©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2016; 22(30): 6841-6850
Published online Aug 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i30.6841
Published online Aug 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i30.6841
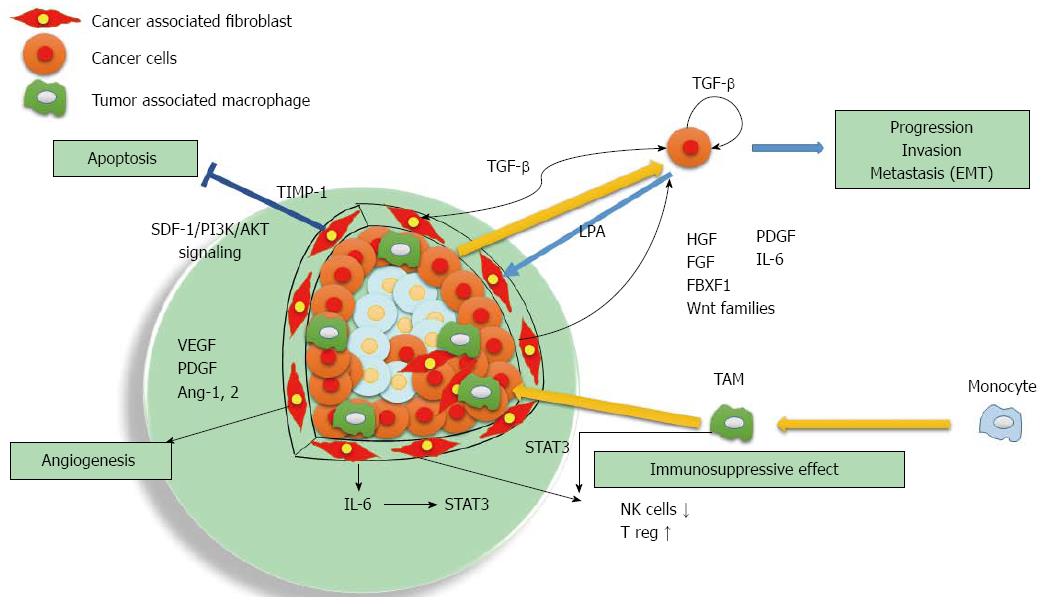
Figure 1 Microenvironment to be formed with cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor-associated macrophages.
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) mainly located at the tumor marginal zone and secreted the various cytokines such as HGF and crosstalk with hepatocellular carcinoma cells and stimulate the tumor progression, invasion and metastasis through the epithelial mesenchymal transition. TIMP-1 suppressed the tumor cell apoptosis via SDF-1/PI3K/AKT signaling. Angiogenesis is occured by the angiogenic factors including VEGF, PDGF, ang-1 and ang-2 secreted by CAFs. TAMs and CAFs make the microenvironment to the immunosuppressive condition to create favorable microenvironment for tumor progression. TAM: Tumor associated macrophage.
- Citation: Kubo N, Araki K, Kuwano H, Shirabe K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(30): 6841-6850
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i30/6841.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i30.6841