©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2016; 22(48): 10680-10686
Published online Dec 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10680
Published online Dec 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10680
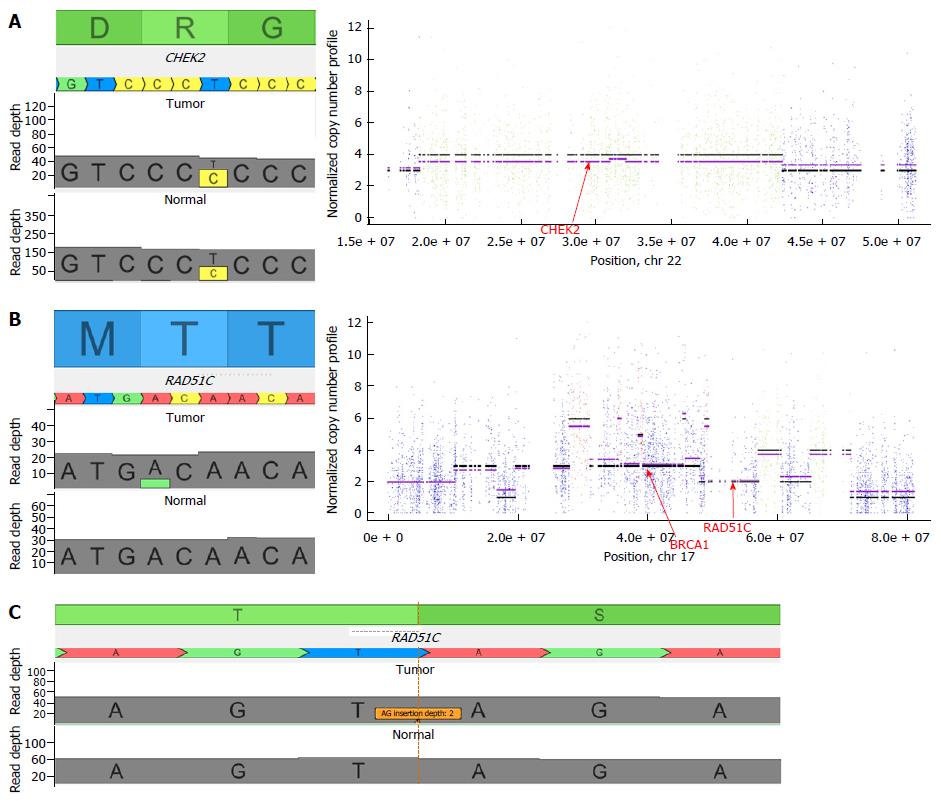
Figure 1 Genetic data of targeted alterations.
A: Patient 1 presented a T>C variation in the CHEK2 gene inducing a constitutive deleterious R117G mutation (left panel). At the chromosomal level, it appeared that chromosome 22 harbored a loss of heterozygosity inducing (right panel) a complete inactivation of CHEK2; B: Patient 2 presented a A>G variation in the RAD51C gene inducing a somatic loss of function T287A mutation (left panel). At the chromosomal level, it appeared that chromosome 17 harbored an important loss of heterozygosity at the RAD51C locus inducing a complete inactivation of RAD51C; C: Patient 2 also harbored an AG insertion resulting in a frameshift truncating mutation in the TP53BP1 gene.
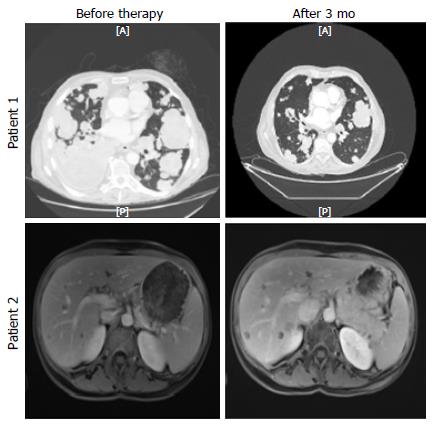
Figure 2 Computed tomography scan of patient 1 before and after 3 mo of olaparib (upper panel), and magnetic resonance imaging of liver metastasis of patient 2 before and after 3 mo of olaparib (lower panel).
- Citation: Ghiringhelli F, Richard C, Chevrier S, Végran F, Boidot R. Efficiency of olaparib in colorectal cancer patients with an alteration of the homologous repair protein. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(48): 10680-10686
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i48/10680.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10680