©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2016; 22(3): 1067-1077
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1067
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1067
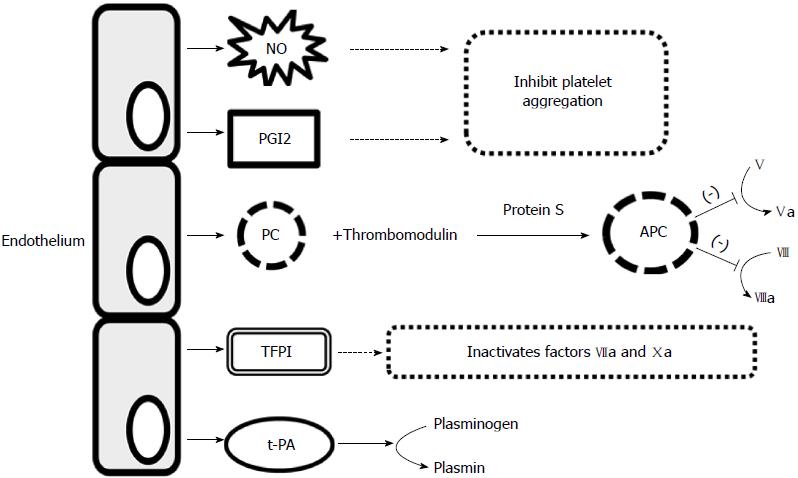
Figure 1 Anticoagulant activity of endothelium.
NO: Nitric oxide; PGI2: Prostacyclin; PC: Protein C; APC: Activated protein C; V, VIII: Coagulation factors; TFPI: Tissue factor pathway inhibitor; t-PA: Tissue-type plasminogen activator.
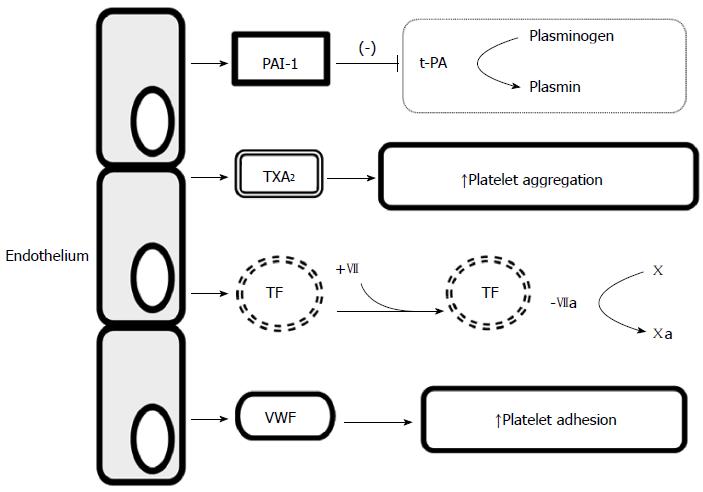
Figure 2 Procoagulant activity of endothelium.
PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1; t-PA: Tissue-type plasminogen activator; TXA2: Thromboxane A2; TF: Tissue factor; VWF: von Willebrand factor.
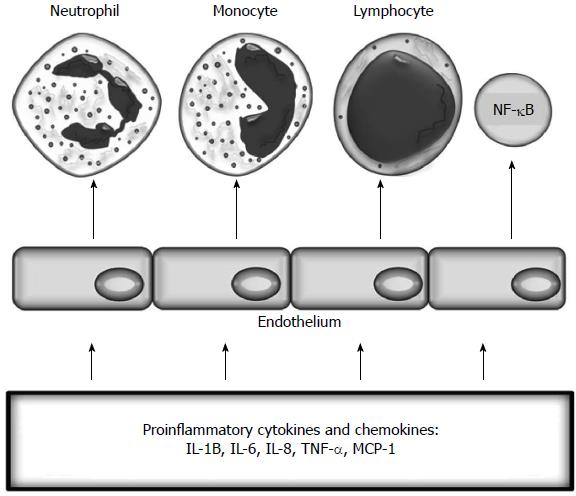
Figure 3 Inflammatory activation of endothelium.
TNF: Tumour necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Cibor D, Domagala-Rodacka R, Rodacki T, Jurczyszyn A, Mach T, Owczarek D. Endothelial dysfunction in inflammatory bowel diseases: Pathogenesis, assessment and implications. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(3): 1067-1077
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i3/1067.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1067