. Note that all reactions of the urea cycle are unidirectional. In the TCA cycle most reactions are reversible, except for the initial reaction of the TCA, the condensation of acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate to form citrate, and the reaction of oxidative decarboxylation of α-keto glutarate to form succinyl-CoA. Note that fumarate gained in the cytosol in the course of urea cycle (UC), to be reused in UC must be transported into the mitochondria to be converted to aspartate.
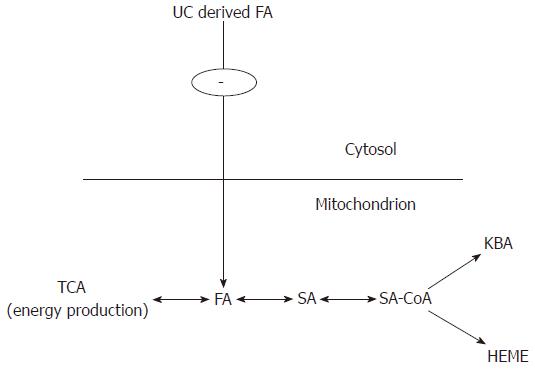
Figure 3 Metabolic exchangeable pool of fumaric acid and succinic acid.
In urea cycle disorders (UCDs) there is decreased or completely absent FA supply from the cytosol. FA deficient supply is proportional to the enzyme activity deficiency.
- Citation: Ivanovski I, Ješić M, Ivanovski A, Garavelli L, Ivanovski P. Metabolically based liver damage pathophysiology in patients with urea cycle disorders - A new hypothesis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(44): 7930-7938
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i44/7930.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i44.7930